Investigating the Rate of Photosynthesis (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Biology): Revision Note
Exam code: 5090
Investigating the Rate of Photosynthesis
As photosynthesis occurs, oxygen gas is produced and released into the surroundings; the volume of oxygen produced can be used as a measure of the rate of photosynthesis
In aquatic plants, the oxygen released can be seen as bubbles released into the water; the number of bubbles produced over a minute can therefore be used as a measure of photosynthetic rate
The more bubbles produced per minute, the faster the rate of photosynthesis
The aquatic plants usually used in this experiment are Elodea or Cabomba, both types of pondweed
It is also possible to collect the oxygen released in a test tube inverted over the top of the pondweed; this allows the volume of oxygen produced to be measured
This gives a more accurate measure of the rate of reaction, as the results are not affected by the different sizes of bubble
This practical can be used to investigate the effect of various factors on the rate of photosynthesis
The effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
The effect of changing light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis can be investigated by placing a lamp at different distances from a beaker that contains pondweed and measuring oxygen production
A lamp that is further away will reduce the light intensity in comparison to a lamp that is close by
Investigating the effect of changing light intensity on photosynthesis diagram

The volume of oxygen produced at different light intensities shows the effect of light intensity on the rate of photosynthesis
The effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis
The effect of changing carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis can be investigated by dissolving different amounts of sodium hydrogen carbonate in water in a beaker

The volume of oxygen produced at different carbon dioxide concentrations shows the effect of carbon dioxide concentration on the rate of photosynthesis
The effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
The effect of changing temperature on the rate of photosynthesis can be investigated by changing the temperature of the water in the beaker
Investigating the effect of changing temperature on the rate of photosynthesis diagram
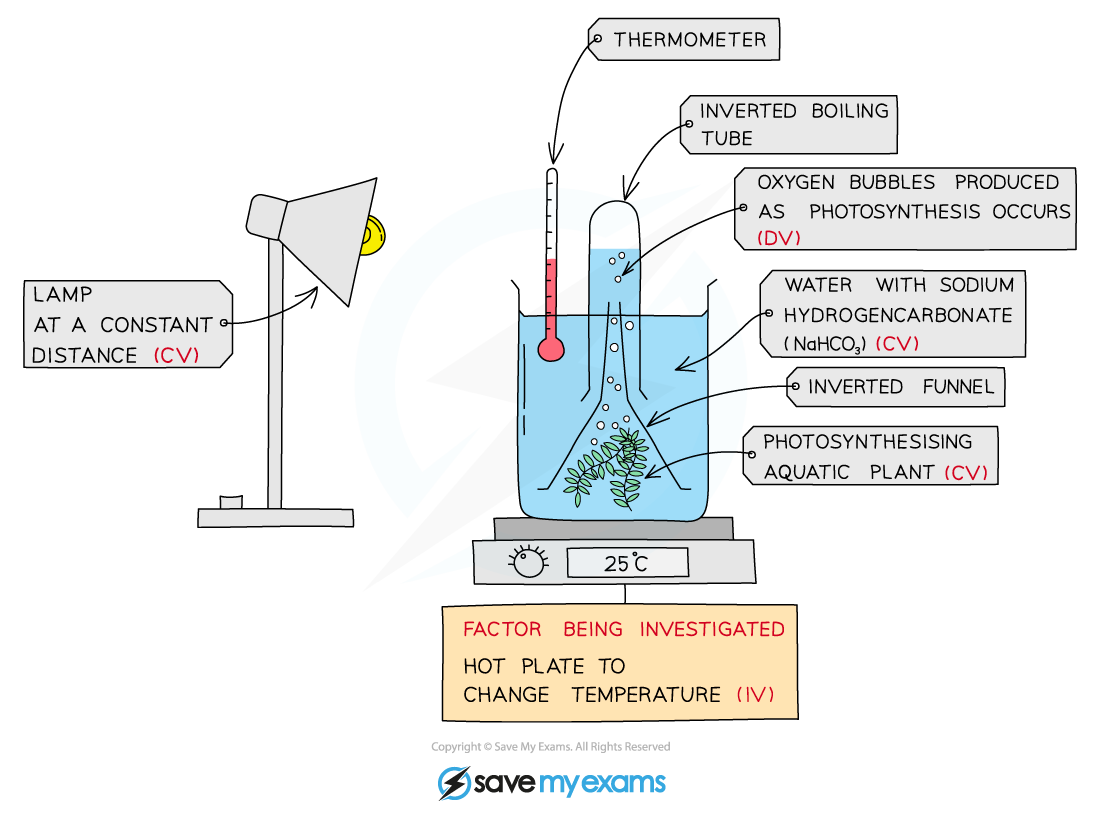
The volume of oxygen produced at different temperatures shows the effect of temperature on the rate of photosynthesis
Using hydrogencarbonate indicator
Hydrogencarbonate indicator shows the carbon dioxide concentration in solution
This is possible because carbon dioxide is an acidic gas when dissolved in water
It is possible to investigate the effect of environmental factors on photosynthesis in a submerged aquatic plant using a pH indicator such as hydrogencarbonate indicator
Carbon dioxide is a reactant in photosynthesis, so measuring the rate at which carbon dioxide is removed from a solution gives a measure of the rate of photosynthesis
Hydrogencarbonate indicator can be used to investigate rate of photosynthesis by placing an aquatic plant in water that contains hydrogencarbonate indicator and measuring colour change under different environmental conditions
E.g. measuring the time taken for colour to change from red to purple at different light intensities
Hydrogencarbonate indicator can be used to investigate the rate of photosynthesis in a plant in relation to the rate of respiration
A plant that is photosynthesising at a faster rate than it is respiring will cause the indicator to turn purple
Carbon dioxide is used up by photosynthesis faster than it is produced in respiration
A plant that is respiring faster than it is photosynthesising, e.g. in the dark, will cause the indicator to turn yellow
Carbon dioxide is produced faster by respiration than it is used up in photosynthesis
Hydrogencarbonate indicator colour table
Concentration of carbon dioxide | Colour of hydrogencarbonate indicator | |
|---|---|---|
Highest | Yellow |  |
High | Orange |  |
Atmospheric level | Red |  |
Low | Magenta |  |
Lowest | Purple |  |
Ensuring validity
When investigating a particular variable, it is essential to keep all other variables constant so that they do not affect the results, e.g.
When investigating changing light intensity, a glass tank should be placed in between the lamp and the beaker to absorb heat from the lamp and so avoid changing the temperature of the water
When investigating temperature or carbon dioxide concentration, the lamp should always be placed at a constant distance from the plant
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When describing the oxygen released during these experiments, you should always refer to the volume of gas, or the number of bubbles, rather than using vague terms such as 'amount'.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?