Equation for the Intensity of Radiation (Edexcel International AS Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: XPH11
Equation for the Intensity of Radiation
Progressive waves transfer energy
The amount of energy passing through a unit area per unit time is the intensity of the wave
Therefore, the intensity is defined as power per unit area
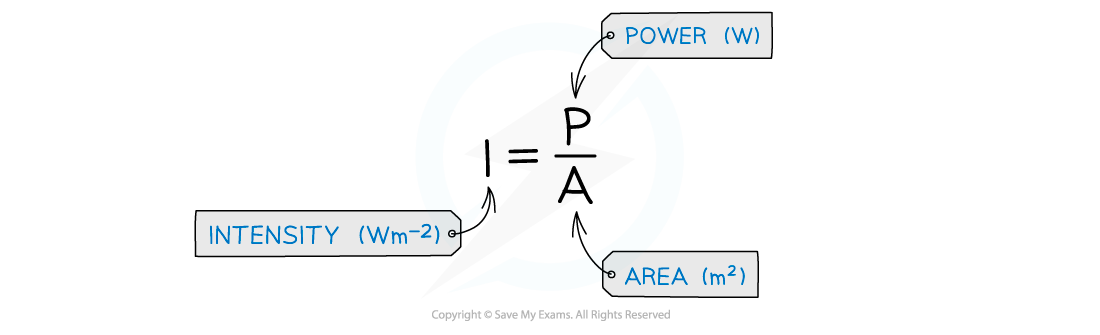
Intensity is equal to the power per unit area
The area the wave passes through is perpendicular to the direction of its velocity
The intensity of a progressive wave is also proportional to its amplitude squared and frequency squared
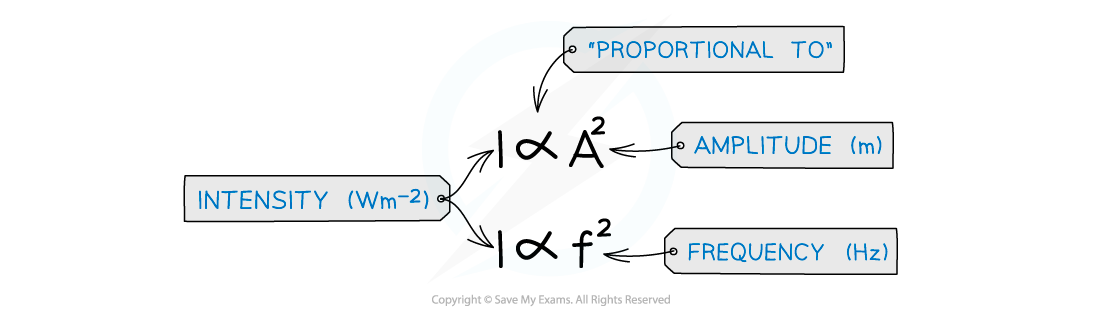
Intensity is proportional to the amplitude2 and frequency2
This means, if the frequency or the amplitude is doubled, the intensity increases by a factor of 4 (22)
Spherical Waves
A spherical wave is a wave from a point source that spreads out equally in all directions
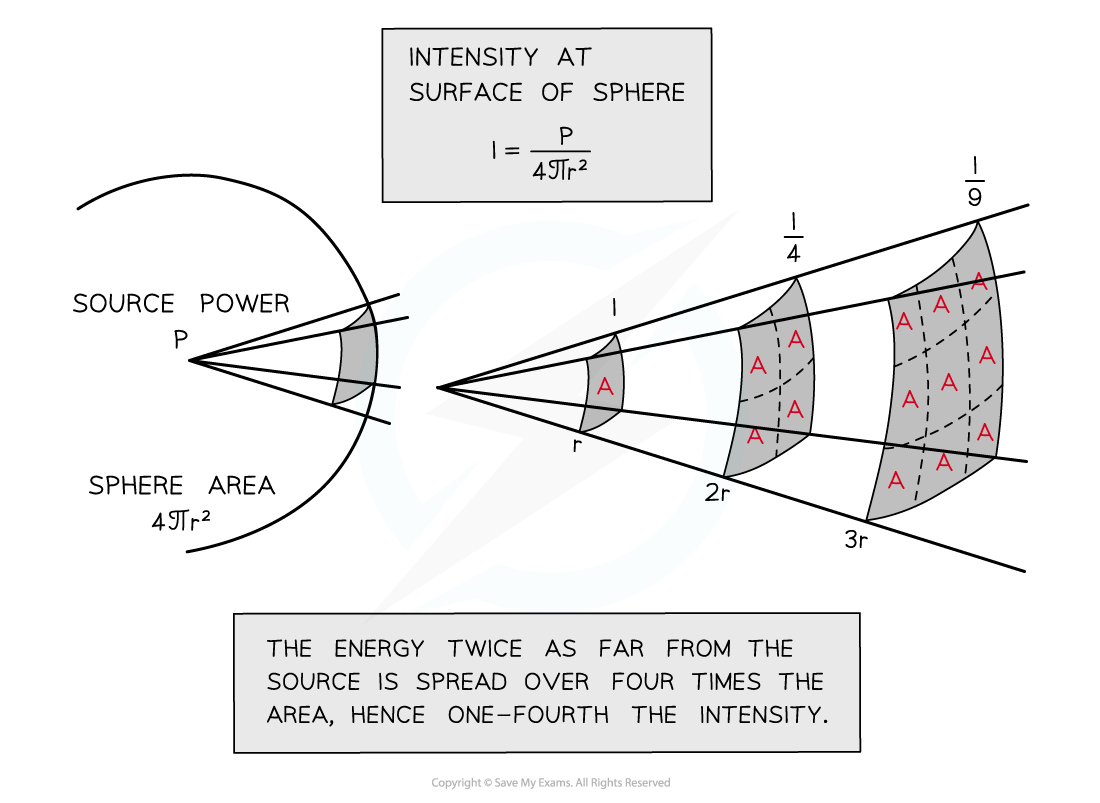
The area the wave passes through is the surface area of a sphere: 4πr2
As the wave travels further from the source, the energy it carries passes through increasingly larger areas as shown in the diagram below:
