The Weak Interaction (AQA A Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 7408
The Weak Interaction
The weak interaction is responsible for the radioactive decay of atoms
The exchange particle that carries this force is the W–, W+ or Z0 boson
The type of exchange particle depends on the type of interaction
β decay
β– and β+ decay are examples of the weak interaction in action
In β– decay, a neutron turns into a proton emitting an electron and an anti-electron neutrino
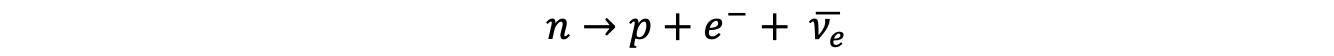
The W– boson is the exchange particle in this interaction

Feynman diagram showing beta minus decay. The W– boson is the exchange particle
In β+ decay, a proton turns into a neutron emitting a positron and an electron neutrino

The W+ boson is the exchange particle in this interaction

Feynman diagram showing beta plus decay. The W+ boson is the exchange particle
Electron Capture & Electron–Proton Collisions
Electrons and protons are attracted to each other via the electromagnetic interaction
However, when they interact with each other, it is the weak interaction that facilitates the collision
Both electron capture and electron-proton collisions have the same decay equation

Electron capture is when an atomic electron is absorbed by a proton in the nucleus resulting in the release of a neutron and an electron neutrino
This decay is mediated by the W+ boson
Electron-proton collisions are similar; when an electron collides with a proton, a neutron and an electron neutrino are emitted
This decay is mediated by the W– boson

Feynman diagrams for electron capture and an electron-proton collision. These are equal except for the sign of the W boson
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Notice that the sign of the W boson matches that of the beta decay. The W– boson is exchanged in beta minus decay and W+ boson is exchanged in beta plus decay.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?