Wave Behaviour (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Reflection, Refraction & Diffraction
All waves, whether transverse or longitudinal, can be reflected, refracted and diffracted
Reflection
Reflection occurs when:
A wave hits a boundary between two media and does not pass through, but instead stays in the original medium
The law of reflection states:
The angle of incidence = The angle of reflection
When waves hit an object, such as a barrier, they can be reflected:
Reflection

When waves reflect off a barrier, the angle of reflection, r, is equal to the angle of incidence, i
Refraction
Refraction occurs when:
A wave passes a boundary between two different transparent media and undergoes a change in direction
When waves enter a different medium, their speed can change
This effect is called refraction, and it can have two other effects:
The wavelength of the waves can increase or decrease
The waves can change direction
Refraction
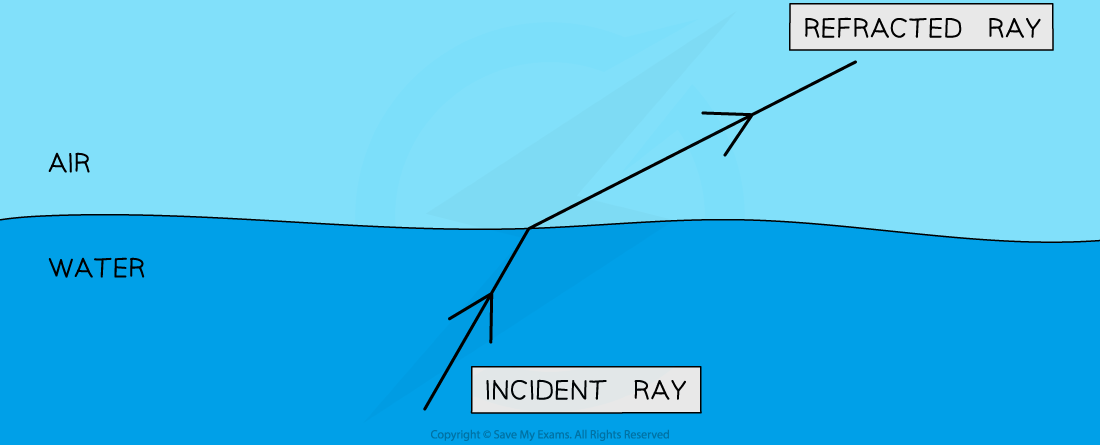
Waves can change direction when moving between materials with different densities
If the waves slow down, the waves will bunch together, causing the wavelength to decrease
The waves will also start to turn slightly towards the normal
If the waves speed up then they will spread out, causing the wavelength to increase
The waves will also turn slightly away from the normal
Diffraction
When waves pass through a narrow gap, the waves spread out
This effect is called diffraction
Diffraction

Diffraction: when a wave passes through a narrow gap, it spreads out
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When drawing waves being reflected take care to:
Make sure that the angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection
Keep the wavelength of the waves the same
Similarly, when waves are diffracted the wavelength remains constant.
Refraction is the only wave effect in which the wavelength changes.
Remember:
Refraction is the name given to the change in the speed of a wave when it passes from one medium to another. The change in direction is a consequence of this.
Factors Affecting Diffraction
Diffraction, as shown above, only generally happens when the gap is smaller than the wavelength of the wave
As the gap gets bigger, the effect gradually gets less pronounced until, in the case that the gap is very much larger than the wavelength, the waves no longer spread out at all
Diffraction and Gap Size

The size of the gap (compared to the wavelength) affects how much the waves spread out
Diffraction can also occur when waves pass an edge
Diffraction around an Edge

When a wave goes past the edge of a barrier, the waves can curve around the edge

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?