Gases & Absolute Temperature (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Absolute Temperature
The Kelvin temperature scale begins at absolute zero
Absolute zero, or 0 K, is equal to −273 °C
An increase of 1 K is the same change as an increase of 1 °C
It is not possible to have a temperature lower than 0 K
This means a temperature in Kelvin will never have a negative value
To convert between temperatures θ in the Celsius scale, and T in the Kelvin scale, use the following conversion:
θ / °C = T / K − 273
T / K = θ / °C + 273
Kelvin Scale and Celsius Scale

Conversion chart relating the temperature on the Kelvin and Celsius scales
Worked Example
Convert the following values between the Kelvin (absolute) and Celsius scales of temperature.
(a) 0 K = ...................... °C
(b) 0 °C = ...................... K
(c) 20 °C = ...................... K
Answer:
(a)
Step 1: Choose whether to add or subtract 273 to the value
The question is in Kelvin therefore subtract 273 to convert to Celsius
Step 2: Do the calculation
Step 3: Write the answer with units
0 K = −273 °C
(b)
Step 1: Choose whether to add or subtract 273 to the value
The question is in Celsius therefore add 273 to convert to kelvin
Step 2: Do the calculation
Step 3: Write the answer with units
0 °C = 273 K
Part (c)
Step 1: Choose whether to add or subtract 273 to the value
The question is in Celsius therefore add 273 to convert to kelvin
Step 2: Do the calculation
Step 3: Write the answer with units
20 °C = 293 K
Did this video help you?
The Gas Laws
The gas laws describe the relationships between the pressure, volume and temperature of a gas
Pressure & Volume at Constant Temperature
If the temperature of a gas remains constant, the pressure of the gas changes when it is:
Compressed – decreasing the volume causes pressure to increase
Expanded – increasing the volume causes pressure to decrease
Decreasing Volume Increases Pressure

Pressure increases when a gas is compressed
Similarly, a change in pressure can cause a change in volume
A vacuum pump can be used to remove the air from a sealed container
The diagram below shows the change in volume of a tied up balloon when the pressure of the air around it decreases:
Decreasing Pressure Increases Volume

Decreasing pressure from the air surrounding the balloon on the right allows the pressure from the air particles within to increase the volume of the balloon
When a gas is compressed, the molecules will hit the walls of the container more frequently
This creates a larger overall net force on the walls which increases the pressure
Volume & Temperature at Constant Pressure
If a gas is placed in a container which allows it to expand and compress (e.g. a piston) then its pressure can be kept constant
As a result, changes in temperature at constant pressure will affect the volume only
If the pressure of a gas remains constant, the volume of the gas changes when:
The gas gets hotter – increasing the temperature causes the gas to expand (volume increases)
The gas gets cooler – decreasing the temperature causes the gas to compress (volume decreases)
Relationship between Volume & Temperature
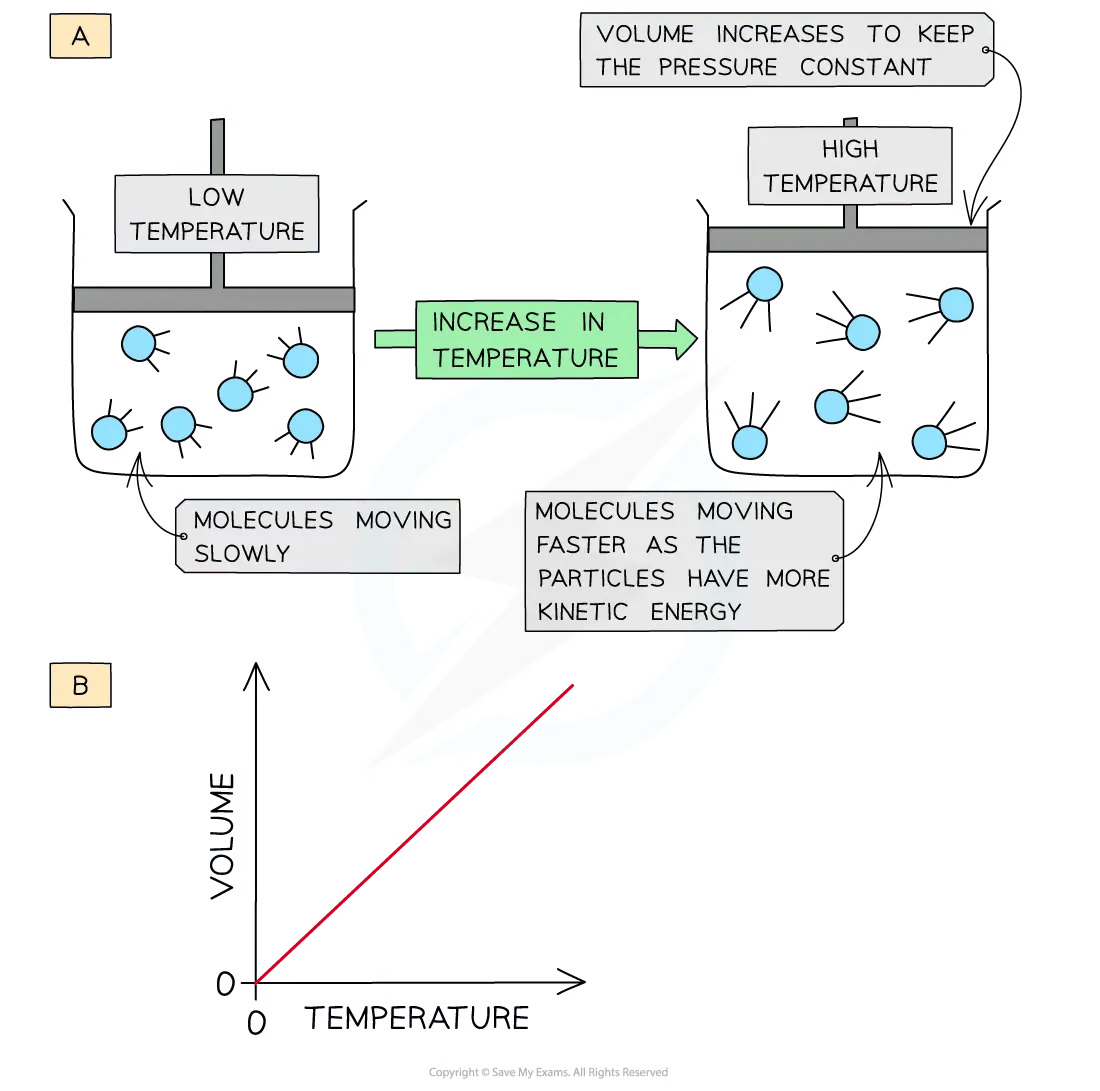
At constant pressure, an increase in the temperature of the gas causes it to expand
In the diagram above:
Diagram A shows molecules expanding into a greater volume as the temperature increases
Diagram B shows that the volume of the gas is directly proportional to the temperature
Pressure & Temperature at Constant Volume
If the temperature of a gas is increased, the particles move faster and gain kinetic energy
As a result, they will collide more often leading to an increase in pressure
If the volume of a gas remains constant, the pressure of the gas changes when:
The gas gets hotter – increasing the temperature causes the pressure to increase
The gas gets cooler – decreasing the temperature causes the pressure to decrease
Relationship between Pressure & Temperature

