Linear Magnification (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Linear Magnification
The magnification of a lens is equal to the ratios of the image height and the object height
This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle:
Magnification Formula Triangle

Magnification, image height and object height formula triangle
The magnification depends on:
The distance of an object from the lens
The power of the lens
The units for height are unimportant, provided that both the object and image are measured in the same units
For example, both in cm, or both in mm
Therefore, magnification does not have units as it is a ratio
If the magnification is:
> 1, then the image is magnified
= 1, then the object and image are the same size
< 1, then the image is diminished
Worked Example
A person sees an image from a magnifying glass.

Calculate the magnification of this image. Clearly show your working on the diagram.
Answer:
Step 1: Measure the height of the object and image from the scale
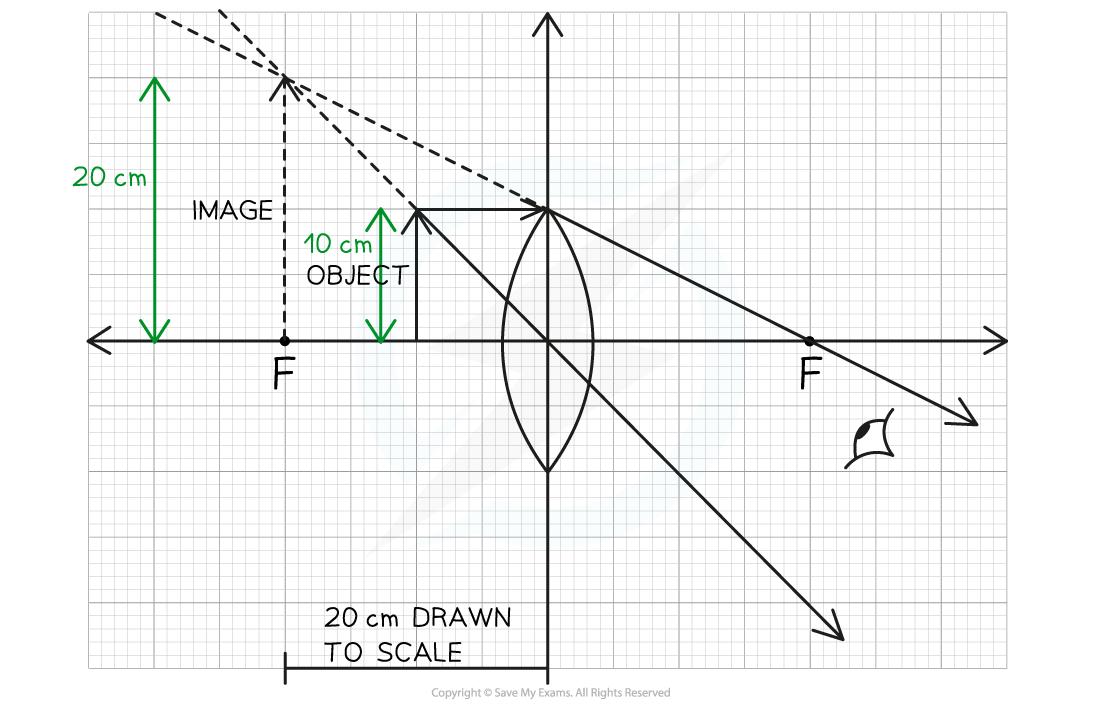
The object is 10 cm
The image is 20 cm
Step 2: Substitute values into the magnification equation

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?