Pressure & Forces (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Did this video help you?
Pressure
Pressure is defined as
The force applied per unit area
For example, when a drawing pin is pushed downwards:
It is pushed into the surface, rather than up towards the finger
This is because the sharp point is more concentrated (a small area) creating a larger pressure
Equal Forces but Inequal Pressures
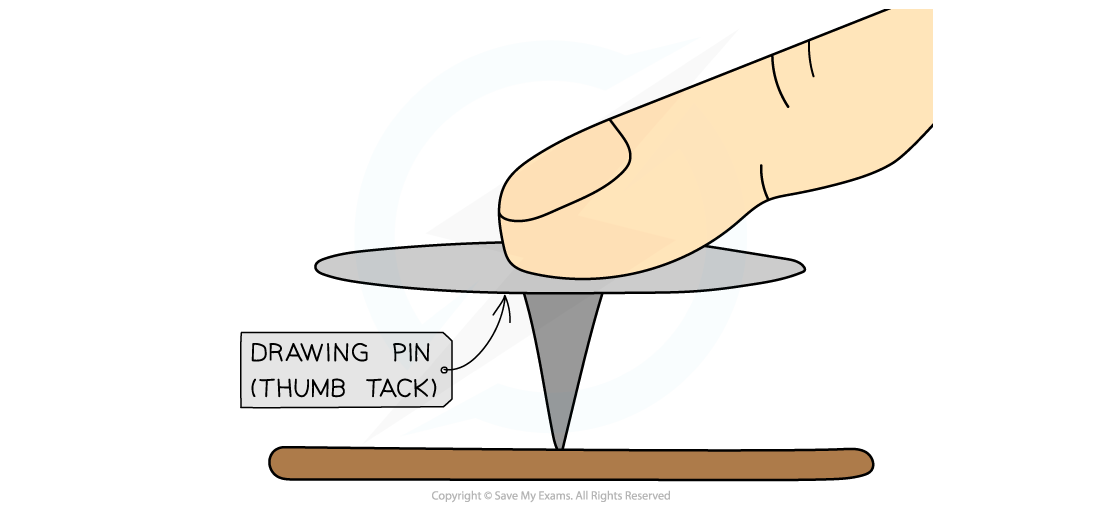
When you push a drawing pin, it goes into the surface (rather than your finger)
Example 1: Tractors
Tractors have large tyres
This spreads the weight (force) of the tractor over a large area
This reduces the pressure which prevents the heavy tractor from sinking into the mud
Example 2: Nails
Nails have sharp pointed ends with a very small area
This concentrates the force, creating a large pressure over a small area
This allows the nail to be hammered into a wall
