Fission & Fusion (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Fission & Fusion
Nuclei can join together, or split up, to form new nuclei
These processes are known are
Nuclear fission
Nuclear fusion
Nuclear Fission
There is a lot of energy stored within the nucleus of an atom
This energy can be released in a nuclear reaction such as fission
Nuclear fission is defined as:
The splitting of a large, unstable nucleus into two smaller nuclei
Isotopes of uranium and plutonium both undergo fission and are used as fuels in nuclear power stations
During fission, when a neutron collides with an unstable nucleus, the nucleus splits into two smaller nuclei (called daughter nuclei) as well as two or three neutrons
Gamma rays are also emitted
How does nuclear fission work?
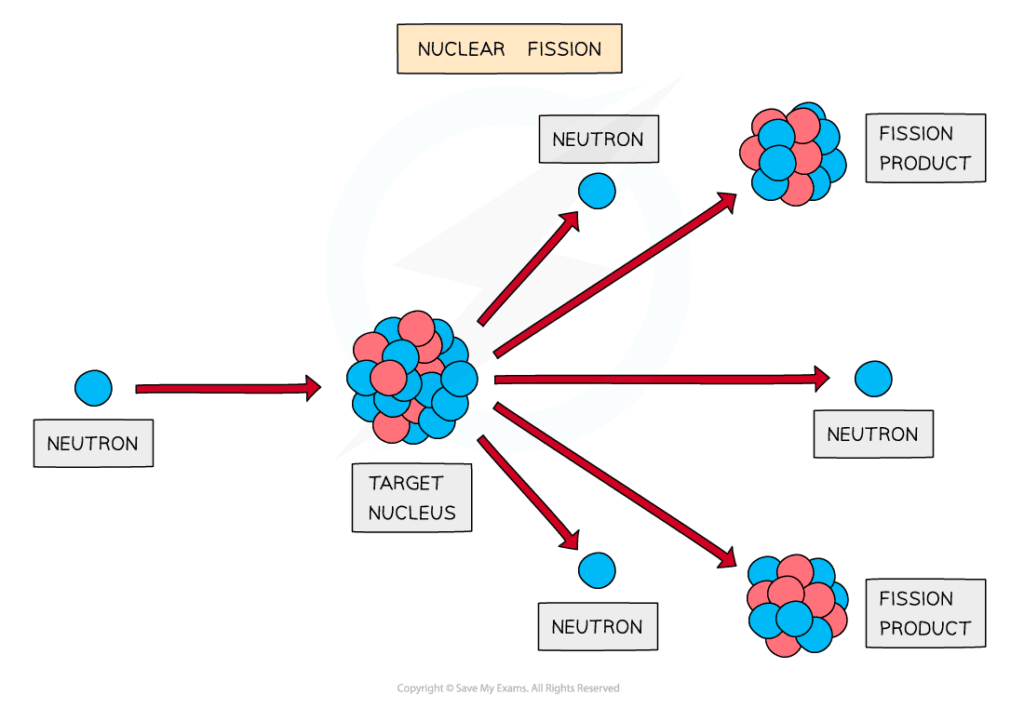
A neutron is fired into the target nucleus, causing it to split into two smaller nuclei
The products of fission move away very quickly
Energy transferred is from nuclear potential energy to kinetic energy
The mass of the products (daughter nuclei and neutrons) is less than the mass of the original nucleus
This is because the remaining mass has been converted into energy which is released during the fission process
Nuclear Fusion
Small nuclei can react to release energy in a process called nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is defined as:
When two light nuclei join to form a heavier nucleus
This process requires extremely high temperatures to maintain
This is why nuclear fusion has proven very hard to reproduce on Earth
Stars use nuclear fusion to produce energy
In most stars, hydrogen atoms are fused together to form helium and produce lots of energy
How does nuclear fusion work?

Two hydrogen nuclei are fusing to form a helium nuclei
The energy produced during nuclear fusion comes from a very small amount of the particle’s mass being converted into energy
Albert Einstein described the mass-energy equivalence with his famous equation:
Where:
E = energy released from fusion in Joules (J)
m = mass converted into energy in kilograms (kg)
c = the speed of light in metres per second (m/s)
Therefore, the mass of the product (fused nucleus) is less than the mass of the two original nuclei
This is because the remaining mass has been converted into energy which is released when the nuclei fuse
The amount of energy released during nuclear fusion is huge:
The energy from 1 kg of hydrogen that undergoes fusion is equivalent to the energy from burning about 10 million kilograms of coal
An example of a nuclide equation for fusion is:
+ energy
Where:
is deuterium (isotope of hydrogen with 1 proton and 1 neutron)
is hydrogen (with one proton)
is an isotope with helium (with two protons and one neutron)
Worked Example
The nuclear equation for a fission reaction is

