Orbital Motion (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: YPH11
Orbital Motion
Newton's Law of Gravitation & Orbits
Since most planets and satellites have a near circular orbit, the gravitational force FG between the sun or another planet provides the centripetal force needed to stay in an orbit
This centripetal force is perpendicular to the velocity of the planet
Consider a satellite with mass m orbiting Earth with mass M at a distance r from the centre travelling with linear speed v
Equating the gravitational force from Newton's Law of Gravitation to the centripetal force for a planet or satellite in orbit gives:
FG = Fcentripetal
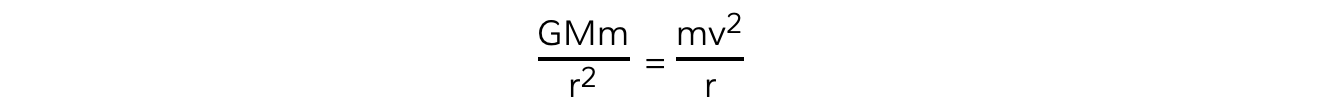
The mass of the satellite m will cancel out on both sides to give:
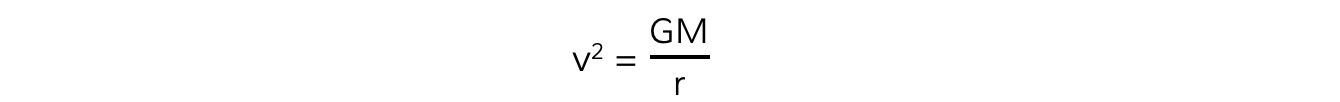
Where:
v = linear speed of the mass in orbit (m s–1)
G = Newton's Gravitational Constant (N m2 kg–2)
M = mass of the object being orbited (kg)
r = orbital radius (m)
This means that all satellites, whatever their mass, will travel at the same speed v in a particular orbital radius r
Newton's Laws of Motion & Orbits
Newton's first law of motion states that a body remain at rest or at constant velocity unless a resultant force acts on it
Bodies in orbit do have a resultant force acting on them
This is the gravitational force due to the mass M being orbited
This force is a centripetal force because it acts towards the centre of M, perpendicular to the velocity of the planet or satellite
