The Universe (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Did this video help you?
Astronomical Distances
Astronomical distances, such as the distances between stars and galaxies, are so large that physicists use a special unit to measure them called the light-year
One light-year is defined as:
The distance travelled by light through (the vacuum of) space in one year
The speed of light is the universal speed limit, nothing can travel faster than the speed of light
But over astronomical distances, light actually travels pretty slowly
The diameter of the Milky Way is approximately 100 000 light-years
This means that light would take 100 000 years to travel across it
One light year is equal to 9.5 × 1012 km, or 9.5 × 1015 m
Redshift
Usually, when an object emits waves, the wavefronts spread out symmetrically
If the wave source moves, the waves can become squashed together or stretched out
The Doppler Effect
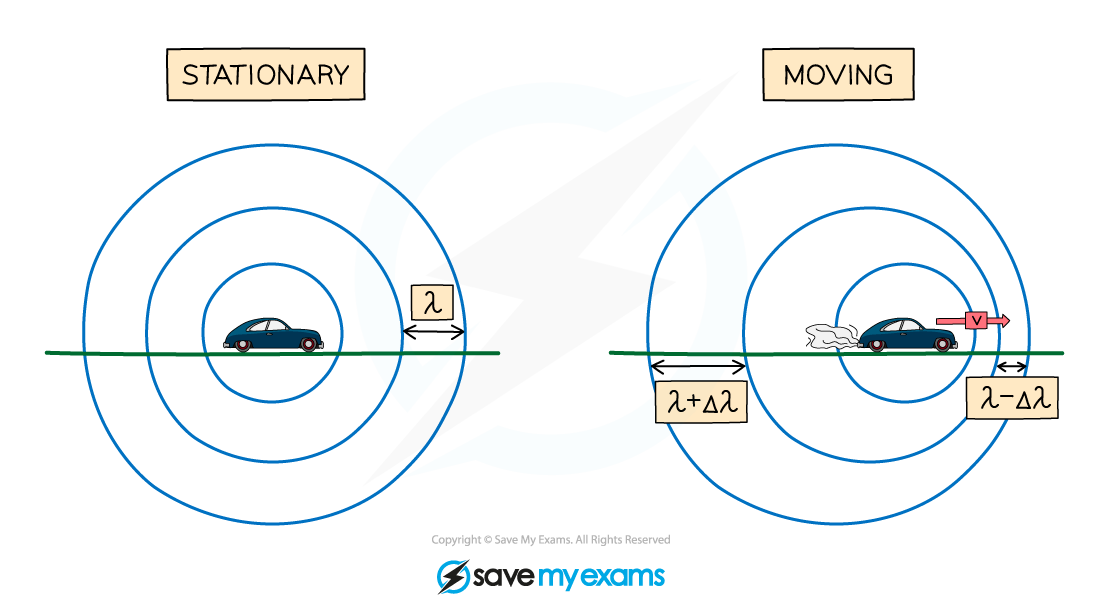
Diagram showing the wavefronts produced from a stationary object and a moving object
A moving object will cause the wavelength, λ, (and frequency) of the waves to change:
The wavelength of the waves in front of the source decreases and the frequency increases
The wavelength behind the source increases and the frequency decreases
This effect is known as the Doppler effect
The Doppler effect also affects light
If an object moves away from an observer the wavelength of light increases
This is known as redshift as the light moves towards the red end of the spectrum
Redshift is defined as:
An increase in the observed wavelength of electromagnet radiation emitted from receding stars and galaxies
Redshift & Blueshift

