Combustion of Alkanes (Edexcel International AS Chemistry) : Revision Note
Problems of Pollution - General
When alkanes are burnt in excess (plenty of) oxygen, complete combustion will take place and all carbon and hydrogen will be oxidised to carbon dioxide and water respectively
When alkanes are burnt in only a limited supply of oxygen, incomplete combustion will take place and not all the carbon is fully oxidised
Some carbon is only partially oxidised to form carbon monoxide
Incomplete combustion often takes place inside a car engine due to a limited amount of oxygen present
With a reduced supply of oxygen, carbon will be produced
Solid carbon particles (or particulates) released from incomplete combustion clump together to form soot which gradually falls back to the ground

Car exhaust fumes include toxic gases such as carbon monoxide (CO), oxides of sulfur, oxides of nitrogen (NO/NO2) and volatile organic compounds (VOCs)
When released into the atmosphere, these pollutants have serious environmental consequences damaging nature and health
Carbon monoxide
CO is a toxic and odourless gas which can cause dizziness, loss of consciousness and eventually death
The CO binds well to haemoglobin which therefore cannot bind oxygen and carbon dioxide
Oxygen is transported to organs
Carbon dioxide is removed as waste material from organs
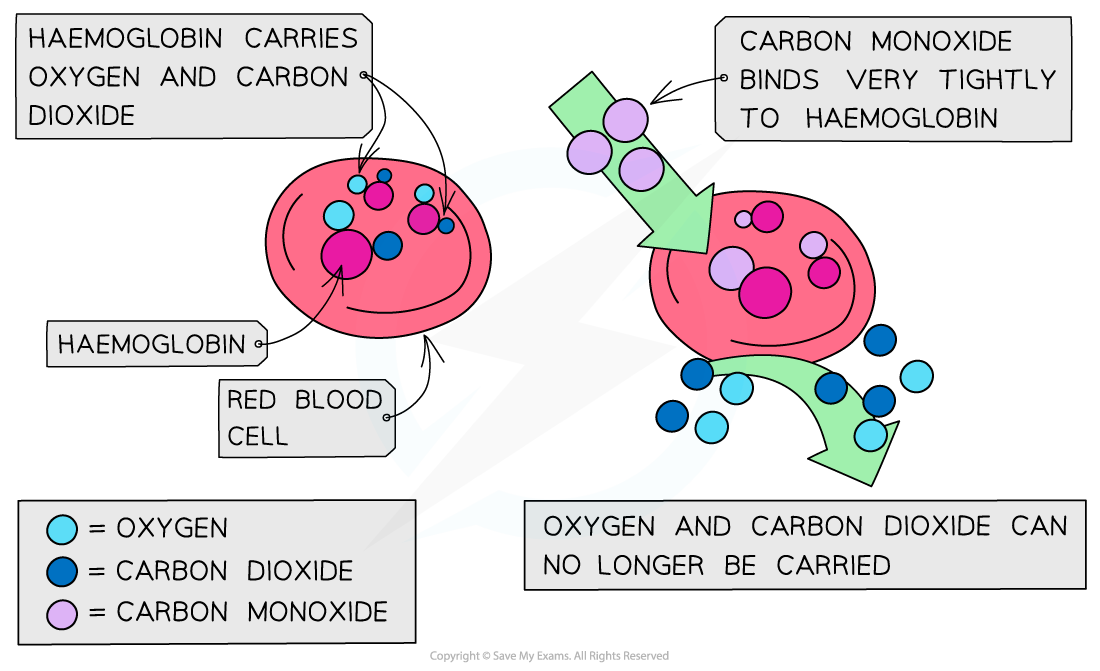
The high affinity of CO to haemoglobin prevents it from binding to O2 and CO2
Oxides of sulfur
Some of the crude oil products from fractional distillation, cracking and reforming contain sulfur atoms
When these molecules are combusted, the sulfur atoms form sulfur dioxide and sulfur trioxide
Both of these sulfur oxides are acidic
S + O2 → SO2
2SO2 + O2 → 2SO3
When these acidic sulfur oxides dissolve into water in the atmosphere, they form sulfurous and sulfuric acid
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3
SO3 + H2O → H2SO4
Both of these acids contribute to acid rain, which is responsible for various environmental issues:
Damage / death of aquatic life
Damage / death to crops and forests
Release of carbon dioxide from carbonate rocks and building materials
Corrosion of metallic structures
Oxides of nitrogen
Normally, nitrogen is too unreactive to react with oxygen in air
However, in a car engine, high temperatures and pressures are reached causing the oxidation of nitrogen to take place:
N2 + O2 → 2NO
N2 + 2O2 → 2NO2
The oxides of nitrogen are then released in the exhaust fumes into the atmosphere
Car exhaust fumes also contain unburnt hydrocarbons from fuels and their oxides (VOCs)
In air, the nitrogen oxides can react with these VOCs to form peroxyacetyl nitrate (PAN) which is the main pollutant found in photochemical smog
PAN is also harmful to the lungs, eyes and plant-life
Nitrogen oxides can also dissolve and react in water with oxygen to form nitrous and nitric acid
3NO2 + O2 → HNO2 + 2HNO3
Both of these acids are a cause of acid rain, which can corrode buildings, endanger plant and aquatic life (as lakes and rivers become too acidic) as well as directly damaging human health
Pollutants, their Effect & Removal Table


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
