Mismatch Between Demand & Supply
Reliance on Fossil Fuels
- The majority of countries still continue to rely on fossil fuels for most of their energy needs
- In the twentieth century, oil took over from coal as the most used fossil fuel
- Today, oil is now being challenged by gas as the number one fossil fuel
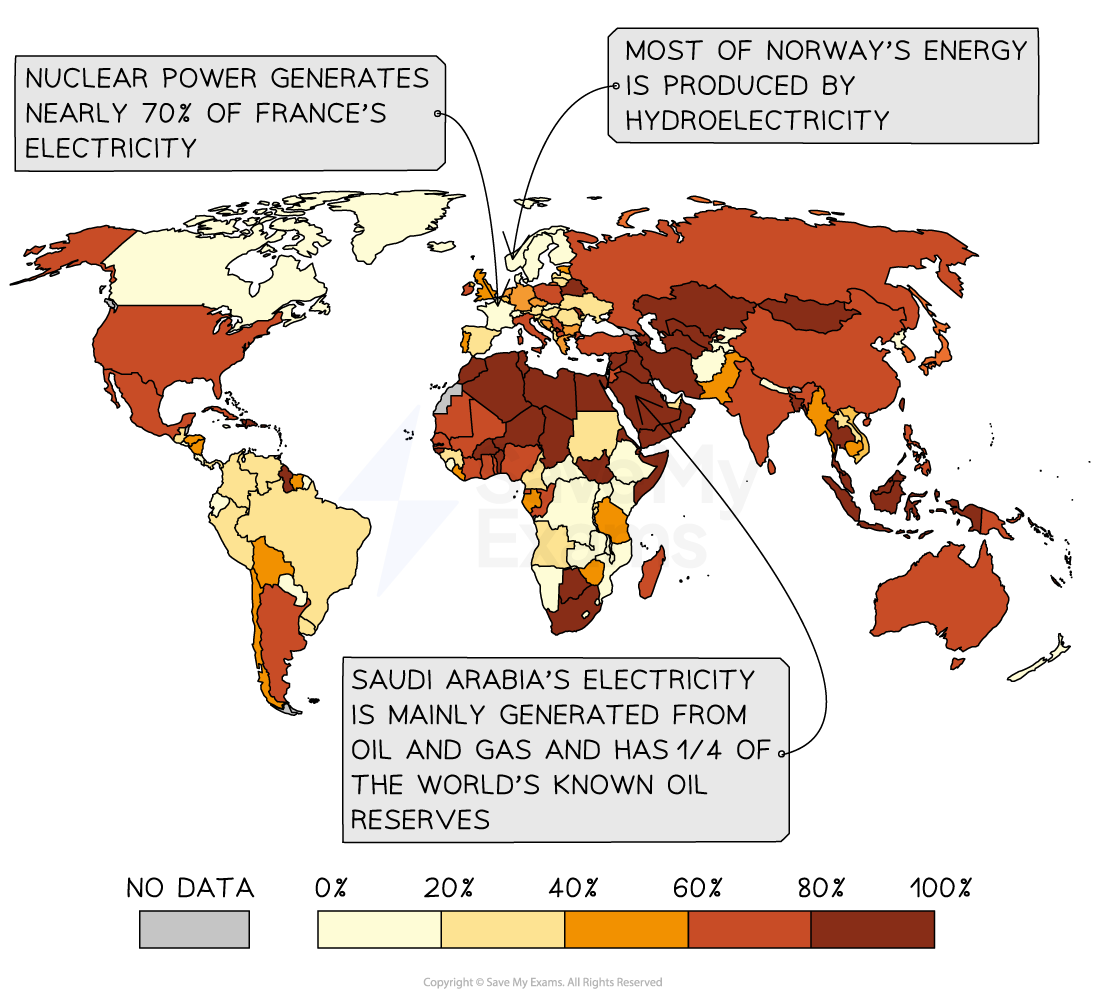
Electricity Production from Fossil Fuels (2022)
Mismatch Between Supply and Demand
- Coal
- Whilst the consumption of coal is decreasing in comparison to oil and gas, production is increasing
- China and the USA remain the two largest consumers of coal and are also the largest producers of coal
- There is a small mismatch as the main producers of coal are usually the main consumers e.g., China and the USA
- Oil
- There is a significant mismatch as the main suppliers of oil are members of OPEC and the consumers are in Europe
- Gas
- Gas supply is dominated by the USA and Russia and the major importers are Western European countries and Japan
Exam Tip
Do not assume and write in the exam that the increasing use of oil and gas has been because of the exhaustion of coal reserves

