Core Practical 10: Investigating Collisions using ICT (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: YPH11
Core Practical 10: Investigating Collisions using ICT
Aims of the Experiment
To investigate conservation of momentum in two directions
Considering if collisions are elastic
Constructing a diagram of 2D collisions
Use of ICT software is required
'Tracker' is recommended by Edexcel
Equipment List
Small spheres
Of two different diameters (ball bearings are ideal)
Digital camera able to record video
Support to allow it to be positioned directly above the collision
Computer with Tracker installed
30 cm ruler
Micrometer or calipers
Balance
Graph paper
Method

1. Measure the mass of the spheres using the balance and record
2. Measure the diameter of the spheres using a micrometer or Vernier calipers
3. Mark an approximately central point on the graph paper
This will be where the stationary sphere is placed
4. Start the camera recording
5. Within the area of the graph paper, roll a sphere into the stationary one
6. Replace the stationary sphere in its initial place and repeat the experiment up to three times
A slightly different angle of approach should be used for each collision
7. Download the video file from the camera to the computer that runs Tracker
Load the clip into the program.
Analysing the Results
Use Tracker to analyse the video clips.
Input the mass and diameter of each sphere when prompted
Use the ‘velocity overlay’ feature so that the software can analyse velocities
The Tracker software allows for frame-by-frame analysis of the movement of the spheres
Orientate the axes to make the velocity of the moving ball along one of the axes
Record the momentum of each ball as indicated in Tracker
Construct a vector diagram from the results
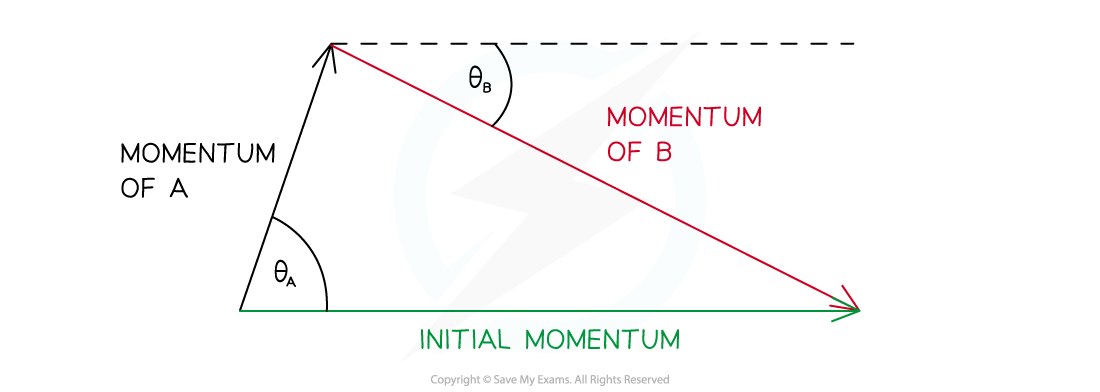
Evaluating the Experiment
ICT is used in this experiment because
The events happen to swiftly for the unaided eye to take readings
ICT generally provides more precise and reliable data
Systematic errors:
Parallax error from camera to the table
The precision of the balance may give a wide range of possible values for mass
If possible use a more precise balance
The spheres may have damage
Check there is no damage to the surface of each sphere before using
The Tracker axes may not be correctly aligned when analysing
Random errors:
The collision event may happen between frames
From variations in the table surface
This could cause loss or gain of kinetic energy due to friction or slopes
The sphere may not travel far enough to hit the second stationary sphere
Discard this result and release with greater initial velocity
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It can be helpful to practice a few collisions before making your final readings. This will help you become familiar with how fast to release the sphere.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?