Calculate the number of neutrons N emitted in this reaction.
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the nucleon number on the left side of the equation
LHS: 235 + 1 = 236
Step 2: Calculate the nucleon number on the right side of the equation
RHS: 96 + 138 + N = 233 + N
Step 3: Equate the nucleon number for both sides of the equation
LHS = RHS
236 = 233 + N
Step 4: Rearrange for the number of neutrons N
N = 236 – 233 = 3
Therefore, 3 neutrons are produced in this fission reaction
Fission Reactions
The processes involved in nuclear fission can be shown in different ways, such as diagrams and nuclear equations
Fission of Uranium-235

Large nuclei can decay by fission to produce smaller nuclei and neutrons with a lot of kinetic energy
The diagram above is useful because it shows clearly the different parts of the fission reaction
An example of a nuclide equation for fission is:
energy
Where:
is an unstable isotope of Uranium
is a neutron
us an unstable isotope of Krypton
is an unstable isotope of Barium
This equation represents a fission reaction in which
A Uranium-235 nucleus is hit by a neutron
It splits into two smaller nuclei – a Krypton nucleus and a Barium nucleus
Three neutrons are released in the process which can go on to trigger further fission reactions
The sum of the top (nucleon) numbers on the left-hand side equals the sum of top number on the right-hand side:
235 + 1 = 92 + 141 + (3 × 1)
The same is true for the lower (proton) numbers:
92 + 0 = 36 + 56 + (2 × 0)
Worked Example
The nuclear equation for a fission reaction is

Calculate the number of neutrons N emitted in this reaction.
Answer:
Step 1: Calculate the nucleon number on the left side of the equation
LHS: 235 + 1 = 236
Step 2: Calculate the nucleon number on the right side of the equation
RHS: 96 + 138 + N = 233 + N
Step 3: Equate the nucleon number for both sides of the equation
LHS = RHS
236 = 233 + N
Step 4: Rearrange for the number of neutrons N
N = 236 – 233 = 3
Therefore, 3 neutrons are produced in this fission reaction
Chain Reactions
Only one extra neutron is required to induce a Uranium-235 nucleus to split by fission
During the fission, it produces two or three neutrons which move away at high speed
Each of these new neutrons can start another fission reaction, which again creates further excess neutrons
This process is called a chain reaction
Chain Reaction Analogy

The neutrons released by each fission reaction can go on to create further fissions, like a chain that is linked several times – from each chain comes two more
Controlled Chain Reactions
In a nuclear reactor, a chain reaction is required to keep the reactor running
When the reactor is producing energy at the correct rate, the number of free neutrons in the reactor needs to be kept constant
This means some must be removed from the reactor
To do this, nuclear reactors contain control rods
These absorb neutrons without becoming dangerously unstable themselves
Uncontrolled Chain Reactions
Because each new fission reaction releases energy, uncontrolled chain reactions can be dangerous
The number of neutrons available increases quickly, so the number of reactions does too
A nuclear weapon uses an uncontrolled chain reaction to release a huge amount of energy in a short period of time as an explosion
Nuclear Reactors
In a nuclear reactor, a chain reaction is required to keep the reactor running
When the reactor is producing energy at the required rate, two factors must be controlled:
The number of free neutrons in the reactor
The energy of the free neutrons
The main components of a nuclear reactor are:
control rods
a moderator
Nuclear reactor diagram

The overall purpose of the reactor is to control chain reactions and collect the heat energy produced from nuclear reactions to generate electricity
Control rods
Purpose of control rods: To absorb neutrons
Control rods are made of a material which absorbs neutrons without becoming dangerously unstable themselves
The number of neutrons absorbed is controlled by varying the depth of the control rods in the reactor core
Lowering the rods further decreases the rate of fission, as more neutrons are absorbed
Raising the rods increases the rate of fission, as fewer neutrons are absorbed
This is adjusted automatically so that exactly one fission neutron produced by each fission event goes on to cause another fission
In the event the nuclear reactor needs to shut down, the control rods can be lowered all the way so no reactions can take place
Moderator
Purpose of a moderator: To slow down neutrons
The moderator is a material that surrounds the fuel rods and control rods inside the reactor core
The fast-moving neutrons produced by the fission reactions slow down by colliding with the molecules of the moderator, causing them to lose some momentum
The neutrons are slowed down so that they are in thermal equilibrium with the moderator
These neutrons are called thermal neutrons
This ensures neutrons can react efficiently with the uranium fuel

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?