Thylakoids & the Stroma (Cambridge (CIE) A Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 9700
Thylakoids & the stroma
Plant cells contain chloroplasts which are the site of photosynthesis
Chloroplasts are filled with a fluid known as the stroma
The system of membranes found in the stroma of the chloroplast consists of a series of flattened fluid-filled sacs known as thylakoids
In places, these thylakoids stack up to form structures known as grana (singular; granum)
The light-dependent stage of photosynthesis occurs in the thylakoid membranes and the thylakoid spaces (the spaces inside the thylakoids)
The thylakoid membranes contain the pigments, enzymes and electron carriers required for the light-dependent reactions
The membranes of the grana create a large surface area to increase the number of light-dependent reactions that can occur
This membrane system provides a large number of pigment molecules in an arrangement that ensures as much light as necessary is captured
The pigment molecules are arranged in light-harvesting clusters known as photosystems
In a photosystem, the different pigment molecules are arranged in funnel-like structures the thylakoid membrane
Each pigment molecule passes energy down to the next pigment molecule in the cluster until it reaches the primary pigment reaction centre
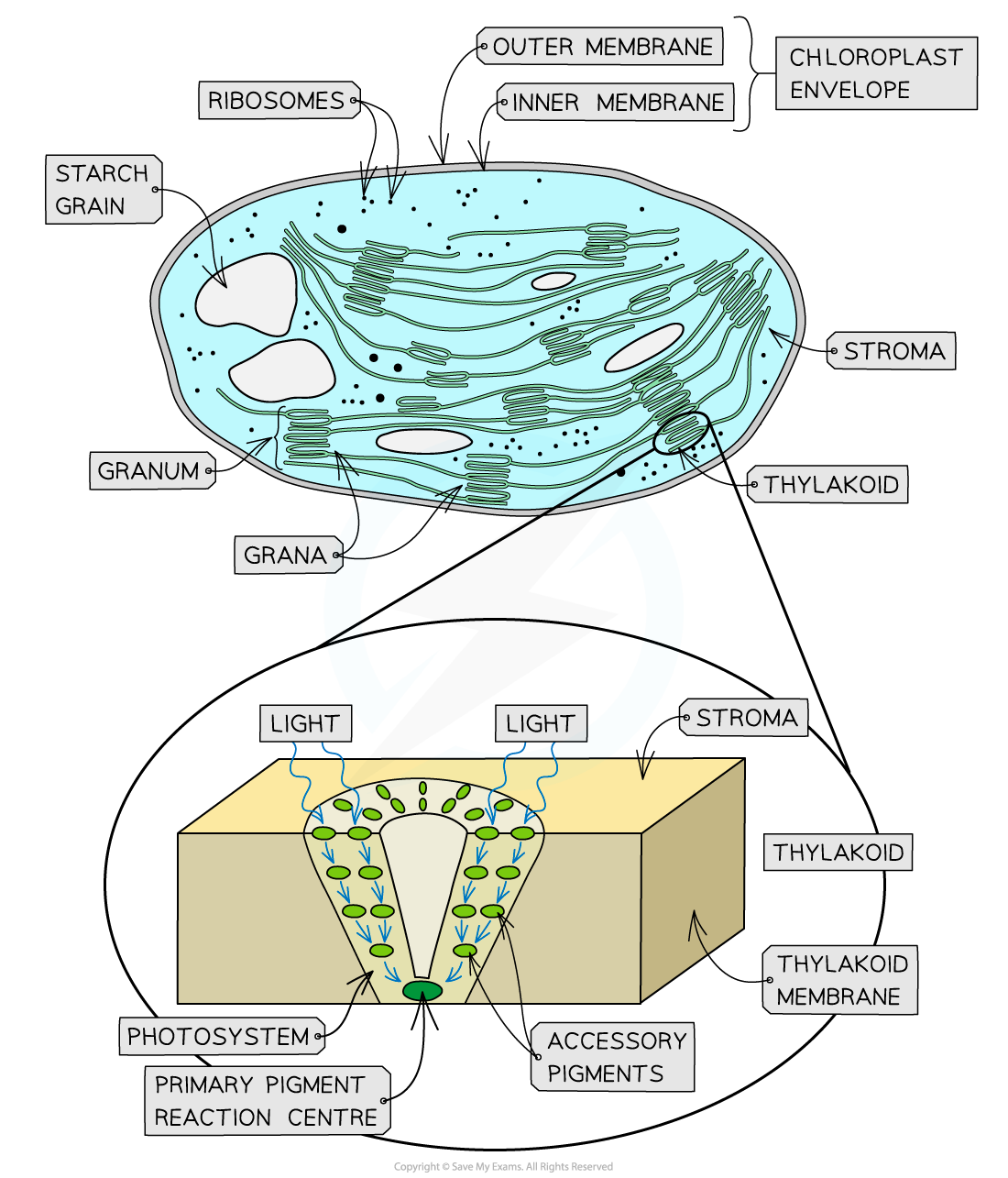
The stroma is the fluid that fills the chloroplasts and surrounds thylakoids
CO2, sugars, enzymes and other molecules are dissolved in the stroma fluid
The stroma is the site of the light-independent stage of photosynthesis
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Don’t get confused between the light-dependent and light-independent reactions—you need to know where each of these sets of reactions occurs.
The photosynthetic pigments required to absorb light energy are only found in the thylakoid membranes, meaning that the reactions that occur here are dependent on light (light-dependent)!

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?