Syllabus Edition
First teaching 2018
Last exams
Diseconomies of Scale (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Business Studies): Revision Note
Exam code: 7115
Diseconomies of scale
As a firm continues increasing its scale of output, it will reach a point where its average costs (AC) will start to increase
The reasons for the increase in the average costs are called diseconomies of scale
Explaining diseconomies of scale
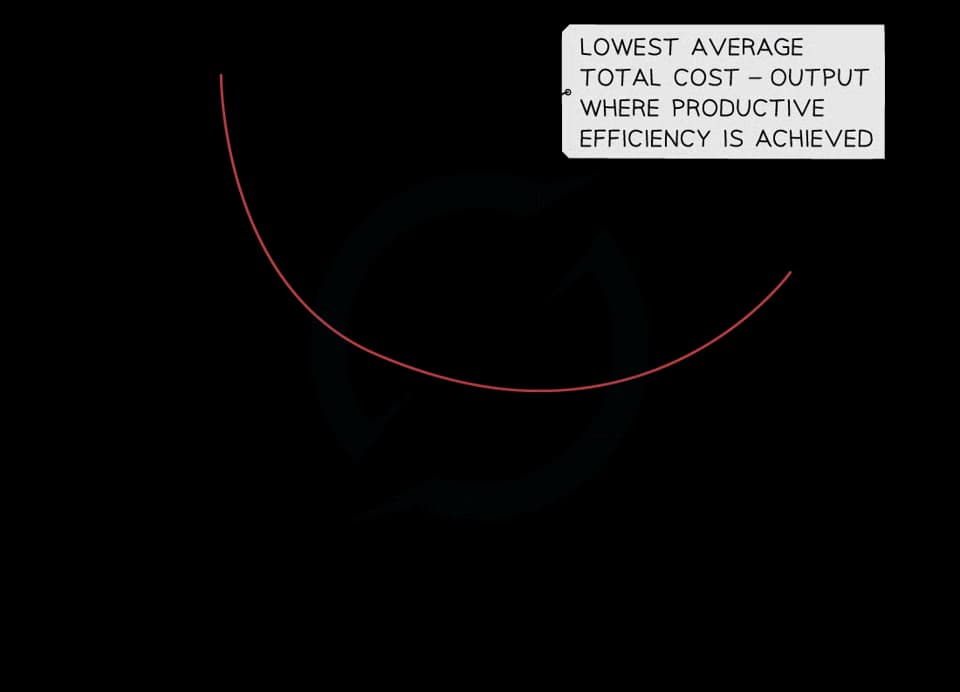
Diagram analysis
At some level of output, a firm will not be able to reduce costs any further. This point is called productive efficiency
Beyond this level of output, the average cost will begin to rise as a result of diseconomies of scale
This indicates that there is an optimal level of output that exists when the state of technology and capital (machinery) is fixed
Different types of diseconomies of scale
Diseconomies of scale highlight that it is possible for a business to become so large that it becomes less and less efficient
A business experiencing diseconomies of scale may reconsider its organisational structure to improve communication and coordination problems
Many very large businesses often break themselves up into autonomous smaller units, which can communicate more effectively
The causes of diseconomies of scale
Type of diseconomy of scale | Explanation |
|---|---|
Poor communication |
|
Weak coordination |
|
Lack of commitment from employees |
|

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?