The Sun as a Star (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
The Milky Way
Galaxies are made up of billions of stars
The Universe is made up of many different galaxies
The Sun is one of the billions of stars in a galaxy called the Milky Way
Other stars in the Milky Way galaxy are much further away from Earth than the Sun is
Some of these stars also have planets which orbit them
Our Place in Space

Our solar system is just one out of potentially billions in our galactic neighbourhood, the Milky Way. There are estimated to be more than 100 billion galaxies in the entire universe
The Sun
The Sun lies at the centre of the Solar System
The Sun is a star which makes up over 99% of the mass of the solar system
The fact that most of the mass of the Solar System is concentrated in the Sun is the reason the smaller planets orbit the Sun
The planets are kept in orbit due to the gravitational pull of the Sun
The Sun is a medium-sized star consisting of mainly hydrogen and helium
It radiates most of its energy in the infrared, visible and ultraviolet regions of the electromagnetic spectrum
The Sun

Our Sun (Image courtesy of NASA)
Stars come in a wide range of sizes and colours, from yellow stars to red dwarfs, from blue giants to red supergiants
These can be classified according to their colour
Warm objects emit infrared and extremely hot objects emit visible light as well
Therefore, the colour they emit depends on how hot they are
A star's colour is related to its surface temperature
A red star is the coolest (at around 3000 K)
A blue star is the hottest (at around 30 000 K)
Temperature & Colour of Stars

The colour of a star correlates to its temperature
Did this video help you?
Nuclear Fusion in Stars
In the centre of a stable star, hydrogen atoms undergo nuclear fusion to form helium
The equation for the reaction is shown here:
The equation shows
(deuterium) and
(tritium) which are both isotopes of hydrogen
They can be formed through other fusion reactions in the star
A huge amount of energy is released in the reaction
This provides a pressure that prevents the star from collapsing under its gravity
Nuclear Fusion in Stars
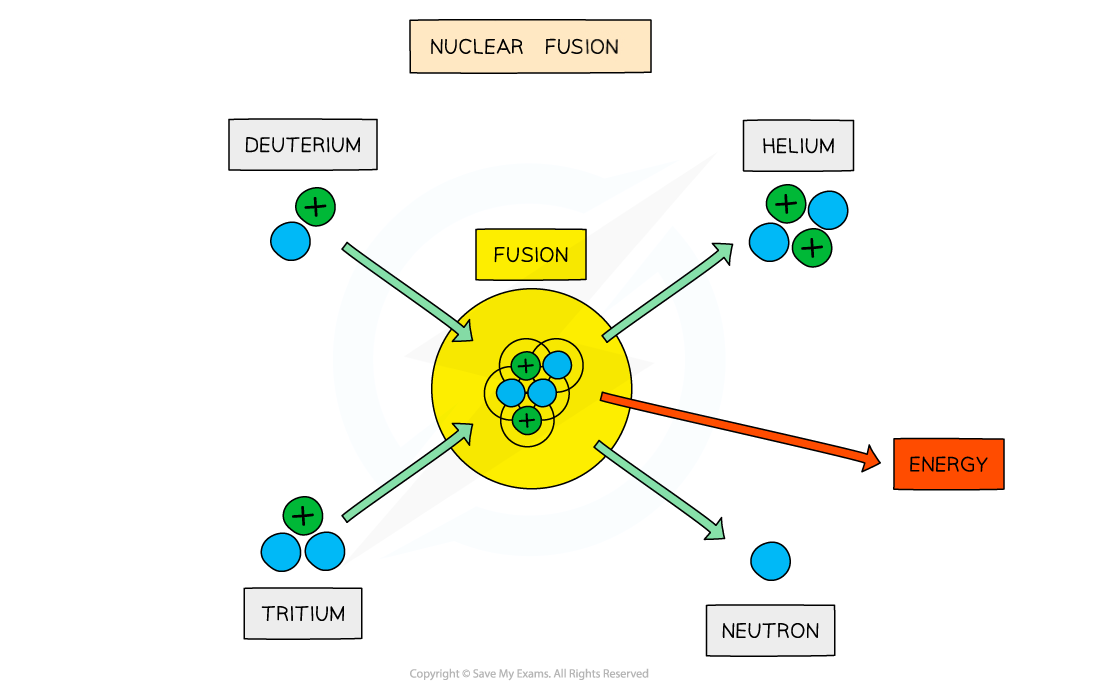
The fusion of deuterium and tritium to form helium with the release of energy
Worked Example
An example of a hydrogen fusion reaction which takes place in stars is shown here.
Which of the following is a valid reason as to why hydrogen fusion is not currently possible on Earth?
A. Hydrogen fusion produces dangerous radioactive waste
B. Hydrogen nuclei require very high temperatures to fuse together
C. Hydrogen is a rare element that would be difficult to get large amounts of
D. Hydrogen fusion does not produce enough energy to be commercially viable
Answer: B
Hydrogen nuclei have positive charges
So two hydrogen nuclei would have a repulsive force between them
High temperatures are required to give the nuclei enough energy to overcome the repulsive force
The answer is not A because the product of the hydrogen fusion shown in the reaction is helium
Helium is an inert gas
The answer is not C because hydrogen is a very abundant element
It is the most common element in the universe
The answer is not D because hydrogen fusion would produce a huge amount of energy

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?