Economies of Scale (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Business Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 7115
Economies of Scale
As a business grows, it is able to increases its scale of output which generates efficiencies that lower its average costs (AC) of production
These efficiencies are called economies of scale
Economies of scale help large firms lower their costs of production beyond what small firms are able to achieve
Economies of scale can result in lower average (or unit) costs, not lower total costs
The total costs will increase, but at a decreasing rate per unit
Explaining economies of scale
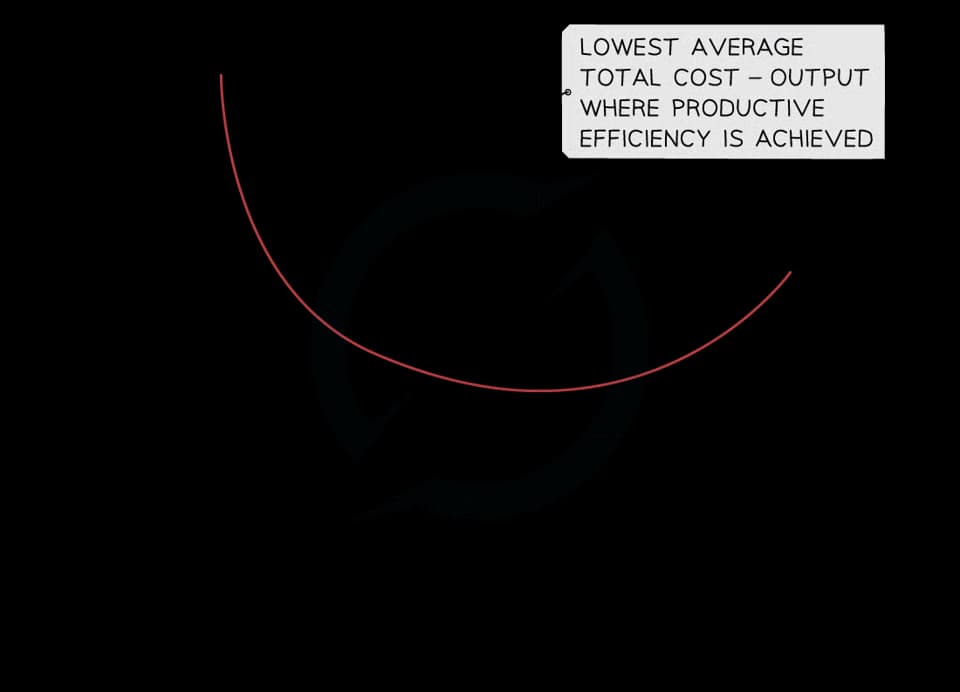
Diagram analysis
With relatively low levels of output, the firms average costs are high
As the firm increases its output, it begins to benefit from economies of scale which lower the average cost per unit
The business will reach a level of output at which costs are minimised
Beyond this point, diseconomies of scale will occur and the average cost will start to rise again
Different types of economies of scale
Economies of scale are generated by several internal factors, some of which the business has control over
Businesses will attempt to benefit from as many of these economies as possible in order to lower their costs and increase their profit
The different economies of scale
Type of economy of scale | Explanation |
|---|---|
Purchasing economy |
|
Managerial economy |
|
Marketing economy |
|
Financial economy |
|
Technical economy |
|
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When explaining economies of scale, make sure that you fully explain how each type lowers the average costs for the business. This is different from only saying that it lowers the average cost. E.g., Bulk purchases result in the business benefitting from cheaper raw materials, which lowers the cost per unit

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?