Asexual Reproduction (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Biology) : Revision Note
Asexual Reproduction
Asexual reproduction does not involve sex cells or fertilisation
Only one parent is required so there is no fusion of gametes and no mixing of genetic information
As a result, the offspring are genetically identical to the parent and to each other (clones)
Asexual reproduction is defined as a process resulting in genetically identical offspring from one parent
Examples of Asexual Reproduction
Bacteria produce exact genetic copies of themselves in a type of asexual reproduction called binary fission:
Binary Fission Diagram
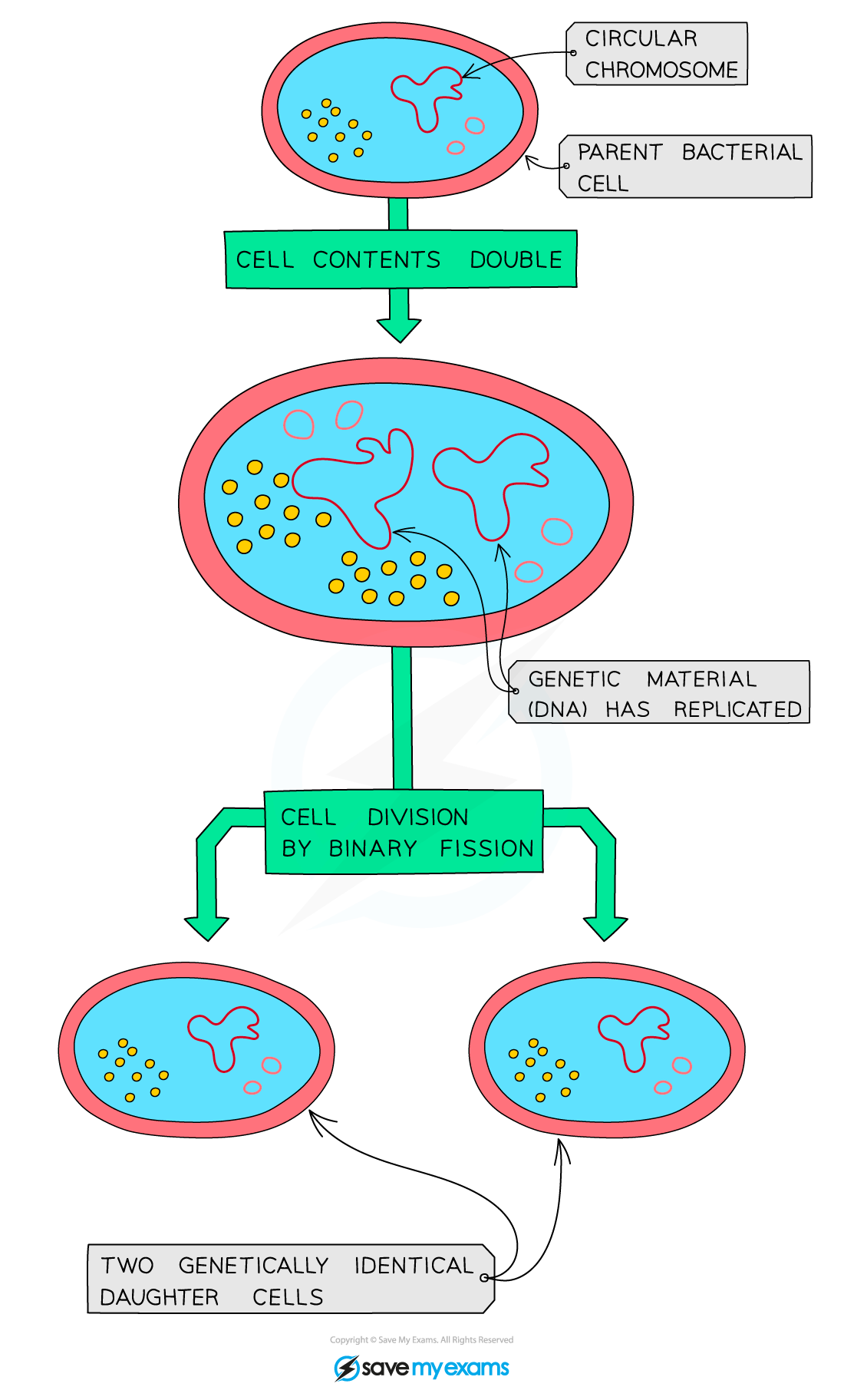
Bacteria produce exact genetic copies of themselves in a type of asexual reproduction called binary fission
Plants can reproduce asexually using bulbs and tubers
These are food storage organs from which budding can occur, producing new plants which are genetically identical to the parent plant
Old potatoes stored for too long start budding or 'chitting' as this process begins
Budding of Bulbs & Tubers Diagram

Some plants develop underground food storage organs that will develop into next years plants - they can take different forms, such as bulbs or tubers
Some plants grow side shoots called runners that contain tiny plantlets on them
A good example of this is strawberry plants
These will grow roots and develop into separate plants, again being genetically identical to the parent plant
Runners in Asexual Plant Reproduction Diagram

Some plants grow side shoots called runners that contain tiny plantlets on them. These will grow roots and develop into separate plants.
Advantages & Disadvantages of Asexual Reproduction
Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
Population can be increased rapidly when conditions are right. | Limited genetic variation in population. Offspring are genetically identical to their parents. |
Can exploit suitable environments quickly. | Population is vulnerable to changes in conditions and may only be suited for one habitat. |
More time and energy efficient. | Disease is likely to affect the whole population as there is no genetic variation. |
Reproduction is completed much faster than sexual reproduction. |
|
Specifically in crop plants, asexual reproduction can be advantageous as it means that a plant that has good characteristics (high yield, disease-resistant, hardy) can be made to reproduce asexually and the entire crop will show the same characteristics

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
