Velocity-Time Graph for an Oscillator (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: YPH11
Velocity-Time Graph for an Oscillator
The velocity of an object in simple harmonic motion can be represented by a graph of velocity against time

Key features of the velocity-time graph:
It is 90o out of phase with the displacement-time graph
Velocity is equal to the rate of change of displacement
So, the velocity of an oscillator at any time can be determined from the gradient of the displacement-time graph:

An oscillator moves the fastest at its equilibrium position
Therefore, the velocity is at its maximum when the displacement is zero
Worked Example
A swing is pulled 5 cm and then released.
The variation of the horizontal displacement x of the swing with time t is shown on the graph below.
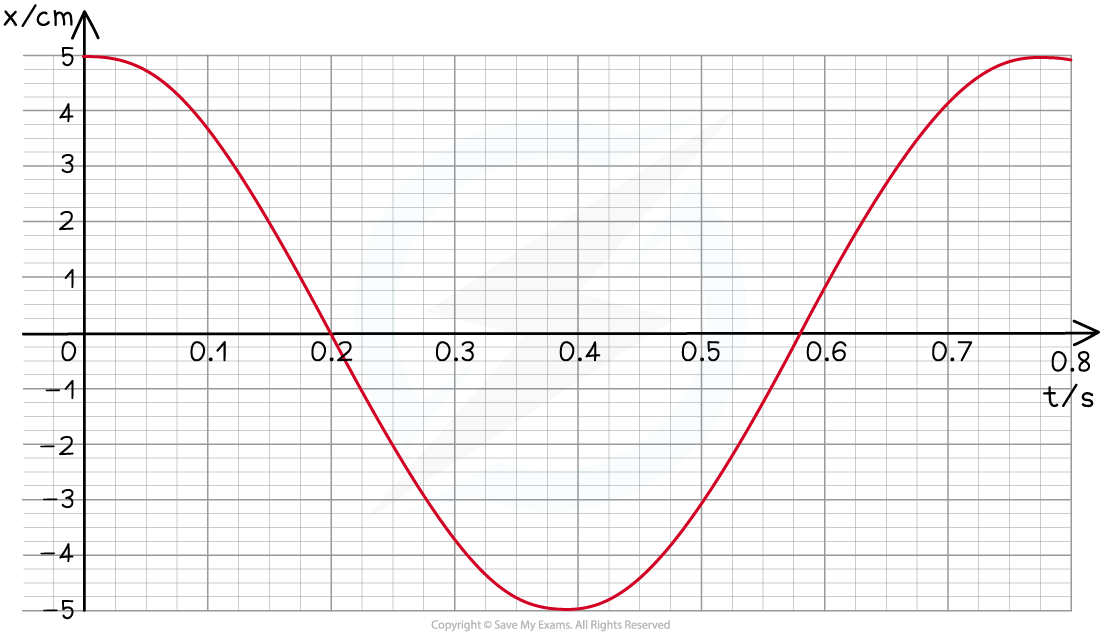
The swing exhibits simple harmonic motion.
Use data from the graph to determine at what time the velocity of the swing is first at its maximum.
Answer:
Step 1: The velocity is at its maximum when the displacement x = 0
Step 2: Reading value of time when x = 0
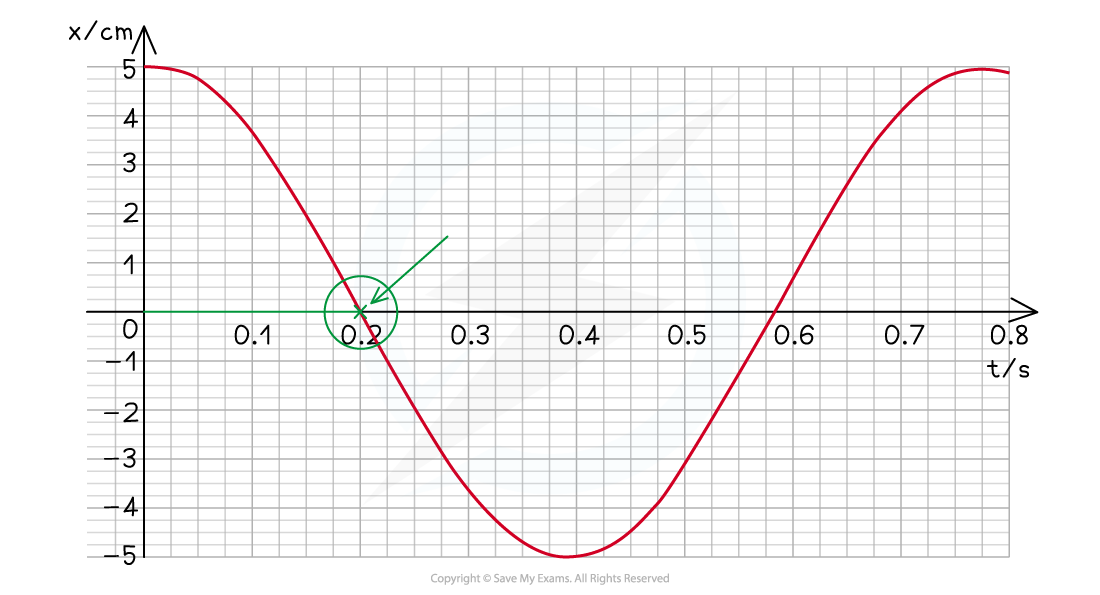
From the graph this is equal to 0.2 s
Examiner Tips and Tricks
These graphs might not look identical to what is in your textbook, depending on where the object starts oscillating from at t = 0 (on either side of the equilibrium, or at the equilibrium). However, if there is no damping, they will all always be a general sine or cosine curves.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?