Therefore, since the direction of a planet or satellite orbiting in circular motion is constantly changing, it must be accelerating
This is called centripetal acceleration
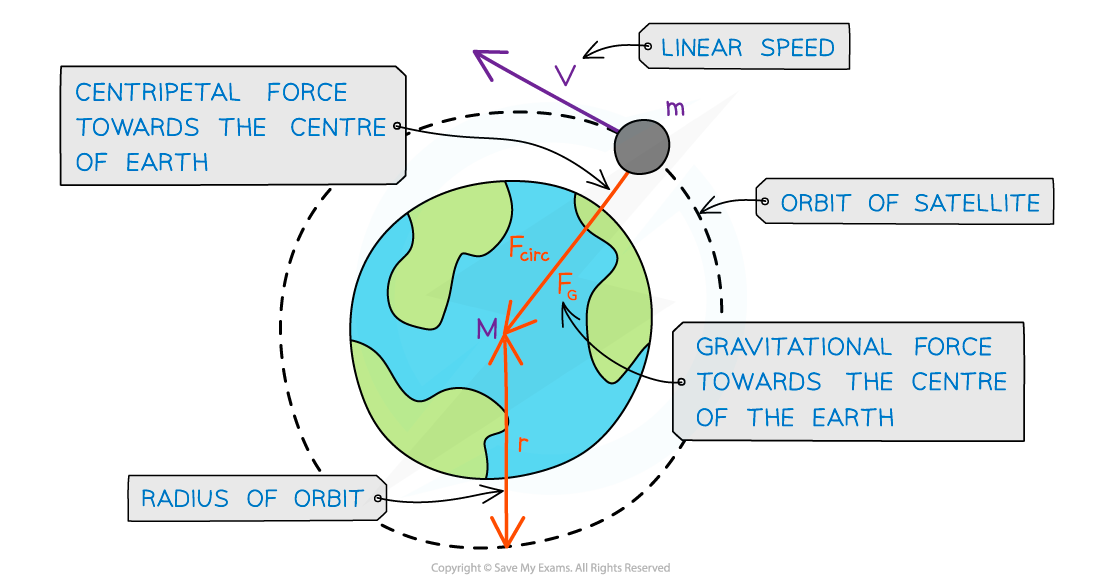
A satellite in orbit around the Earth travels in circular motion
Time Period & Orbital Radius Relation
A planet or a satellite orbits in circular motion
Therefore, its orbital time period T is the time taken to travel the circumference of the orbit 2πr
This means the linear speed, or orbital speed v is:
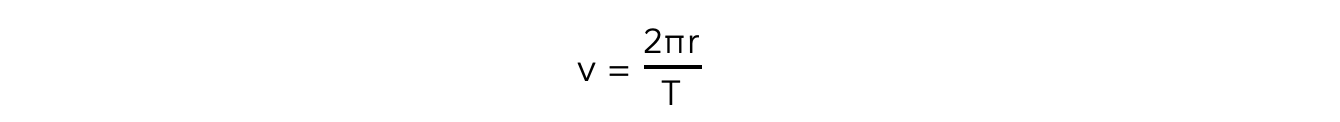
This is a result of the well-known equation speed = distance / time
Equating the two equations for orbital speed gives:
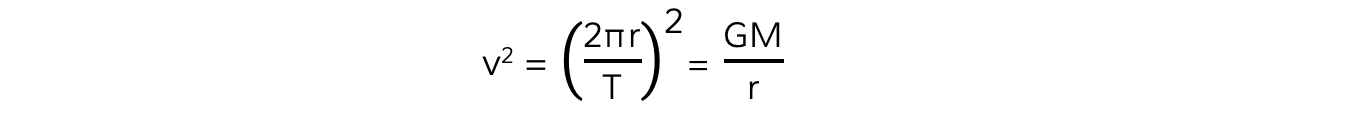
Squaring out the brackets and rearranging for T2 gives the equation relating the time period T and orbital radius r:
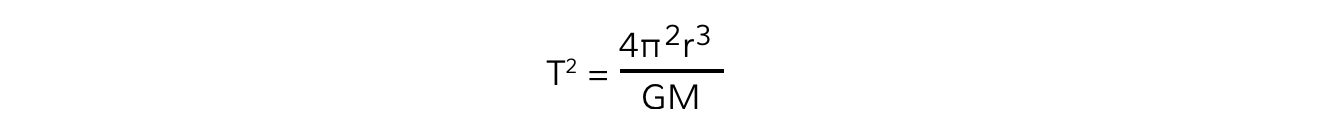
Where:
T = time period of the orbit (s)
r = orbital radius (m)
G = Newton's Gravitational Constant (N m2 kg–2)
M = mass of the object being orbited (kg)
The equation shows the relationship between the orbital period and the orbital radius for any planet or satellite in orbit
It is summarised mathematically as:
Worked Example
A binary star system constant of two stars orbiting about a fixed point B.The star of mass M1 has a circular orbit of radius R1 and mass M2 has a radius of R2. Both have linear speed v and an angular speed ⍵ about B.