The pressure at the surface of a fluid can be calculated using the equation:
Where:
P is pressure (Pa)
F is force (N)
A is area (m2)
Pressure is measured in the units Pascals (Pa)
The area should always be the cross-sectional area of the object
This means the area where the force is at right angles to it
This equation can be rearranged with the help of a formula triangle:
Formula Triangle for Pressure
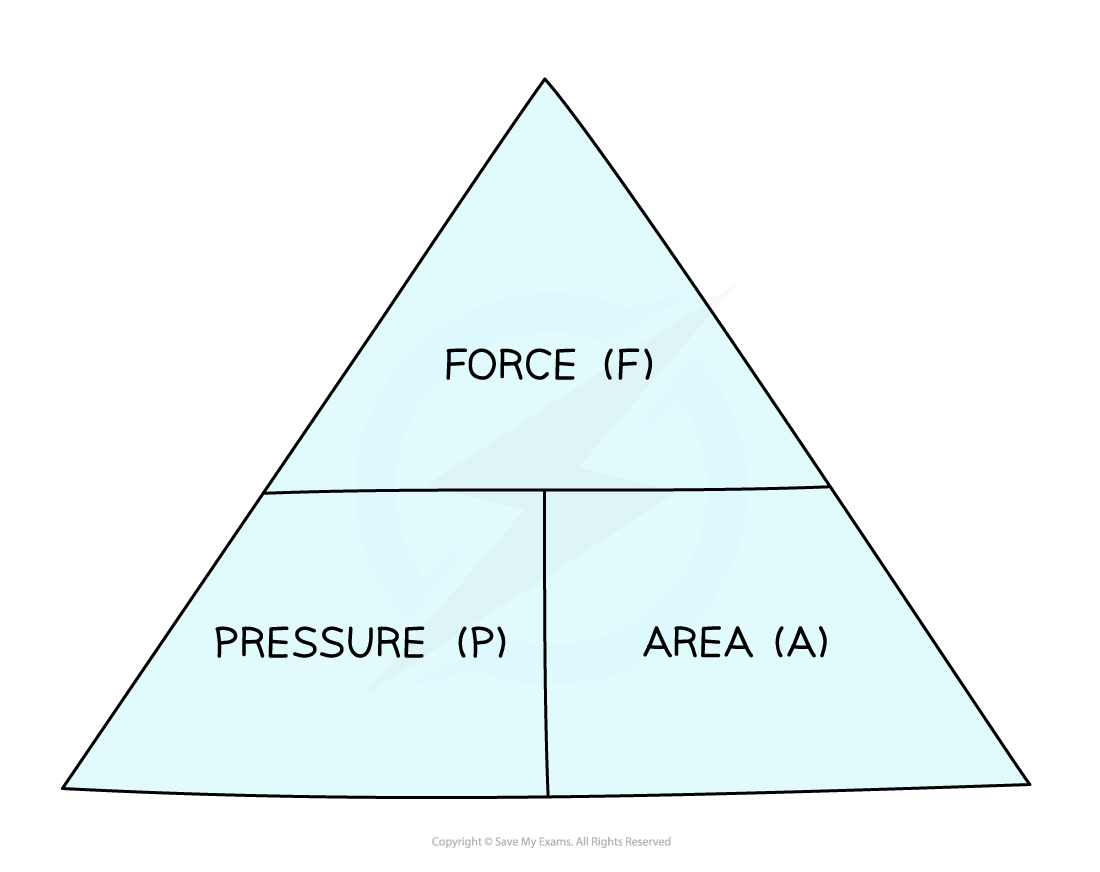
Pressure, force, area formula triangle
This equation tells us that:
If a force is spread over a large area it will result in a small pressure
If it is spread over a small area it will result in a large pressure
Pressure of High Heels vs Flat Shoes
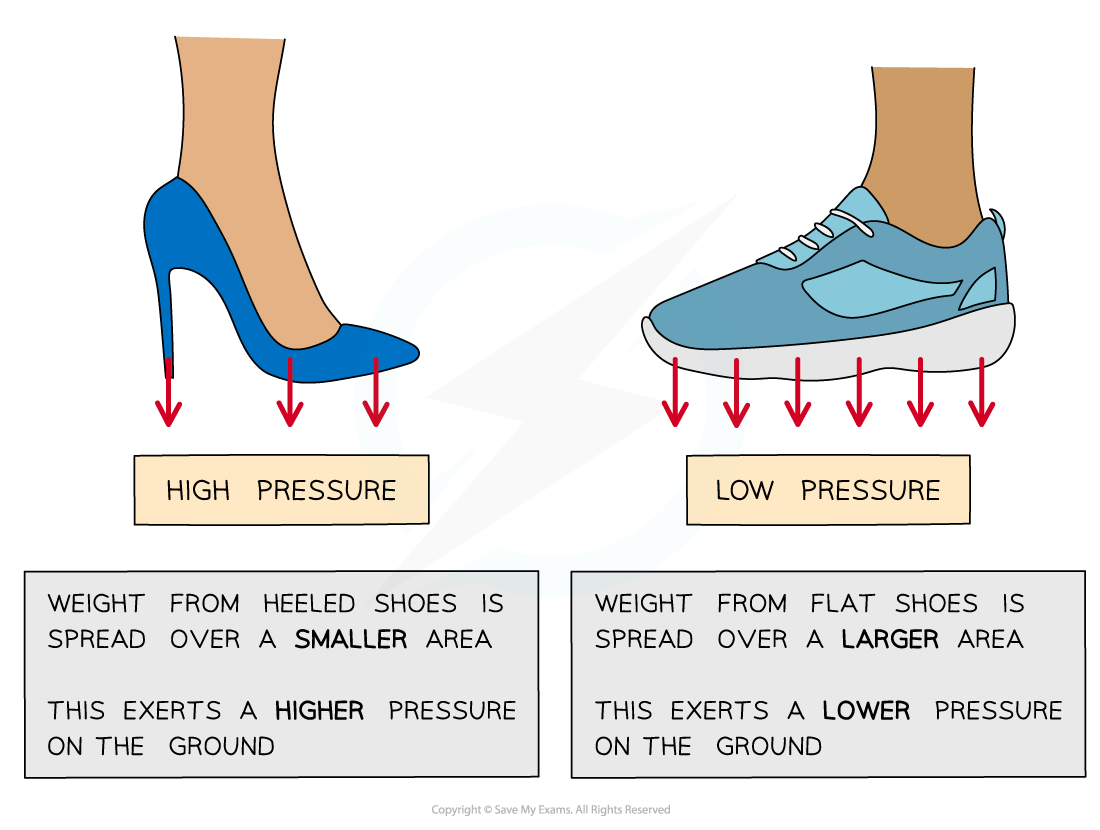
High heels produce a higher pressure on the ground because of their smaller area, compared to flat shoes

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?