Damping & Plastic Deformation (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: YPH11
Damping & Plastic Deformation
Damping an oscillator affects its amplitude of oscillation:
When damping is increased the amplitude decreased
damping and amplitude are inversely proportional to each other
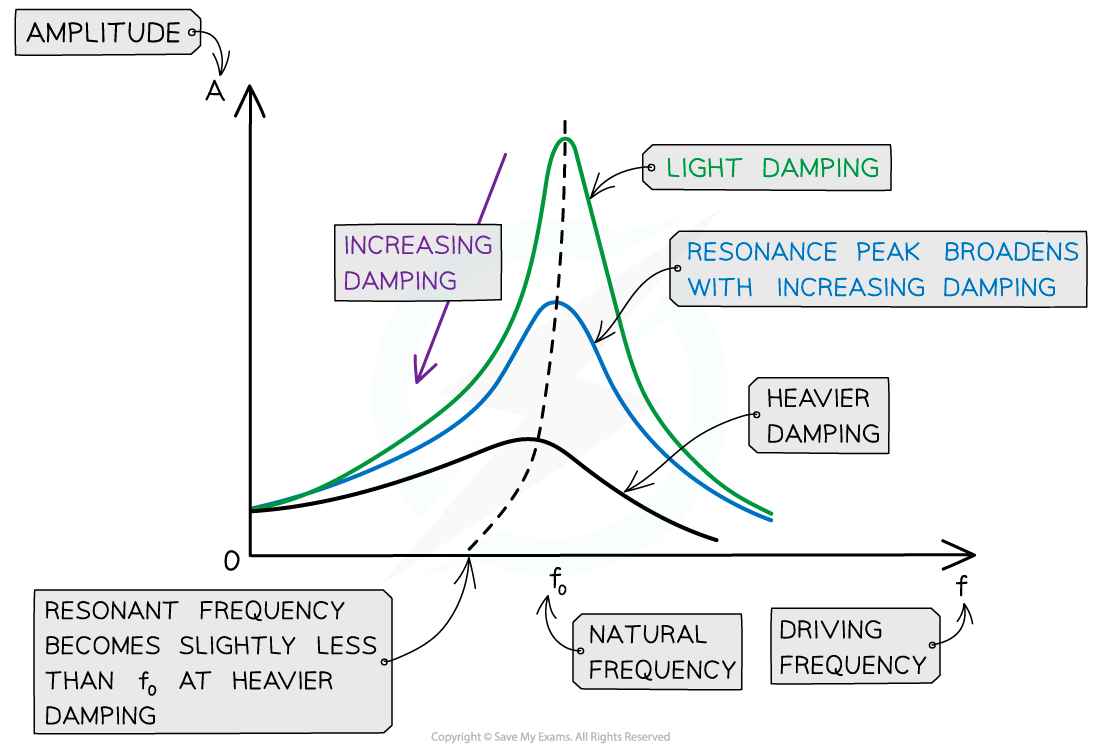
As damping is increased, resonance peak lowers, the curve broadens and moves slightly to the left
A Ductile material can be stretched for a long time before it snaps
We can say it undergoes a large amount of plastic deformation before it is permanently deformed

Examples of ductile materials include:
Most metals (particularly copper, gold and silver)
Non-metals are generally not ductile
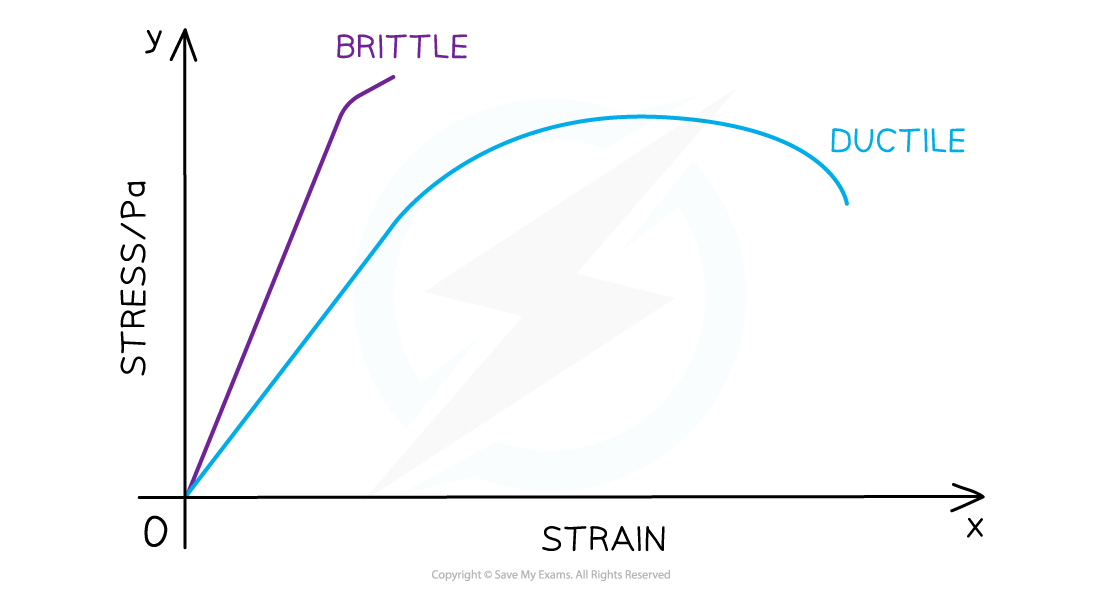
Brittle and ductile materials on a stress-strain graph. These are the same on a force-extension graph too
The amplitude of oscillations can be reduced due to the plastic deformation of a ductile material
This happens because energy from the oscillations is used to deform the material
The kinetic energy of the oscillator is reduced and transferred into the deformation of the material
A climbing rope is different from a rescue rope or a bungee cord:
A climbing rope is designed to extend when loaded suddenly
The rope stretches to reduce the amplitude of the oscillation when a climber falls onto it
It provides critical damping by immediately stopping the climber from bouncing

A climber uses a dynamic rope that stretches when she falls onto it. This reduces the amplitude of her oscillation and the force she experiences reducing injury.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?