Heating in Circuits (Edexcel GCSE Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 1PH0
Written by: Katie M
Updated on
The Heating Effect of Current
When charge passes through a component, such as a resistor, some of the energy is transferred from the electrons to the component by heating, therefore increasing its temperature
The energy will dissipate (spread out) into the environment via thermal conduction, convection and radiation
This is used to an advantage to by devices like electric heaters
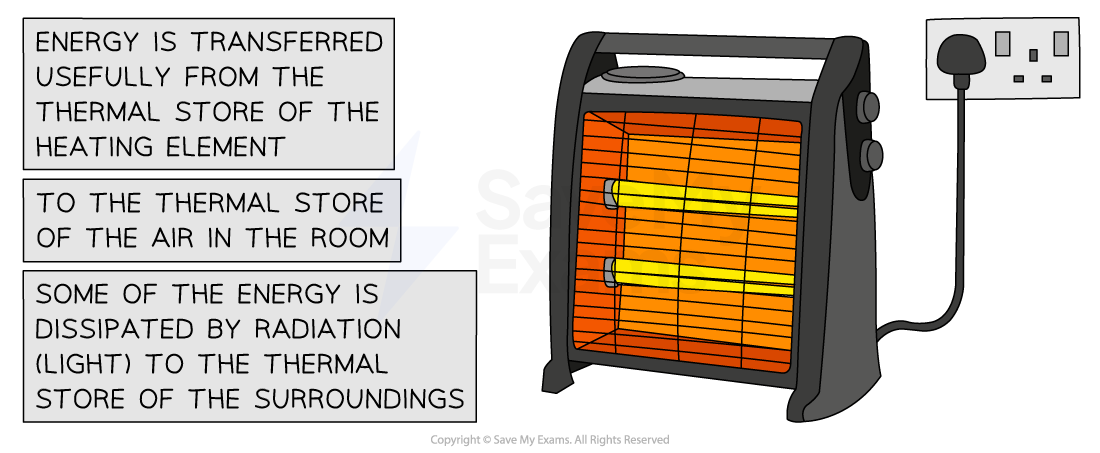
The heating effect of current can be used for many applications such as electric heaters
However, wasted thermal energy makes a device less efficient and if too much current flows through a component, the heating effect can be very dangerous
This can burn someone if they touch it or cause a fire
Dissipation of Thermal Energy
When an electrical current does work against electrical resistance:
Electrical energy is dissipated as thermal energy in the surroundings
The heat that is produced will dissipate via thermal conduction, convection and radiation
The amount of heat produced depends on two factors:
Current: The greater the current, the more heat that is produced
Resistance: The higher the resistance, the more heat that is produced (for a given current)
Note that reducing the resistance can cause the current to increase
This could actually increase the amount of heat produced

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