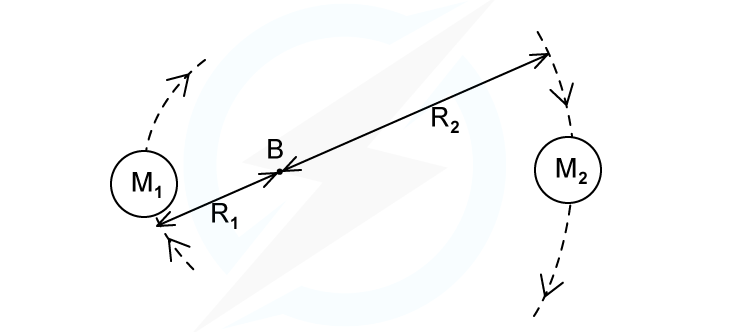
State the following formula, in terms of G, M2, R1 and R2
(i) The angular speed ⍵ of M1
(ii) The time period T for each star in terms of angular speed ⍵
Answer:
Part (i)
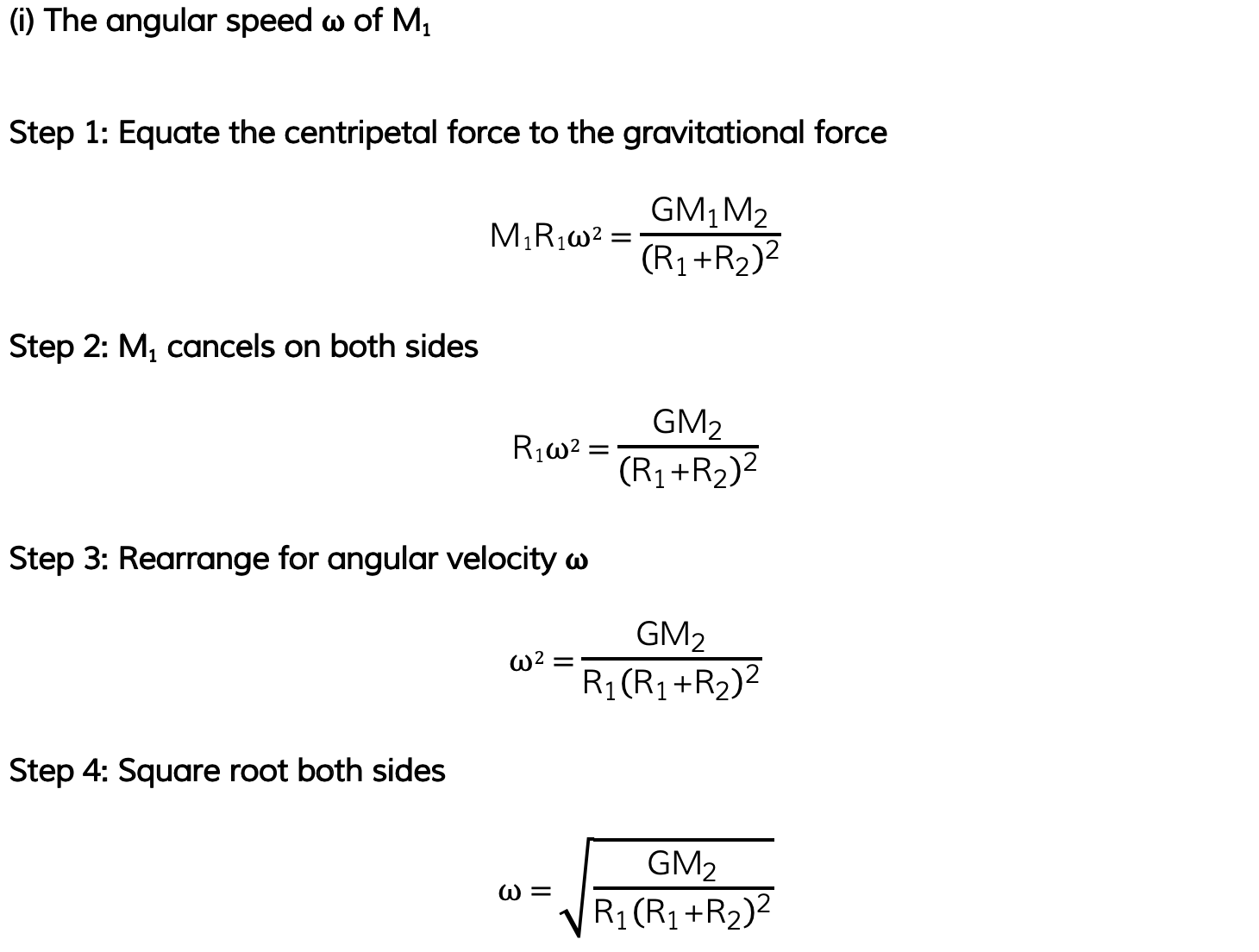
Part (ii)
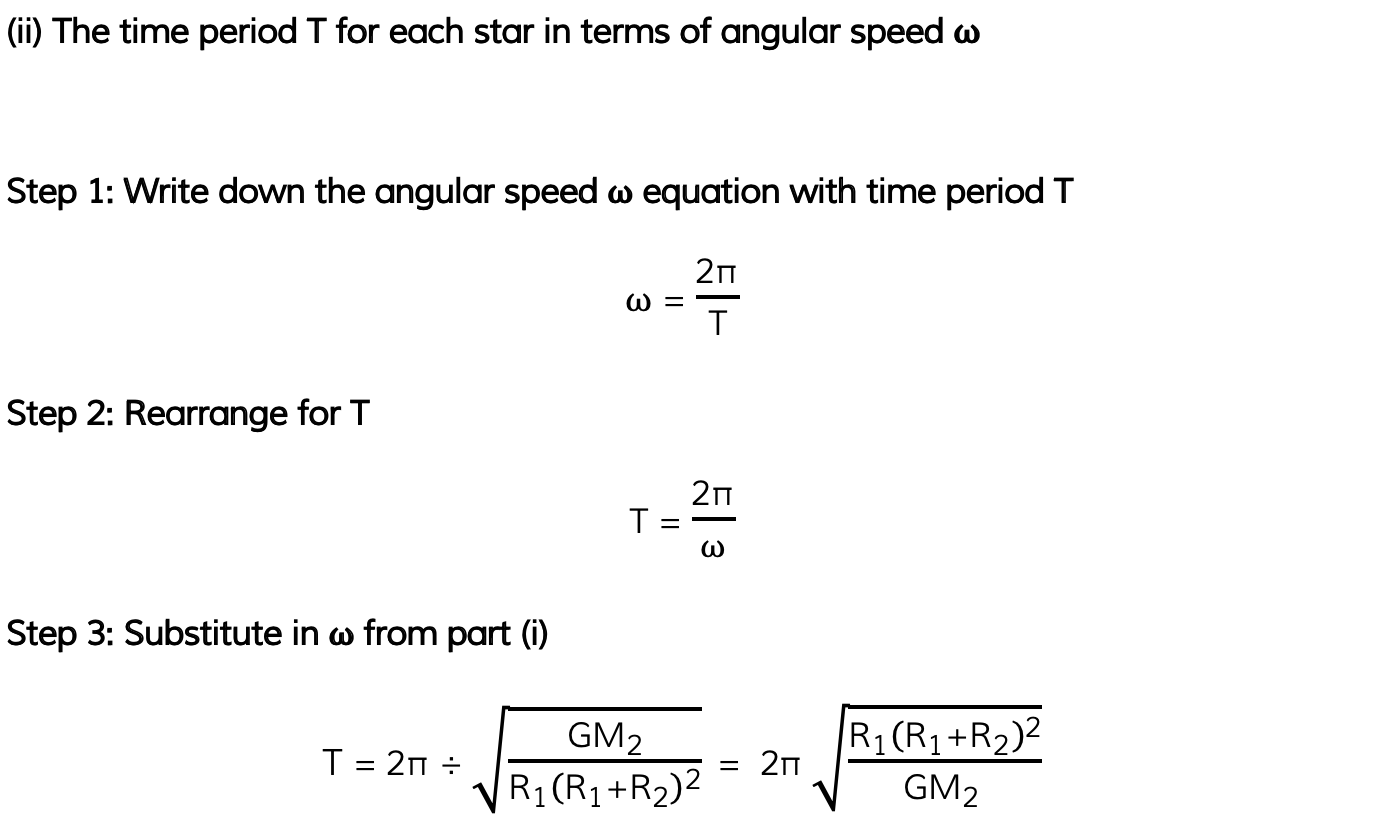
Examiner Tips and Tricks
This worked example helps you practise two crucial techniques that are often examined:
The centripetal force is expressed as
or equivalently as
. In our case the angular speed is given in the question, so it is best to use the latter expression
when equating the centripetal force to the gravitational force.
The gravitational force is given as
but note that the distance r in this question is given as a sum, R1 + R2. You should remember that r is defined as the distance between the centre of masses of M and m, therefore, r = R1 + R2 and so r2 = (R1 + R2)2.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?