Homeostasis: Temperature Control (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 5090
Did this video help you?
The Skin & Homeostasis
Control of body temperature is a homeostatic mechanism
Homeostasis is the maintenance of a constant internal environment
This means that internal conditions within your body (such as temperature, blood pressure, water concentration, glucose concentration etc) need to be kept within set limits in order to ensure that reactions in body cells can function and therefore the organism as a whole can live
The human body maintains the temperature at which enzymes work best, around 37°C
If body temperature increases over this temperature, enzymes will denature and become less effective at catalysing reactions such as respiration
The brain is responsible for regulating body temperature through responses in specialist structures within the skin
Fatty tissue under the dermis acts as a layer of insulation to prevent too much body heat being lost through the skin
The Structure of the Skin

A cross-section of human skin
Maintaining a Constant Internal Temperature
Temperature Regulation & the Hypothalamus
Regulation is controlled by the hypothalamus of the brain which contains receptors sensitive to the temperature of the blood
The skin also has temperature receptors and sends nervous impulses to the brain via sensory neurones
The brain responds to this information by sending nerve impulses to effectors in the skin to maintain the temperature within a narrow range of the optimum, 37°C
Fatty tissue under the dermis acts as a layer of insulation to prevent too much body heat being lost through the skin
Negative feedback loop for thermoregulation
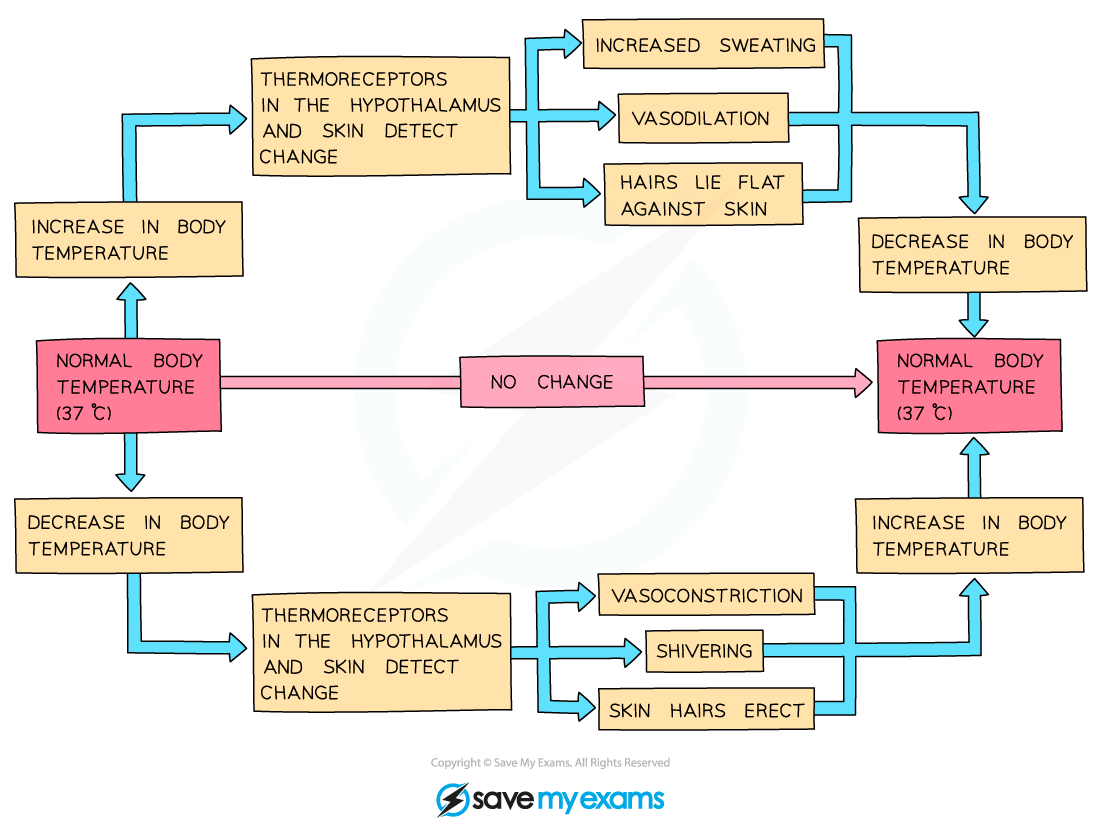
Homeostatic responses to changes in body temperature
Responses to changes in temperature
When we are hot | When we are cold |
|---|---|
Sweat is secreted by sweat glands, this cools the skin by evaporation. Heat energy from the body is lost when liquid water in sweat becomes water vapour (a state change) | Skeletal muscles contract rapidly and we shiver. These involuntary muscle contractions need energy from respiration and some of this is released as heat |
Hairs lie flat against the skin allowing air to freely circulate, this increases heat transfer to the environment by radiation. | Erect hairs trap a layer of air around the skin which acts as an insulator, preventing heat loss by radiation. |
Vasodilation occurs | Vasoconstriction occurs |
Vasoconstriction & Vasodilation
When we are cold blood flow in capillaries slows down because arterioles leading to the skin capillaries get narrower - this is known as vasoconstriction
This reduces the amount of heat lost from blood by radiation as less blood flows through the surface of the skin
When we are hot blood flow in capillaries increases because blood vessels to the skin capillaries get wider - this is known as vasodilation
This cools the body as blood (which carries heat around the body) is flowing at a faster rate through the skin’s surface and so more heat is lost by radiation
Vasodilation diagram

Responses in the skin when hot
Vasoconstriction diagram

Responses in the skin when cold

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?