Contents
Geometry and measures is one of the key strands within the mathematics GCSE, so mastering shapes is crucial for success in GCSE maths.
In this article we will identify the key areas of 2D shapes and 3D objects that you need to know, we’ll take a look at some real-life applications of shape problems and we’ll have a go at some tricky GCSE problems. Along the way you may also find some geometrically related jokes, after all, enjoying maths is a sine of good humour, right?
So what are we waiting for? Let’s dive into learning all you need to know about mastering shapes in your exams!
2D Shapes
2D shapes only exist in 2 dimensions, that is to say they have length and width but they lack depth. Knowing the key properties of 2D shapes, such as for triangles, quadrilaterals, circles and more, is vital for success in geometry. Having this knowledge and also the skills to apply it to new and unfamiliar contexts, is immensely useful for solving many real-world problems.
Types of polygons
There is a certain amount of terminology and notation associated with 2D shapes. You need to be able to identify different types of polygons by knowing their names, from 3-sided shapes (triangles) up to 10-sided shapes (decagons), and their properties, i.e. key information about their angles, lines of equal length, parallel lines and diagonals. When you need to remember several key facts, creating a set of flashcards for quick recall practice can be really helpful.
What happened when the maths teacher’s parrot died? Polygon!
Angles in polygons and parallel lines
Another topic area that includes a lot of terminology and key information is that of angles in polygons and parallel lines. The basic angle facts are straightforward to remember but you need to be an expert in spotting the situations in which they arise. Look out for triangles, angles along a straight line and pairs of parallel lines in particular. Angle facts are also frequently used in proof questions, where widely known ‘truths’ are used to build up a line of reasoning by which other facts can be determined.
Parallel lines have so much in common, it’s a shame they’ll never meet…
Symmetry in 2D shapes
Symmetry may sometimes seem intuitive or easy and this is partly because you will have been recognising symmetry in various real-life situations from a very young age. Don’t let this make you complacent as sometimes recognising symmetry or utilising it in an exam question can be more tricky. Being able to recognise symmetry can help you to analyse a situation effectively and aids problem solving.
Why should you never argue with a 90º angle? Because they’re always right!
Finding perimeter and area of 2D shapes
Having a solid understanding of area and perimeter of 2D shapes is useful as it has such wide-ranging real-life applications. If you know the basics for squares, rectangles and triangles, you can expand on these to work out areas and perimeters for much more complex compound shapes. Exam questions will often give you lots of relevant information, which you should annotate on a diagram if you have one. If you are not given a diagram, it is often a very good idea to sketch one.
What did the Area say to the Perimeter when they were arguing? “I would talk to you, but I feel like you're just going around my problem.”
Understanding circles, sectors and arcs
Closely linked to the area and perimeter of polygons, but with additional language and formulas, are circles, sectors and arcs. In order to be able to tackle more difficult shape problems, you need to be secure in calculating the area and circumference of a whole circle and the area, perimeter and arc length of a sector (a ‘pizza slice’ section of a circle). With circles, you do need to remember the formulas.
Why is a circle considered the genius of geometry? Because it has 360 degrees!
Other 2D shape topics
A solid understanding of the 2D shape topics that we’ve looked at already will go a long way in helping you to ace your maths GCSE. However, there are a number of additional shape topics, which build upon these foundations, these include:
3D Shapes
If you’ve mastered 2D shapes, then you can build on that knowledge to deal with 3D objects. In addition to length and width, 3D shapes also have depth, the third dimension.
Types of 3D shapes
For 3D shapes, you need to know the names of the main different types of 3D shapes you will come across including cubes, cuboids, cylinders, prisms, pyramids, cones and spheres. In addition you’ll need to be able to identify the number of vertices, edges and faces in each of the 3D shapes. It’s also useful to be able to break a 3D object down into several 2D shapes as this can simplify more complicated questions.
Where did the square go after killing the triangle? To prism!
Volume
One of the most common areas that is likely to be examined for 3D objects is that of volume. You should know the formulas for calculating the volume of basic 3D objects but you will likely be given the necessary formula to use if a question involves a cone or sphere. When calculating the volume of an object make sure that you substitute your values carefully into the relevant formula as a first line of working, as this may well get you the first mark! It’s all too easy to plug values into a calculator incorrectly and then to just write down an inaccurate answer…
Why was the maths book sad? Because it had a high volume of problems!
Surface area
Similarly to volume, surface area is another topic that frequently appears in exam questions, often it will appear along with volume in the same question. It is often worth sketching out a 2D net of a 3D object to ensure that you don’t miss out any of the faces. It’s also very important to make sure that you read the question carefully. For example, with a cone, at times you will be asked to find the curved surface area and at other times the total surface area.
