Efficiency (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics) : Revision Note
Efficiency of Energy Transfer
The efficiency of a system is a measure of the amount of wasted energy in an energy transfer
Efficiency is defined as:
The ratio of the useful power or energy output from a system to its total power or energy input
If a system has high efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is useful
If a system has low efficiency, this means most of the energy transferred is wasted
The overall efficiency of a typical thermal power station is approximately 30%
This means that 70% of the energy transferred from the power station to the National Grid is wasted energy
In the production of electricity:
Energy is used to heat water to produce steam
The steam turns a turbine
The turbine turns a generator
The generator produces electricity
At each stage of this process, energy is dissipated to the surroundings
Sankey Diagram of a Power Station
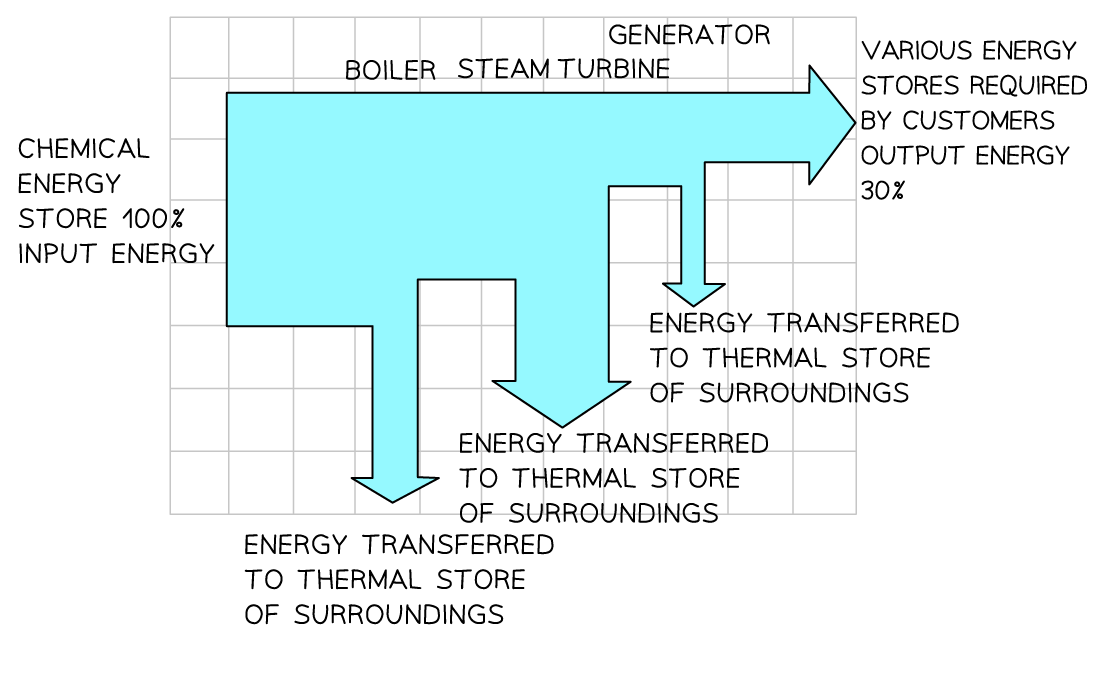
Sankey diagram showing the efficiency of a gas-fired power station
Calculating Efficiency
Efficiency is represented as a percentage, and can be calculated using the equation:
The efficiency equation can also be written in terms of power:
Where power is defined as the energy transferred per unit of time
Worked Example
An electric motor has an efficiency of 35%. It lifts a 7.2 kg load through a height of 5 m in 3 s. Calculate the power of the motor.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the efficiency equation
Step 2: Rearrange to make power input the subject
OR
Step 3: Calculate the power output
ΔE is equal to the change in gravitational potential energy as the load is lifted
Therefore,
Step 4: Substitute the values into the power input equation
OR
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Efficiency can be given in a ratio (between 0 and 1) or percentage format (between 0 and 100 %)
If the question asks for efficiency as a ratio, give your answer as a fraction or decimal.
If the answer is required as a percentage, remember to multiply the ratio by 100 to convert it:
if the ratio = 0.25, percentage = 0.25 × 100 = 25 %
Remember that efficiency has no units

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
