Impulse (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: 5054
Written by: Leander Oates
Updated on
Did this video help you?
Impulse
When a resultant (unbalanced) force acts on a mass, the momentum of that mass will change
The impulse of a force is equal to that force multiplied by the time for which it acts:
impulse = force × change in time
impulse = FΔt
The change in momentum of a mass is equal to the impulse provided by the force:
impulse = change in momentum
impulse = FΔt = Δp
Change in momentum can also be described as:
Δp = Δ(mv)
Δp = mv − mu
Where:
m = mass in kg
v = final velocity in m/s
u = initial velocity in m/s
Therefore:
impulse = FΔt = Δp = mv − mu
An example in everyday life of impulse is when standing under an umbrella when it is raining, compared to hail (frozen water droplets)
When rain hits an umbrella, the water droplets tend to splatter and fall off it and there is only a very small change in momentum
However, hailstones have a larger mass and tend to bounce back off the umbrella, creating a greater change in momentum
Therefore, the impulse on an umbrella is greater in hail than in rain
This means that more force is required to hold an umbrella upright in hail compared to rain
Impulse of Rain & Hail Stones
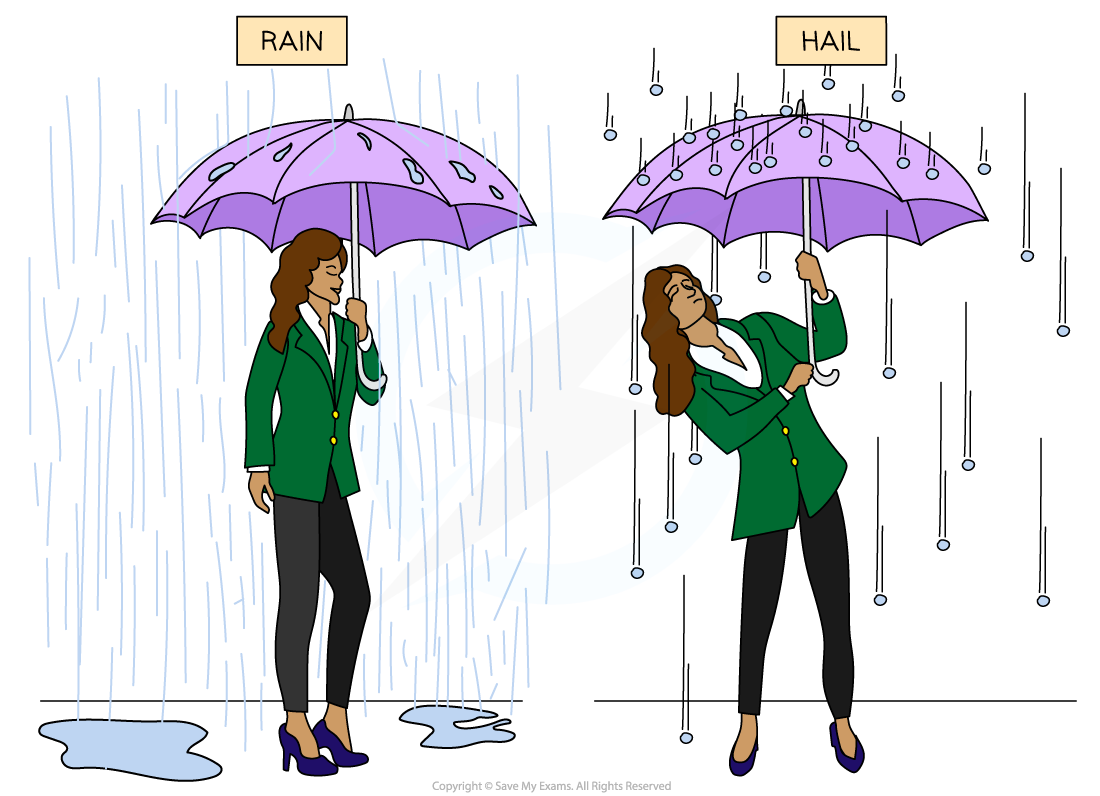
Since hailstones bounce back off an umbrella, compared to water droplets from rain, there is a greater impulse on an umbrella in hail than in rain
Worked Example
A 58 g tennis ball moving horizontally to the left at a speed of 30 m s–1 is struck by a tennis racket which returns the ball back to the right at 20 m s–1.
(i) Calculate the impulse delivered to the ball by the racket
(ii) State which direction the impulse is in
Answer:
(i)
Step 1: Write the known quantities
Taking the initial direction of the ball as positive (the left)
Initial velocity, u = 30 m s–1
Final velocity, v = –20 m s–1
Mass, m = 58 g = 58 × 10–3 kg
Step 2: Write down the impulse equation
Impulse I = Δp = m(v – u)
Step 3: Substitute in the values
I = (58 × 10–3) × (–20 – 30) = –2.9 N s
(ii)
Direction of the impulse
Since the impulse is negative, it must be in the opposite direction to which the tennis ball was initial travelling (since the left is taken as positive)
Therefore, the direction of the impulse is to the right
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that if an object changes direction, then this must be reflected by the change in sign of the velocity. As long as the magnitude is correct, the final sign for the impulse doesn't matter as long as it is consistent with which way you have considered positive (and negative). For example, if the left is taken as positive and therefore the right as negative, an impulse of 20 N s to the right is equal to -20 N s
Force & Momentum
Force can also be defined as the rate of change of momentum on a body
The change in momentum is defined as the final momentum minus the initial momentum
These can be expressed as follows:
Where:
F = force in newtons (N)
Δ (Greek letter delta) = change in
p = momentum in kilogram metres per second (kg m/s)
t = time in seconds (s)

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
