Language of Functions (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Additional Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 4037
Written by: Paul
Updated on
Did this video help you?
Introduction to functions
What is a mapping?
A mapping takes an 'input' from one set of values to an 'output' in another
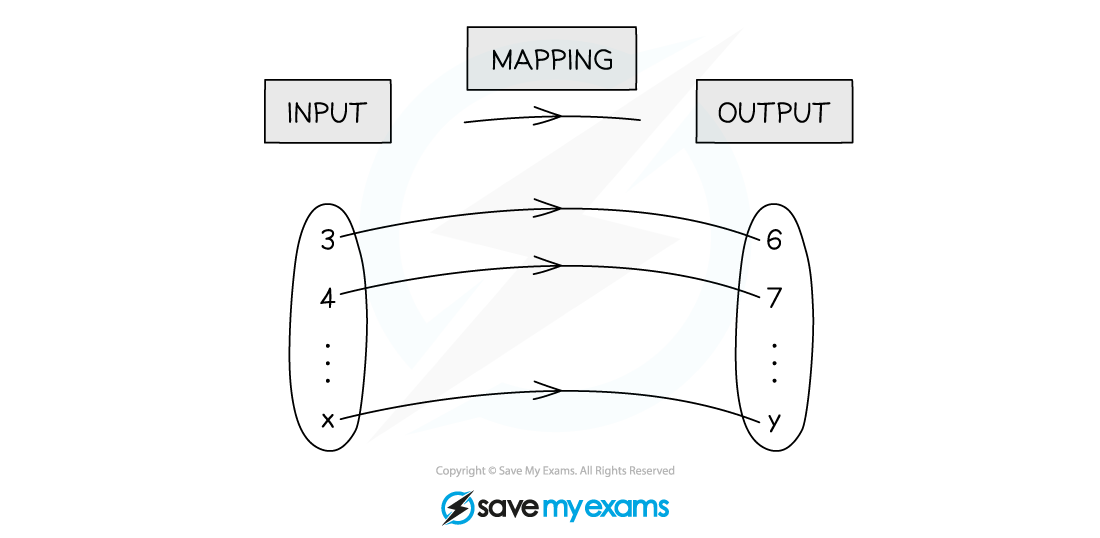
Mappings can be
'many-one' (many 'input' values map to one 'output' value)
'one-one' (one 'input' value maps to one 'output' value)
You may also come across 'many-many' and 'one-many' functions
What is a function?
A function is a mapping where every 'input' value maps to a single 'output'
Therefore only many-one and one-one mappings are functions
What notation is used for functions?
Functions are denoted by
, etc
e.g.
These would be pronounced as 'f of x', 'g of x', etc
There is an alternative notation
e.g.
Which may be pronounced 'the function f maps x to x-squared minus three x plus two'
How does a function work?
A function has an input
and output
Whatever goes in the bracket (instead of
) with f, replaces the
on the other side
This is the input
If the input is known, the output can be calculated
For example, given the function
If the output is known, an equation can be formed and solved to find the input
For example, given the function
If
, the equation
can be formed
Solving this equation gives an input of 7
Worked Example
A function is defined as .
a) Find .
The input is , so substitute 7 into the expression everywhere you see an
.
Calculate.
b) Find .
The input is so substitute
into the expression everywhere you see an
.
Expand the brackets and simplify.
A second function is defined .
c) Find the value of for which
.
Form an equation by setting the function equal to -16.
Solve the equation by first adding 4 to both sides, then dividing by 3.
Domain & range
What is the domain of a function?
The domain of a function is the set of values that are allowed to be the ‘input’
A function is only fully defined once its domain has been stated
If a domain is not stated then it is assumed that the domain is the largest set of possible values
e.g. the largest set of possible values for the function
would be
Restrictions on a domain can turn many-one functions into one-one functions

What is the range of a function?
The range of a function is the set of values of all possible ‘outputs’
The type of values in the range depend on the domain

How do I find a range from a given domain?
The domain of a function is the set of values that are used as inputs
The range of a function is the set of values that are given as outputs
Finding the range of a function involves determining all possible output values from a given domain
This may need to be done by calculating each output value individually by applying the function to each input value
Or by considering the shape or pattern of the function
To graph a function we use the inputs as the x-coordinates and the outputs as the y-coordinates
corresponds to the coordinates (2, 5)
Graphing the function can help you visualise the range
For example the range of the function
for a domain of all real values of
will be
as the y-coordinates on the graph are all greater than or equal to zero
Worked Example
The many-one function, , is given by
for all values of .
a) State the range of .
The 'output' from the function is a squared value and so will be positive, or zero.
b) The domain of is changed to
. Write down the changed range of
.
As ,
The modulus function
What is the modulus function?
The modulus function makes any 'input' positive
This is sometimes called the absolute value (of the input)
The modulus function is indicated by a pair of vertical lines being written around the input
Similar to how brackets are used
e.g.
What is the relationship between a function and its modulus?
For an 'output' such that
, then
Both the function and its modulus are positive
For an 'output' such that
, then
The function value is negative, but its modulus is positive

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
