Consequences of Thermal Energy Transfer (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Simple Consequences of Energy Transfer
Conduction
The main means of thermal energy transfer in solids
When heated, atoms vibrate more, knocking into each other and transferring energy from atom to atom as a result
Conduction in Solids

Energy from the kinetic store of a vibrating particle is transferred to the kinetic store of a neighbouring particle. In this way, energy is transferred throughout the solid.
Metals are especially good at conducting heat as the delocalised electrons can collide with the atoms, helping to transfer the vibrations through the material and hence transfer heat better
Delocalised Electrons in a Metal

Delocalised electrons in metals speed up thermal conduction
If a question mentions metals, the answer will probably have something to do with conduction
Trapped air is a very good insulator. Air is a gas and so is a poor conductor. Trapping air prevents it from circulating and forming a convection current
Hot Coffee Heating a Hand by Conduction
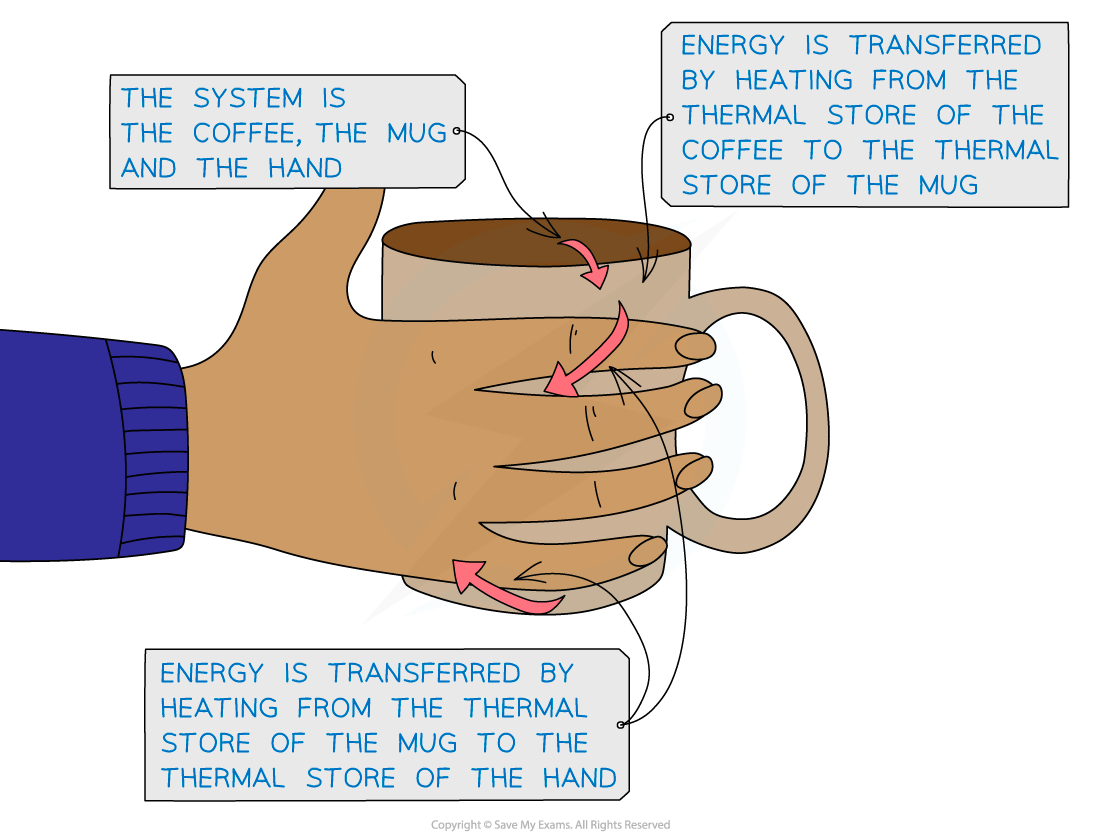
Thermal energy is transferred from the hot coffee to the mug and to the cold hands
Other common examples of conduction are:
Heating a pan on a hob
Heating water in a kettle
A lizard warming its belly on a hot rock
Convection
The means of thermal energy transfer in liquids and gases
Convection cannot occur in solids because the in solids the particles are not free to move
When a fluid (a liquid or a gas) is heated:
The molecules push each other apart, making the fluid expand
This makes the hot fluid less dense than the surroundings
The hot fluid rises, and the cooler (surrounding) fluid moves in to take its place
Eventually, the hot fluid cools, contracts and sinks back down again
The resulting motion is called a convection current
Convection Current