Intensity is proportional to the amplitude squared
Assuming there’s no absorption of the wave energy, the intensity I decreases with increasing distance from the source
Note the intensity is proportional to 1/r2
This means when the source is twice as far away, the intensity is 4 times less
The 1/r2 relationship is known in physics as the inverse square law
Worked Example
The intensity of a progressive wave is proportional to the square of the amplitude of the wave. It is also proportional to the square of the frequency. The variation with time t of displacement x of particles when two progressive waves Q and P pass separately through a medium are shown on the graphs
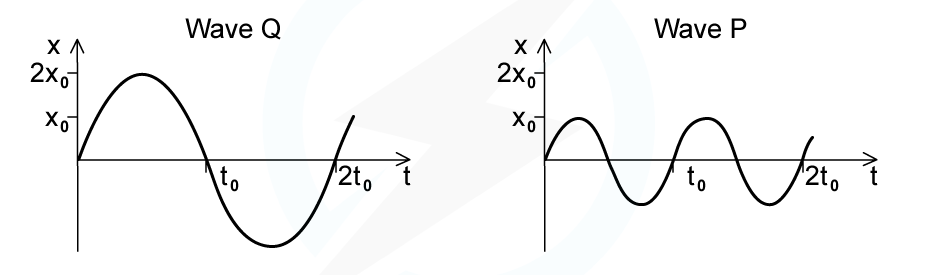
The intensity of wave Q is I0. What is the intensity of wave P?
Answer:


Examiner Tips and Tricks
The key concept with intensity is that it has an inverse square relationship with distance (not a linear one). This means the energy of a wave decreases very rapidly with increasing distance

Unlock more, it's free!
Was this revision note helpful?
