Atomic Mass Unit (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Atomic Mass Unit
The unified atomic mass unit (u or sometimes a.m.u) is roughly equal to the mass of one proton or neutron:
1 u = 1.66 × 10−27 kg
This value is provided on the exam data sheet
The a.m.u is commonly used in nuclear physics to express the mass of subatomic particles. It is defined as
The mass of exactly one-twelfth of an atom of carbon-12
Therefore, one atom of carbon-12 has a mass of exactly 12 u
Since mass and energy are interchangeable, the a.m.u can also be expressed in MeV
1 u is equivalent to 931.5 MeV
Table of common particles with mass in a.m.u
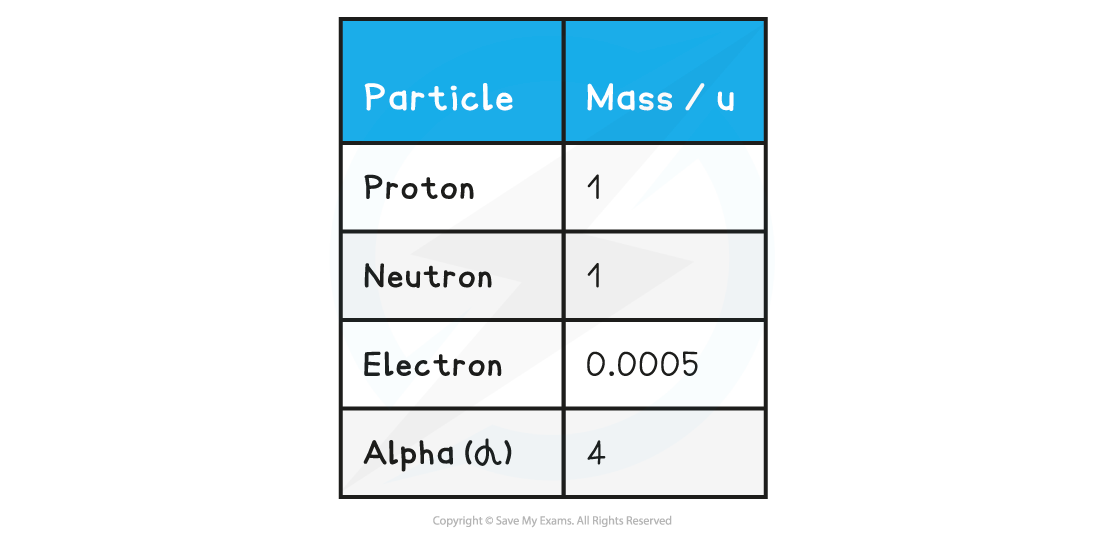
The mass of an atom in a.m.u is roughly equal to the sum of its protons and neutrons (nucleon number)
For example, the mass of Uranium-235 is roughly equal to 235u
However, note that the actual mass is slightly lower than the expected mass, due to mass-energy equivalence
a.m.u might be quoted in kg or MeV since mass and energy are equivalent via
MeV is a unit of energy whilst kg is a unit of mass
Worked Example
Estimate the mass of the nucleus of the element copernicium-285 in kg. Give your answer to 2 decimal places.
Answer:


You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
