Forces as Vectors (AQA GCSE Combined Science: Trilogy): Revision Note
Exam code: 8464
Forces as Vectors
Forces are vector quantities as they are described by both magnitude and direction
The magnitude of a force is measured in newtons
The direction of a force can be described as left, right, up, down or even using angles

A free body diagram of an object with two forces acting on it
The direction of a force can be imagined using a number line
Numbers to the left of zero are negative as are forces pointing left
Numbers to the right of zero are positive as are forces pointing right

Vectors represented as positive or negative vectors depending on their direction
Not all forces are directed perfectly horizontally or vertically and thus need to have an angle described
It is useful to describe an angle with respect to the vertical or the horizontal
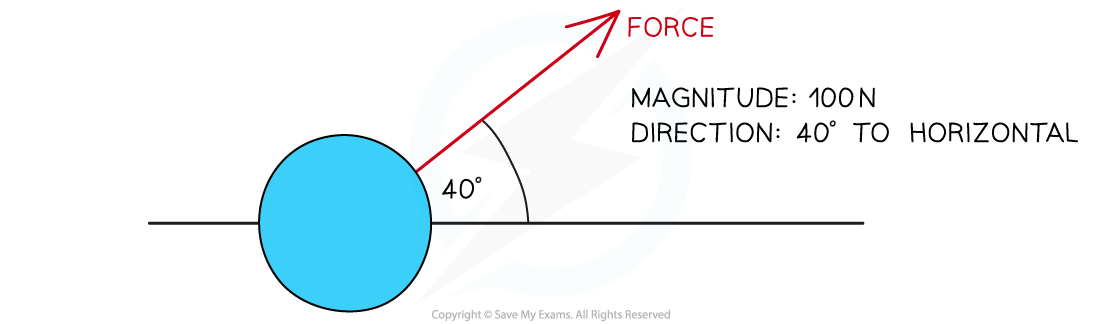
A force of magnitude 100 N directed 40° to the horizontal
Force Pairs
When there is an interaction between two objects, a force is exerted on each object by the other
This is known as a force pair
Examples of these force pairs include:
A laptop resting on a desk
The laptop exerts a downward force on the desk
The desk exerts an upward force on the laptop
A basketball player throwing a basketball
The basketball player exerts a push force on the ball
The ball exerts a push force on the basketball player
A person standing on the Earth
The Earth exerts a gravitational pull force on the person
The person exerts a gravitational pull force on the Earth
Force pairs can be represented by arrows in vector diagrams

The force pairs present with respect to a rock being pushed by a person
The person pushes on the rock, and the rock pushes on the person
The rock pushes on the ground, and the ground pushes on the rock
The person pushes on the ground, and the ground pushes on the person

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?