At constant volume, an increase in the temperature of the gas increases the pressure due to more collisions on the container walls
In the diagram above:
Diagram A shows molecules in the same volume colliding with the walls of the container more often as the temperature increases
Diagram B shows that the temperature of a gas is directly proportional to the gas pressure
Examiner Tips and Tricks
You are required to be able to describe the links between pressure & volume and pressure & temperature qualitatively. This means that the correct use of terms such as ‘collision’, ‘kinetic energy’ and ‘frequency’, will be really important.
Did this video help you?
Boyle's Law
For a fixed mass of a gas held at a constant temperature:
pV = constant
Where:
p = pressure in pascals (Pa)
V = volume in metres cubed (m3)
This means that the pressure and volume are inversely proportional to each other
When the volume decreases (compression), the pressure increases
When the volume increases (expansion), the pressure decreases
This relationship is known as Boyle’s Law and can also be written as:
This means the pressure is inversely proportional to the volume of a gas
Graph Showing Boyle's Law

Boyle's Law shows that pressure is inversely proportional to volume
The relationship between the pressure and volume for a fixed mass of gas at constant temperature can also be written as:
Where:
P1 = initial pressure (Pa)
P2 = final pressure (Pa)
V1 = initial volume (m3)
V2 = final volume (m3)
Notice that volume and pressure are measured in m3 and Pa respectively
In calculations, if units are given in cm3 or MPa this is a rare case where calculations can be done using the original units as long as answers are reported in the same, original units
Calculating Changes in Pressure & Volume

Initial pressure and volume, P1 and V1, and final pressure and volume, P2 and V2
Worked Example
A gas occupies a volume of 0.70 m3 at a pressure of 200 Pa.
Calculate the pressure exerted by the gas if it is compressed to a volume of 0.15 m3.
Assume that the temperature and mass of the gas stay the same.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Initial volume, V1 = 0.70 m3
Initial pressure, P1 = 200 Pa
Final volume, V2 = 0.15 m3
Step 2: Write down the relevant equation
Step 3: Rearrange for the final pressure P2
Step 4: Substitute the values into the equation
Examiner Tips and Tricks
It is an easy mistake to make to think that an inversely proportional graph will be a straight line sloping downwards. After all, a directly proportional graph is a straight line (through the origin) which slopes upwards!
The curve above which 'tends towards zero' (meaning the curve gets closer and closer but never touches the axis, or zero is an inversely proportional curve, as the graph below shows.


Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?