Factor & Remainder Theorem (Cambridge (CIE) O Level Additional Maths): Revision Note
Exam code: 4037
Did this video help you?
Factor theorem
What is the factor theorem?
The factor theorem is a useful result concerning the roots and factors of polynomials
In the example below, the polynomial
has three (linear) factors
and
and so it has the three roots
and
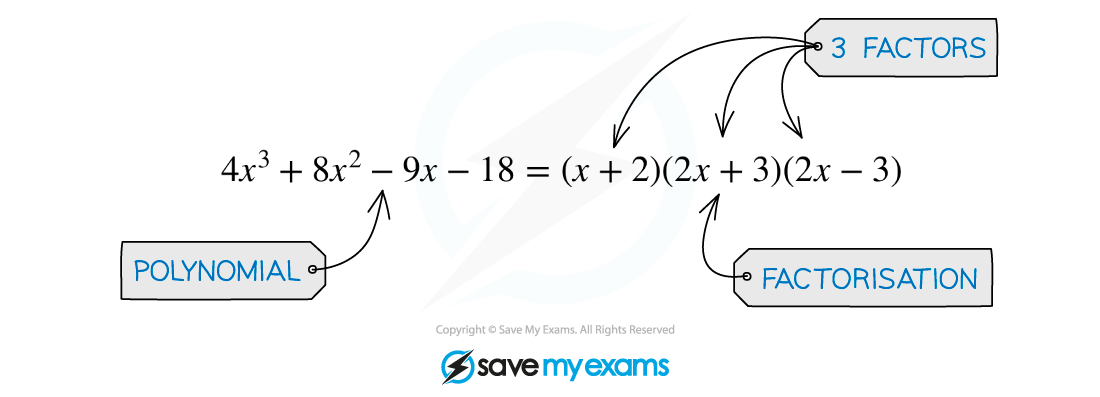
For a polynomial
the factor theorem states that:
i) if , then
is a factor of
( is a root of
)
and
ii) if is a factor of
, then
Examiner Tips and Tricks
In an exam, the values of
you'll need to find that make
are going to be integers close to zero
Try
and
first, then 2 and -2, then 3 and -3
It is unlikely that you'll have to go beyond that
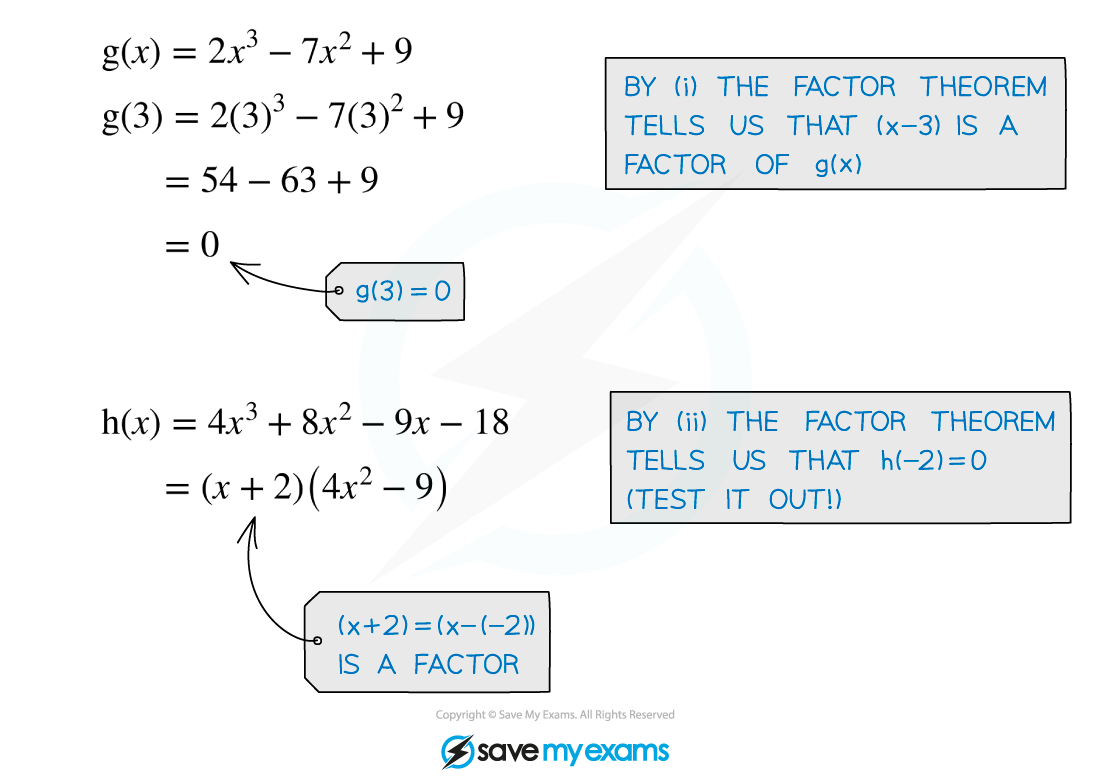
Worked Example
a) Show that is a factor of the polynomial
.
(From part (ii) of our definition of factor theorem ...) ... if is a factor of
then
.
Since ,
is factor of
.
b) Use the factor theorem to find another factor of .
Try first,
Since ,
is not a factor of
.
Try ,
Since ,
is a factor of
.
is another factor of
.
is the third (linear) factor.
Once one factor is known, polynomial division could be used to find the others. (In this case we were specifically asked to use factor theorem.)
Remainder theorem
What is the remainder theorem?
The factor theorem is actually a special case of the more general remainder theorem
The remainder theorem states that when the polynomial
is divided by
the remainder is
You may see this written formally as
In polynomial division
would be the result (at the top) of the division (the quotient)
would be the remainder (at the bottom)
is called the divisor
In the case when
and hence
is a factor of
– the factor theorem!
How do I solve problems involving the remainder theorem?
If it is the remainder that is of particular interest, the remainder theorem saves the need to carry out polynomial division in full
e.g. The remainder from
is
This is because if
and
If the remainder from a polynomial division is known, the remainder theorem can be used to find unknown coefficients in polynomials
g. The remainder from
is 8 so the value of p can be found by solving
, leading to
In harder problems there may be more than one unknown in which case simultaneous equations would need setting up and solving
The more general version of remainder theorem is if
is divided by
then the remainder is
The remainder is still found by evaluating the polynomial at the value of
such that
(the divisor is zero) but it is not necessarily an integer
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Exam questions will use formal mathematical language which can make factor and remainder theorem questions sound more complicated than they are
Ensure you are familiar with the various terms from these revision notes
Worked Example
The polynomial is given by
, where
and
are integer constants.
When is divided by
the remainder is 9.
When is divided by
the remainder is 1.
Find the values of and
.
Remainder theorem: " is the remainder when
is divided by
".
when
:
when
:
Solving simultaneously,

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?