Speed & Velocity (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Physics) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Speed
The speed of an object is the distance it travels per unit time
Speed is a scalar quantity
This is because it only contains a magnitude (without a direction)
For objects that are moving with a constant speed, use the equation below to calculate the speed:
Where:
Speed is measured in metres per second (m/s)
Distance travelled is measured in metres (m)
Time taken is measured in seconds (s)
Different speeds
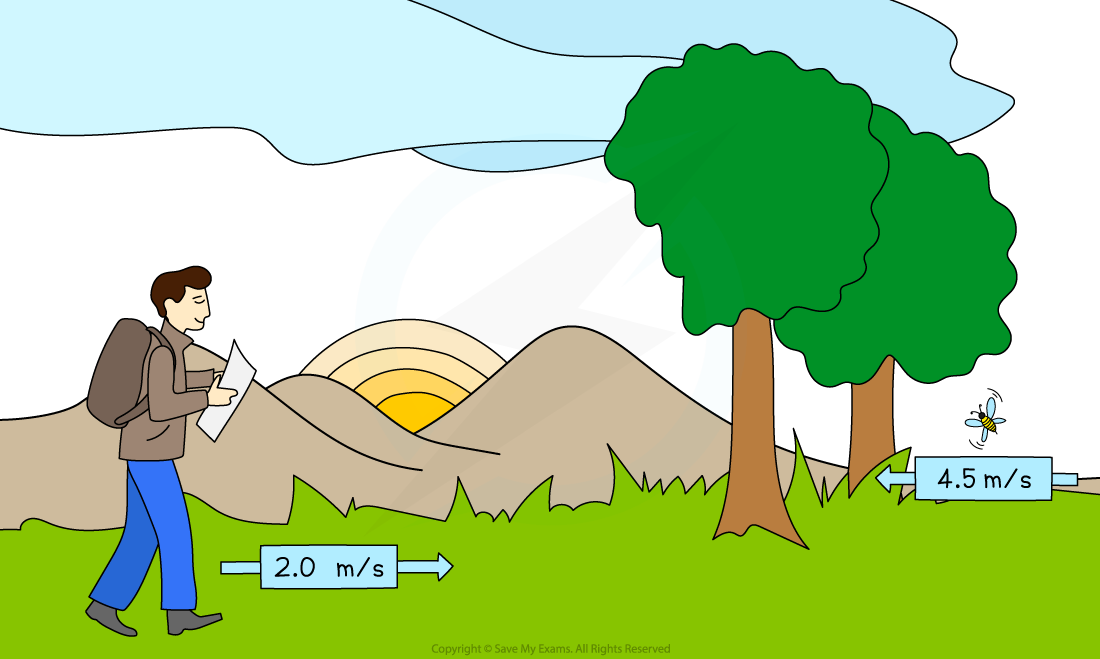
A hiker might have an average speed of 2.0 m/s, whereas a particularly excited bumble bee can have average speeds of up to 4.5 m/s
Average Speed
In some cases, the speed of a moving object is not constant
For example, the object might be moving faster or slower at certain moments in time (accelerating and decelerating)
The equation for calculating the average speed of an object is:
The formula for average speed (and the formula for speed) can be rearranged with the help of the formula triangle below:
Average speed equation triangle

Average speed, total distance and time taken equation triangle
How to Use Formula Triangles
Formula triangles are really useful for knowing how to rearrange physics equations
To use them:
Cover up the quantity to be calculated, this is known as the 'subject' of the equation
Look at the position of the other two quantities
If they are on the same line, this means they are multiplied
If one quantity is above the other, this means they are divided - make sure to keep the order of which is on the top and bottom of the fraction!
In the example below, to calculate speed, cover-up 'speed' and only distance and time are left
This means it is equal to distance (on the top) ÷ time (on the bottom)
Formula triangle example

How to use formula triangles
Worked Example
Planes fly at typical speeds of around 250 m/s. Calculate the total distance travelled by a plane moving at this average speed for 2 hours.
Answer:
Step 1: List the known quantities
Average speed = 250 m/s
Time taken = 2 hours
Step 2: Write the relevant equation
Step 3: Rearrange for the total distance
total distance = average speed × time taken
Step 4: Convert any units
The time given in the question is not in standard units
Convert 2 hours into seconds:
2 hours = 2 × 60 × 60 = 7200 s
Step 5: Substitute the values for average speed and time taken
total distance = 250 × 7200 = 1 800 000 m
Velocity
The velocity of a moving object is similar to its speed, except it also describes the object’s direction
The speed of an object only contains a magnitude - it’s a scalar quantity
Velocity is therefore a vector quantity because it describes both magnitude and direction
e.g. ‘15 m/s south’ or ‘250 mph on a bearing of 030°’
Speed vs. velocity

Two objects can have the same speed but a different velocity
This means velocity can also have a negative value
E.g. a ball thrown upwards at a velocity of 3 m/s comes down at a velocity –5 m/s, if upwards is considered positive
However, their speeds are still 3 m/s and 5 m/s respectively
The equation for velocity is very similar to the equation for speed:
Where:
v = velocity in metres per second (m/s)
s = displacement, measured in metres (m)
t = time, measured in seconds (s)
Velocity is a vector quantity, so it uses displacement, s, rather than distance which is scalar.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
