Reducing the Effects of Environmental Issues (Cambridge (CIE) IGCSE Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 0620 & 0971
Reducing the effects of environmental issues
Two of the main environmental issues are climate change and acid rain
There are strategies that can be used to reduce the impact of these issues
Strategies to reduce climate change
The production of greenhouse gases, specifically carbon dioxide and methane, needs to be reduced drastically to reduce climate change
Reducing carbon dioxide emissions
Some measures that can be taken include:
Being more ‘responsible consumers’ of energy by:
Using hydrogen and renewable energy supplies such as solar or wind energy instead of burning fossil fuels
Using more fuel-efficient vehicles, e.g. electric and hybrid cars
Reducing the number of vehicles on the road, e.g. using public transport, car-sharing
Recycling or reusing products made from crude oil and its derivatives
Reducing household energy consumption, e.g. turning lights out, using more efficient appliances
Reducing deforestation and / or re-forestation
Planting more trees, can help reduce the amount of atmospheric carbon dioxide through photosynthesis
Reducing methane emissions
Reduce the amount of livestock farming
Methane is produced during digestion in animals
Strategies to reduce acid rain
Acid rain is caused by oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide
The effects of acid rain can be reduced by decreasing the amount of oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide that are produced
Catalytic convertors in vehicles can be used to remove oxides of nitrogen
Reducing sulfur dioxide emissions
Using fuels which contain low levels of sulfur
Flue gas desulfurisation
This is the main way to reduce sulfur dioxide emissions
Waste gases from coal fired power stations are passed into a scrubbing chamber
They are sprayed with a wet slurry of calcium oxide and calcium carbonate
The calcium compounds react with sulfur dioxide to produce calcium sulfate
Sulfur dioxide scrubber
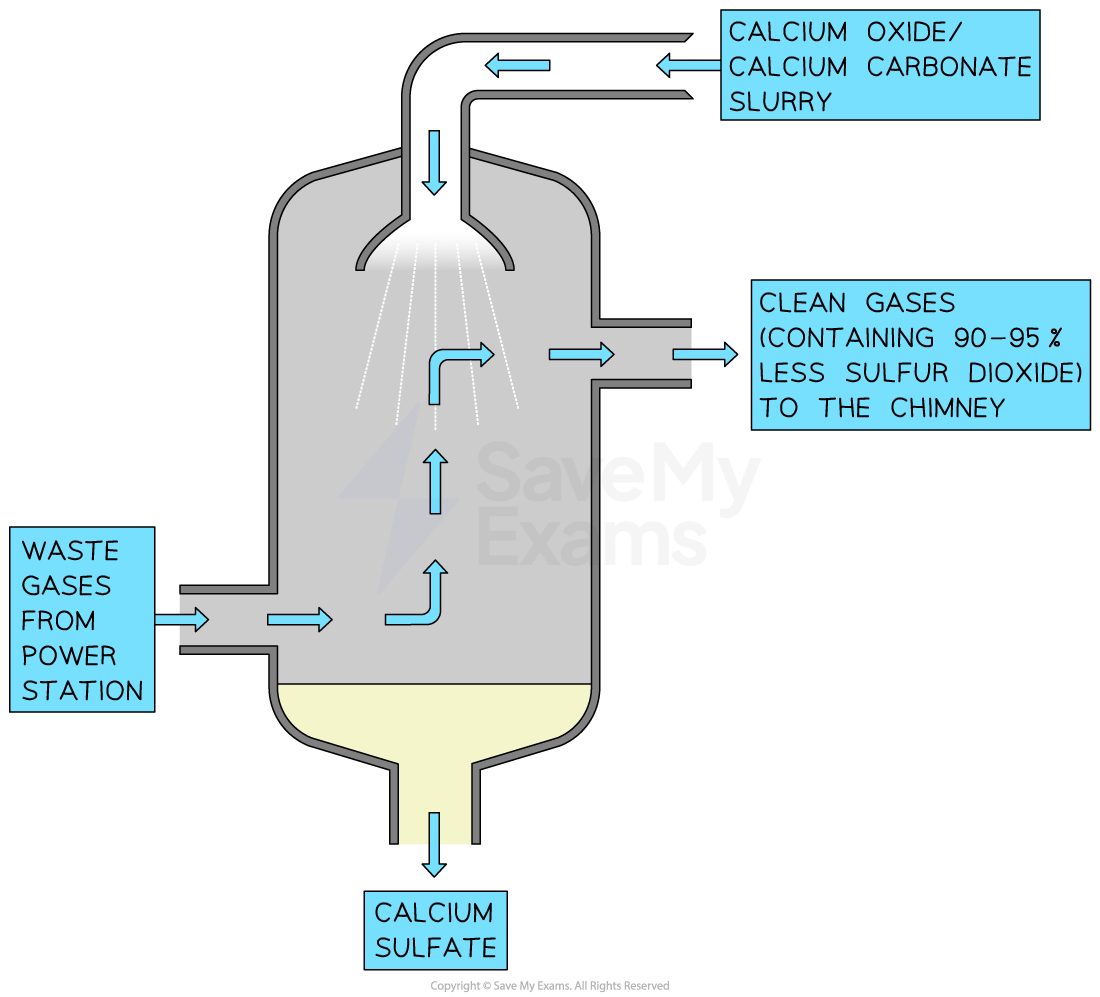
The scrubber sprays a lime slurry over the waste gases to remove 90 - 95% of the sulfur dioxide
Examiner Tips and Tricks
There are many other ways that carbon dioxide, methane, oxides of nitrogen and sulfur dioxide can be reduced, e.g. by reducing energy usage to reduce CO2 emissions but it is only the examples stated above that you need to know.
