Force & Momentum (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 9702
Force & momentum
Force is defined as the rate of change of momentum
Where:
F = force in newtons (N)
p = momentum in kilogram metres per second (kg m s-1)
t = time in seconds (s)
Δ (the Greek letter delta) = change in
Change in momentum, Δp, can also be expressed as:
change in momentum = final momentum − initial momentum
Force and momentum are vector quantities
They can have a positive or negative direction
Worked Example
A car of mass 1500 kg hits a wall at an initial velocity of 15 m s-1.
It then rebounds off the wall at 5 m s-1. The car is in contact with the wall for 0.3 s.
Calculate the average force experienced by the car.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities and assign direction:
Mass,
= 1500 kg
Inital velocity,
= 15 m s-1
Final velocity,
= −5 m s-1
Duration of collision,
= 0.3 s
Step 2: State the equation for force and momentum
Step 3: State the equation for change in momentum
Step 4: Calculate the initial momentum
Step 5: Calculate the final momentum
Step 6: Calculate the change in momentum
Step 7: Calculate the average force exerted on the car
Direction of forces
The force that is equal to the rate of change of momentum is still the resultant force
The force on an object will be negative if the direction of the force opposes the direction of its initial velocity
This means that a force is exerted by the object it has collided with
Forces acting between a car and a wall upon impact
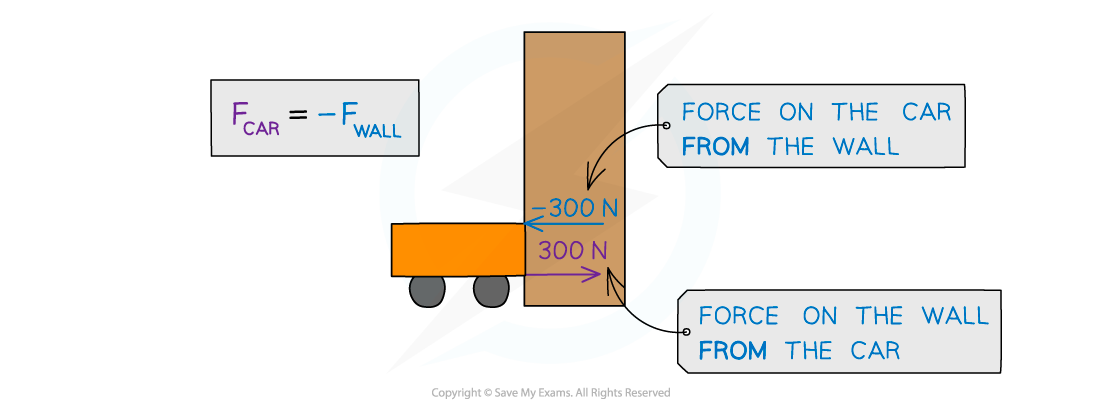
The force exerted by the wall on car will be equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force exerted by the car on the wall: Fcar = –Fwall
A car collides with a wall, and the car exerts a force of 300 N on the wall
The wall also exerts a force of −300 N on the car
The force exerted by the wall on the car is equal in magnitude and opposite in direction to the force exerted by the car on the wall
This is Newton’s third law of motion (see Newton’s laws of motion)
Time of impact
The force exerted is also determined by the time taken for the impact to occur
The same change in momentum, over a longer period of time will exert less force, and vice versa
As Δt increases, F decreases, when Δp remains the same
As Δt decreases, F increases, when Δp remains the same
Worked Example
A tennis player strikes a ball with their racket twice. Each time, the change in momentum of the ball is 0.5 kg m s-1.
During the first strike, the ball is in contact with the racket for 0.2 s. During the second strike, the ball is in contact with the racket for 0.1 s.
Determine which strike the greatest force is exerted on the racket by the ball.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Change in momentum, Δp = 0.5 kg m s-1
Contact time for the first strike, Δt1 = 0.2 s
Contact time for the second strike, Δt2 = 0.1 s
Step 2: Determine the force exerted on the racket during the first strike
Step 3: Determine the force exerted on the racket during the second strike
Step 4: State which strike the greatest force is exerted on the racket
The ball exerts a greater force on the racket during the second strike

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?