Crude Oil - GCSE Chemistry Definition
Reviewed by: Philippa Platt
Last updated
What is crude oil?
Crude oil is a resource found in the Earth's crust. It is a complex mixture of different hydrocarbon compounds of different sizes.
How is crude oil formed?
It takes millions of years to form crude oil. High pressure and temperature act on the remains of plants and animals (biomass). The main component forming crude oil is plankton that was buried in mud.
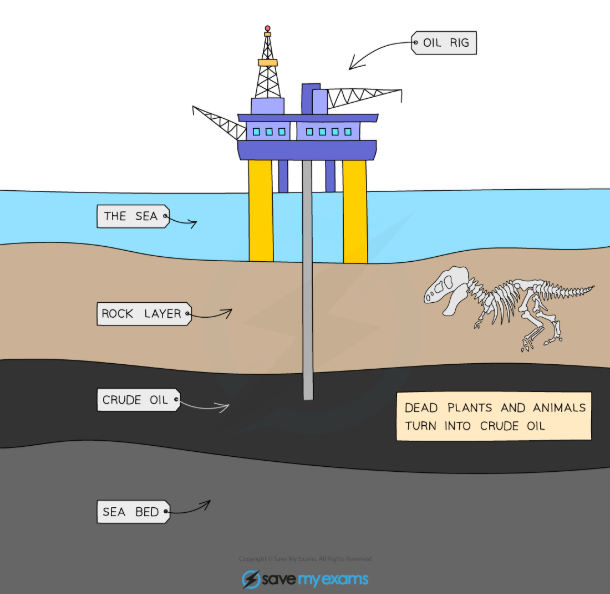
What is crude oil used for?
Crude oil is a finite resource because it is being used up faster than it is being formed. Crude oil is separated into useful fractions through a process called fractional distillation. Each fraction has different boiling points and is used for different purposes, such as:
Petrol for vehicles
Kerosene for aircraft fuel
Bitumen for road surfaces
Additionally, crude oil serves as the starting point for the production of plastics and other petrochemicals, making it essential in modern life.
Examiner-written GCSE Chemistry revision resources that improve your grades 2x
- Written by expert teachers and examiners
- Aligned to exam specifications
- Everything you need to know, and nothing you don’t

Share this article
 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your