A convection current caused by heating from the fire
Heat sources placed at the bottom of things will generally create convection currents. Likewise, cooling units placed high up will cool any rising air, causing it to sink again
Coffee Heats Air through Convection

Thermal energy is transferred from the hot coffee to the air by convection currents rising from the surface
Other common examples of convection are:
A radiator heating a room
Air conditioning cooling a room
Ice cubes cooling a drink
A hot air balloon
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If a question is about a metal, then make sure you talk about conduction. If a question refers to a liquid or gas (that isn't trapped) then make sure you talk about convection.
Thermal Radiation
The only means of thermal energy transfer that does not require a medium
The temperature of a body can be regulated by balancing how much incoming radiation is absorbed and emitted (or reflected)
If an object starts to absorb radiation at a higher rate than it radiates it, then the object will heat up
Likewise, if it loses radiation at a greater rate than it absorbs it, then the object will cool down
This is how an emergency blanket works, to keep a trauma victim warm:
Rescue teams use light-coloured, shiny emergency blankets to keep accident survivors warm
A light, shiny outer surface emits a lot less radiation than a dark, matt (non-glossy) surface
This keeps the patient warm, as less infrared radiation is emitted than if an ordinary blanket had been used
Reflective Blanket Being Used to Keep a Patient Warm

The reflective surface of an emergency blanket reflects the infrared radiation emitted by the body back towards the patient, helping to keep them warm
Other common examples of thermal radiation are:
Heating from sunlight
Using an infrared thermometer to measure temperature
Using a thermal imaging camera
Using night vision
Complex Consequences of Energy Transfer
In real situations there is very rarely only one form of energy transfer
Usually all three happen at once
Thermal Energy Transfers in a Hot Drink
In the diagram below a more complex - and more 'real' - version of the coffee cup is shown
Thermal energy is transferred from hotter areas (the tea) to cooler areas (the cup, hands and air) by the processes of:
Conduction; by direct contact between the tea and the solid sides of the cup and also by direct contact from the cup to the surface it is sitting on
Convection; from the surface of the coffee to the air directly above it
Radiation; from the sides of the hot cup in all directions to the surrounding air
Thermal Energy Transfers Occurring in a Hot Drink

Energy is transferred by conduction, convection and radiation from a hot mug of coffee
Objects will always lose heat until they are in thermal equilibrium (same temperature) with their surroundings
For example, a mug of hot tea will cool down until it reaches room temperature
Eventually the room, tea and cup will all be at the same temperature
Insulation in the Home
Insulating the loft of a house lowers its rate of cooling, meaning less energy is lost to the outside
The insulation is often made from fibreglass (or glass fibre)
This is a reinforced plastic material composed of woven material with glass fibres laid across and held together
The air trapped between the fibres makes it a good insulator
Trapped pockets of air ensure that convection currents cannot be formed, therefore reducing energy transfer by convection
It has a much lower thermal conductivity than the roof material
Several layers of insulation make it very thick and therefore decrease the rate of cooling
Cavity Wall Insulation

Less heat is lost from a building with the help of insulation (filled cavity in walls)
Examiner Tips and Tricks
A common mistake made by candidates when explaining how an insulator keeps something warm is to state something along the lines of “The object warms up the insulator which then warms the object up”.
Avoid giving this kind of answer!
The real explanation is:
The insulator contains trapped air, which is a poor conductor of heat
Trapping the air also prevents it from transferring heat by convection
This reduces the rate of heat loss from the object, meaning that it will stay warmer for longer
Other things to watch out for:
Heat does not rise (only hot gases or liquids rise)
Shiny things do not reflect heat (they reflect thermal radiation)
Black things do not absorb heat (they absorb thermal radiation)
And remember, a good answer will often include references to more than one method of thermal energy transfer.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?