Activity: GCSE Physics Definition
Written by: Ann Howell
Reviewed by: Katie M
Published
Last updated
What is activity?
In GCSE Physics, activity is defined as the rate at which unstable nuclei in a source of radiation decay. Activity is measured in Becquerels (Bq), where 1 Becquerel is equivalent to one nucleus decaying each second.
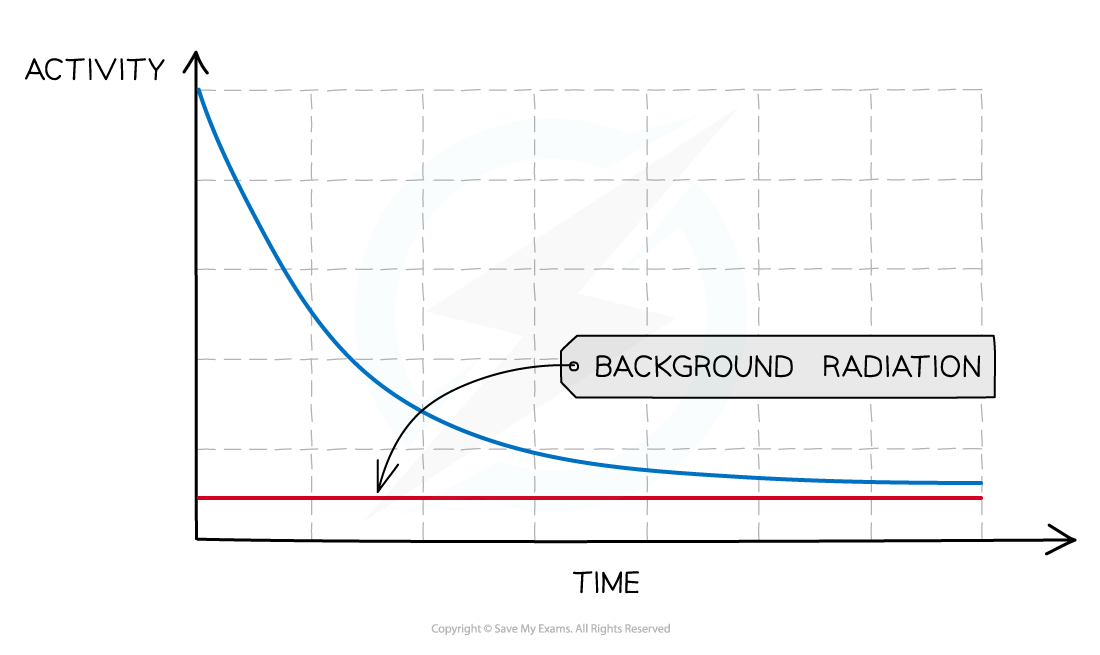
A substance containing radioactive nuclei is a source of radiation. The rate at which a source of radiation decays is defined by its activity. When an isotope decays, the number of unstable nuclei remaining will decrease. As a result, the activity of that isotope will also decrease over time. This can be shown on a graph of activity against time for a decaying source.
Activity revision resources to ace your exams
Activity is covered in many of the GCSE Physics and Combined Science course revision notes either as a separate section in a revision note, for example, AQA GCSE Physics Radioactive Decay and OCR Gateway GCSE Physics Radioactive Decay, or as part of a combined revision note that includes information on activity and decay, for example, Edexcel GCSE Physics Activity & Decay. Once you are ready to test your knowledge you can use our specific exam practice questions, like these for Edexcel GCSE Physics on Radioactive Decay. If you are ready for some general exam revision then you can use the past paper section, for example, the OCR GCSE Physics past papers.
Explore all the Save My Exams GCSE Physics resources
Sign up for articles sent directly to your inbox
Receive news, articles and guides directly from our team of experts.

Share this article


 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your