Antimatter (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Properties of Antimatter
The universe is made up of matter particles (protons, neutrons, electrons etc.)
All matter particles have antimatter counterparts
Antimatter particles are identical to their matter counterpart but with the opposite charge
This means if a particle is positive, its antimatter particle is negative and vice versa
Common matter-antimatter pairs are shown in the diagram below:
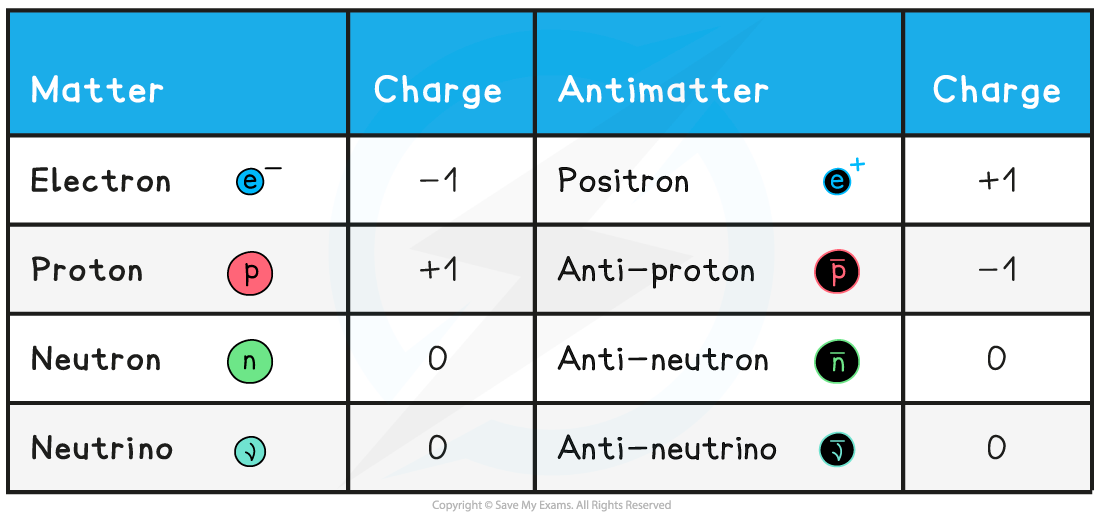
This table summarises the electric charge for typical particle-antiparticle pairs
Apart from electrons, the corresponding antiparticle pair has the same name with the prefix ‘anti-’ and a line above the corresponding matter particle symbol
A neutral particle, such as a neutron or neutrino or photon, is its own antiparticle
Mass of Matter & Antimatter
Although antimatter particles have the opposite charges to their matter counterparts, they still have identical mass and rest mass-energy
The rest mass-energy of a particle is the energy equivalent to the mass of the particle at rest
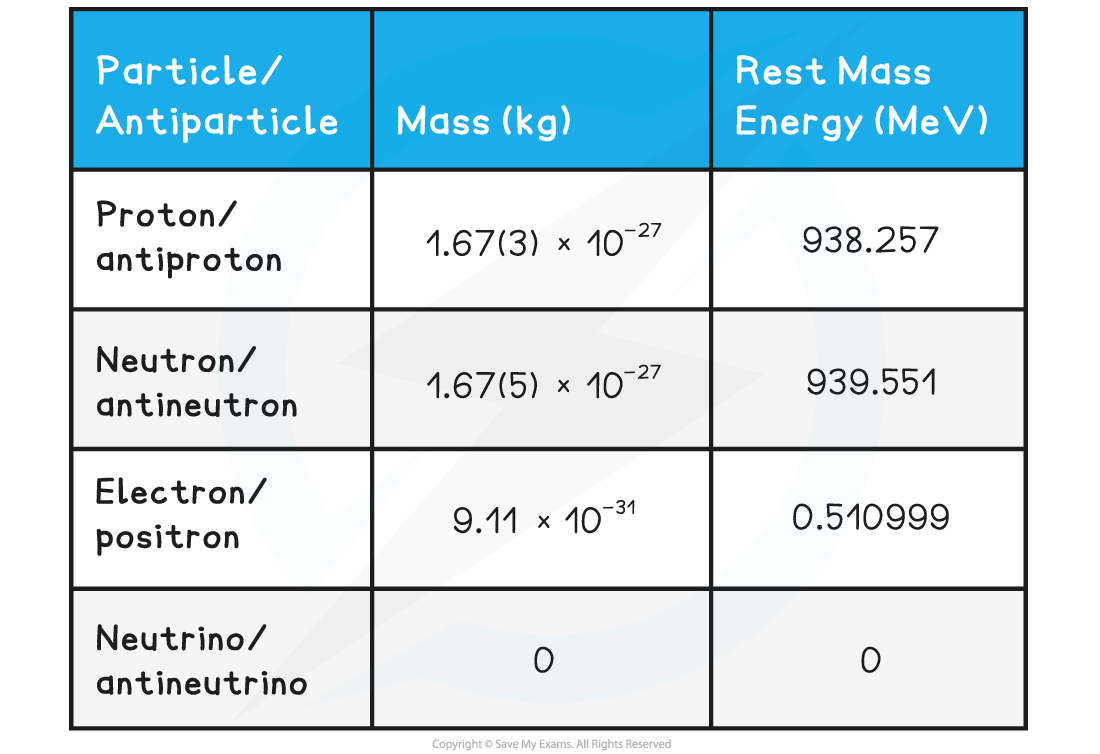
This table summarises typical particle-antiparticle pair masses and rest mass energies
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Though you will not need to memorise individual masses or rest-mass energies, you are expected to remember the mass of a particle-antiparticle pair is identical but they have the opposite electric charge.

You've read 1 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?