Oxides of nitrogen in car engines
Extended tier only
Oxides of nitrogen
These compounds (NO and NO2) are formed when nitrogen and oxygen react in the high pressure and temperature conditions of internal combustion engines and blast furnaces
Exhaust gases also contain unburned hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide
Cars are fitted with catalytic converters which form a part of their exhaust systems
Their function is to render these exhaust gases harmless
Catalytic converters
They contain a series of transition metal catalysts including platinum and rhodium
The metal catalysts are in a honeycomb within the converter to increase the surface area available for reaction
A series of redox reactions occurs which neutralises the pollutant gases
Carbon monoxide is oxidised to carbon dioxide:
2CO + O2 → 2CO2
Oxides of nitrogen are reduced to N2 gas:
2NO → N2 + O2
2NO2 → N2 + 2O2
A single reaction can summarise the reaction of nitrogen monoxide and carbon monoxide within a catalytic convertor:
2NO + 2CO → N2 + 2CO2
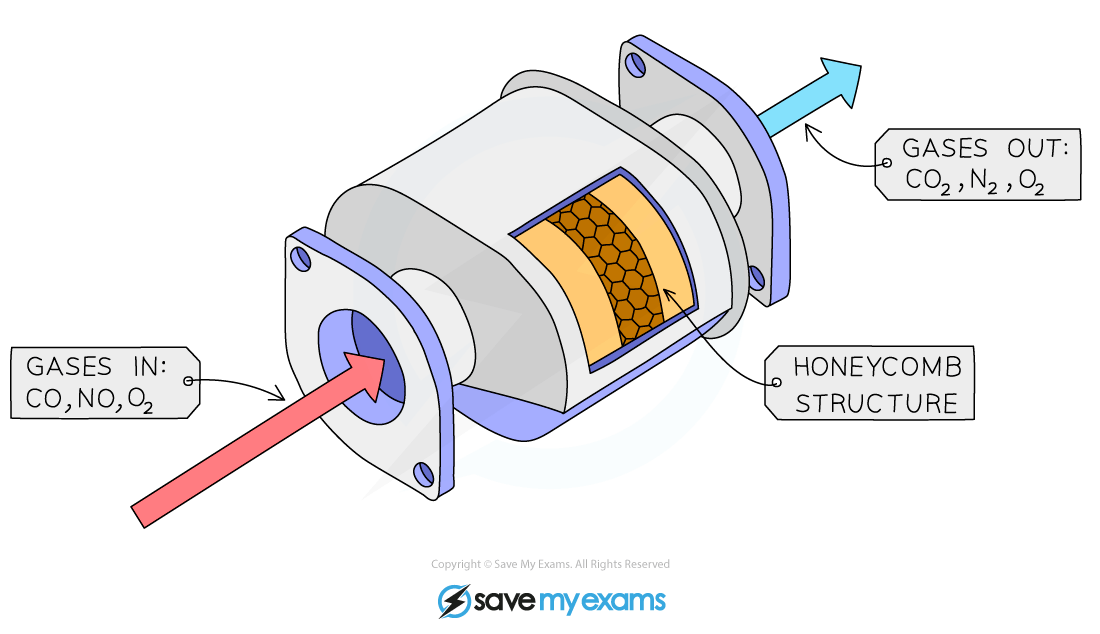
Catalytic converters are designed to reduce the polluting gases produced in car exhausts
Unburned hydrocarbons can also be oxidised to carbon dioxide and water:
C8H18 + 12½O2 → 8CO2 + 9H2O

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?