Reflection of Sound Waves (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Echoes
Sound waves reflect off hard surfaces
The reflection of a sound wave is called an echo
Echo sounding can be used to measure depth or to detect objects underwater
A sound wave can be transmitted from the surface of the water
The sound wave is reflected off the bottom of the ocean
The time it takes for the sound wave to return is used to calculate the depth of the water
This is the distance to the ocean floor plus the distance for the wave to return
The distance the wave travels is twice the depth of the ocean
Ship using Radar
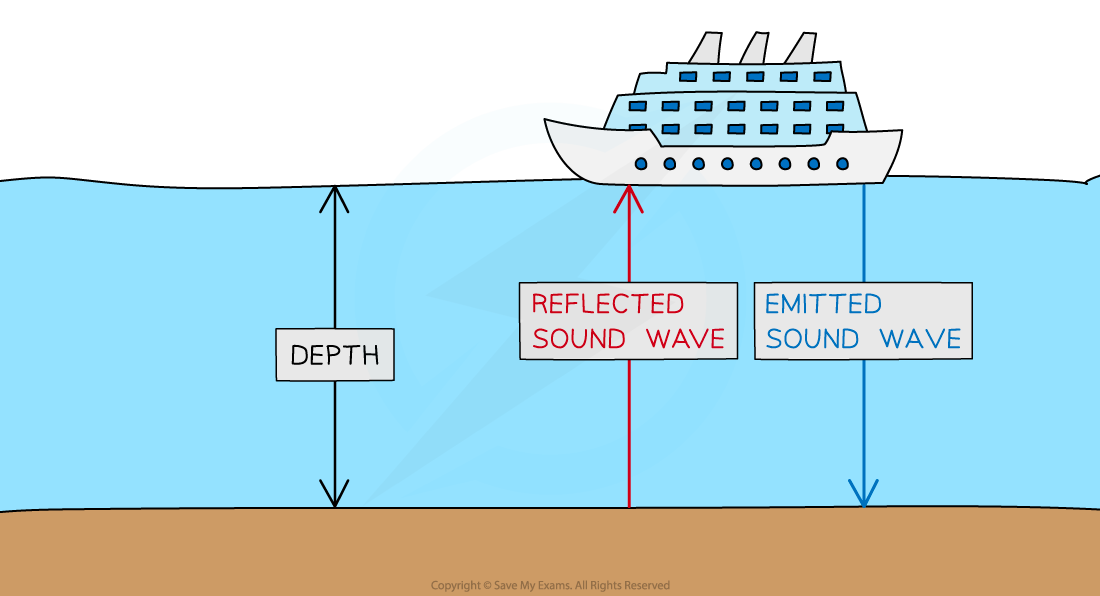
Echo sounding is used to determine water depth
Investigating the Reflection of Sound Waves
Using Echoes to Measure the Speed of Sound

Measuring the speed of sound using echoes
A person stands about 50 m away from a wall (or cliff) using a trundle wheel to measure this distance
The person claps two wooden blocks together and listens for the echo
A second person has a stopwatch and starts timing when they hear one of the claps and stops timing when they hear the echo
The process is then repeated 20 times and an average time calculated
The distance travelled by the sound between each clap and echo will be (2 × 50) m
The speed of sound can be calculated from this distance and the time using the equation:

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?