Did you hear about the surface area expert who lost his job? He didn't measure up.
Other 3D shape topics
Like with 2D shapes, there are some additional topics for 3D shapes that build on all of the earlier work in geometry. Make sure that you revise these topics as well to ensure that your knowledge of shapes is sound. These topics include:
Maths Exercises and Practice Questions
So now that we’ve covered the main areas for 2D and 3D shapes let’s take a quick look at a couple of exam questions that could help.
The 2D shape question below is a really nice question that tests your knowledge and application of that knowledge. You need to recognise the pair of alternate angles formed by the parallel lines (these angles are equal). You now know two angles in one of the triangles, which enables you to calculate the third (they add up to 360º). Finally, knowing the properties of parallelograms (opposite angles are equal) means that you can find the angle x.
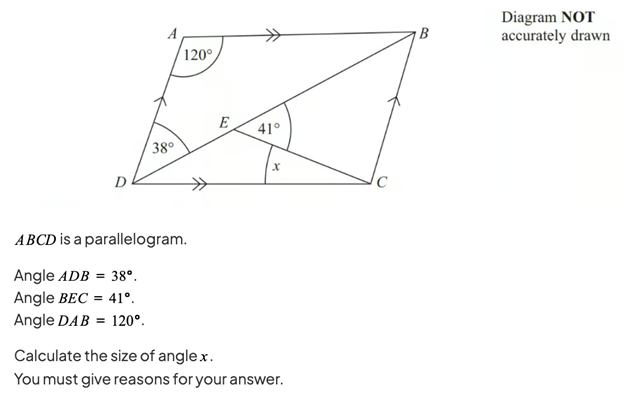
In order to gain full marks answering an exam question like this, you need to show both the calculations that you do and explain each step of your reasoning using the correct mathematical terminology. You can find this question and its student friendly fully worked solution in our Topic Questions on angles in polygons and parallel lines.
This second example is a typical exam question that looks at a 3D problem involving both surface area and volume of an object. Here, given the formula for the volume of the sphere, you can divide this by 2 to find the formula for the volume of a hemisphere. Equating this to the actual volume that you have been given means that you can find the radius of the hemisphere. This can then be substituted into the volume for the surface area of a sphere. A final step is to halve this value to find the curved surface area of the hemisphere and add to it the area of the top circular face that uses the same value for the radius.
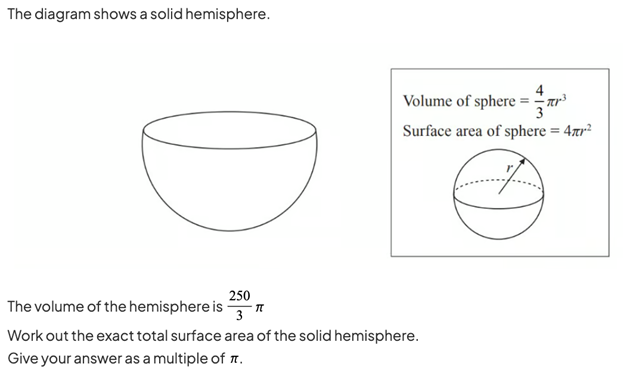
Find the full worked solution in our Topic Questions on volume and surface area.
Real-life applications of shapes
Understanding geometry and its applications goes beyond just passing your GCSE - it equips you with crucial skills for logical thinking, problem-solving, and effective communication in a number of diverse fields.
By learning subject-specific terminology and properties of shapes, you are able to communicate clearly and easily with others about shapes, whether you are discussing the design for a company logo or identifying a particular tool that is needed for a job. Grasping the properties of both 2D and 3D shapes and understanding perimeter, area and volume enables you to develop problems solving strategies applicable to design, construction and manufacturing.
Beyond memorising facts, geometry encourages logical reasoning, interpreting situations, and applying knowledge to find solutions. Mastering geometry lays the foundation for advanced mathematical concepts but it also provides invaluable skills for various careers and daily life scenarios, from art to video game design to forensics.
Get in perfect shape for your GCSE Maths exams!
So there we have it, all the knowledge you need to master shapes in GCSE maths.
But there’s time for some last words of wisdom, so…
What is the best way to pass a geometry test?
Why, the answer is to know all the angles!
Well that and of course signing up to SME to gain full access to all of our amazing revision resources!
Here at Save My Exams, we develop high-quality, affordable revision resources; consider signing up for a Save my Exams subscription to help you get the most out of your revision. We support over 1.5 million students each month in preparing for their exams and achieving successful results, we’d love to help you too.
Sign up for articles sent directly to your inbox
Receive news, articles and guides directly from our team of experts.

Share this article
 written revision resources that improve your
written revision resources that improve your