Light from a star that is moving towards an observer will be blueshifted and light from a star moving away from an observer will be redshifted
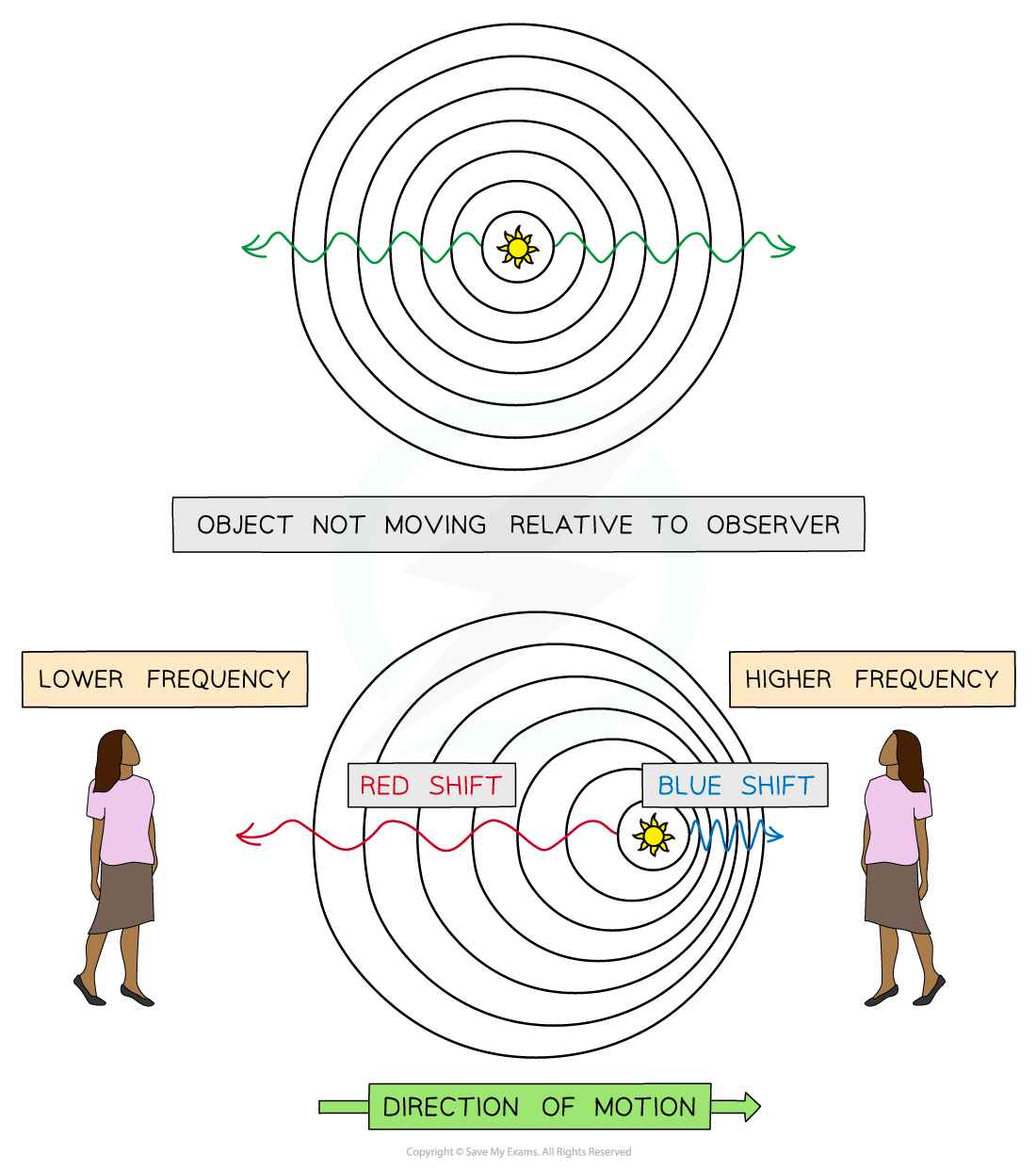
The observer behind the source observes redshift
The Milky Way is just one of billions of galaxies that make up the Universe
Light emitted from distant galaxies appears redshifted when compared with light emitted on Earth
The diagram below shows the light coming to us from a close object, such as the Sun, and the light coming to us from a distant galaxy
Comparison of Light Spectra
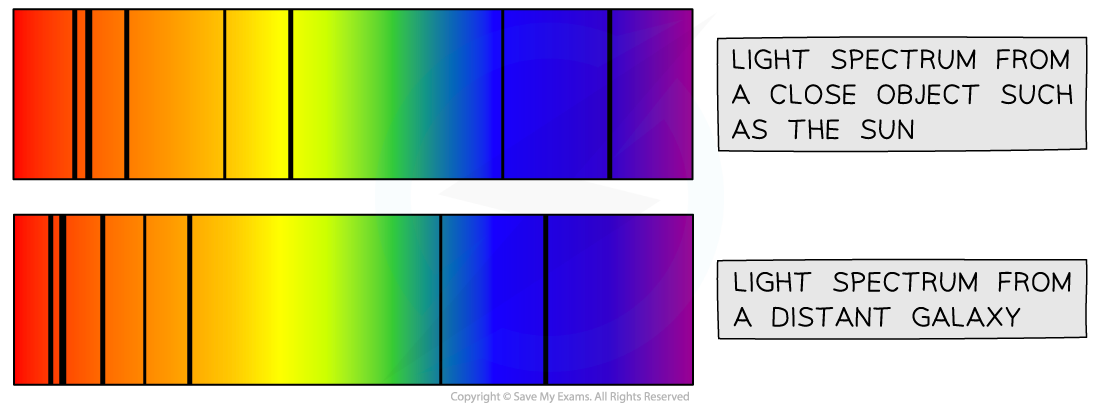
Comparing the light spectrum produced by the Sun and a distant galaxy
The diagram also shows that the light coming to us from distant galaxies is redshifted
The lines on the spectrum are shifted towards the red end
This indicates that the galaxies are moving away from us
If the galaxies are moving away from us it means that the universe is expanding
The observation of redshift from distant galaxies supports the Big Bang theory
Another observation from looking at the light spectrums produced from distant galaxies is that the greater the distance to the galaxy, the greater the redshift
This means that the further away a galaxy is, the faster it is moving away from us
Redshift & Distance from Earth

Graph showing the greater the distance to a galaxy, the greater the redshift
The Big Bang
Around 14 billion years ago, the Universe began from a very small region that was extremely hot and dense
Then there was a giant explosion, which is known as the Big Bang
This caused the universe to expand from a single point, cooling as it does so, to form the universe today
Each point expands away from the others
This is seen from galaxies moving away from each other, and the further away they are the faster they move
Redshift in the light from distant galaxies is evidence that the Universe is expanding and supports the Big Bang Theory
As a result of the initial explosion, the Universe continues to expand
Expansion of the Universe

All galaxies are moving away from each other, indicating that the universe is expanding
An analogy of this is points drawn on a balloon where the balloon represents space and the points as galaxies
When the balloon is deflated, all the points are close together and an equal distance apart
As the balloon expands, all the points become further apart by the same amount
This is because the space itself has expanded between the galaxies
Analogy for the Expanding Universe

A balloon inflating is similar to the stretching of the space between galaxies

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
