Elastic & Inelastic Collisions (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Elastic & Inelastic Collisions
In both collisions and explosions, momentum is always conserved
However, kinetic energy might not always be
A collision (or explosion) is either:
Elastic – if the kinetic energy is conserved
Inelastic – if the kinetic energy is not conserved
Collisions happen when objects strike against each other
Elastic collisions are commonly those where objects colliding do not stick together; instead, they strike each other then move away in opposite directions
Inelastic collisions are commonly those where objects collide and stick together after the collision
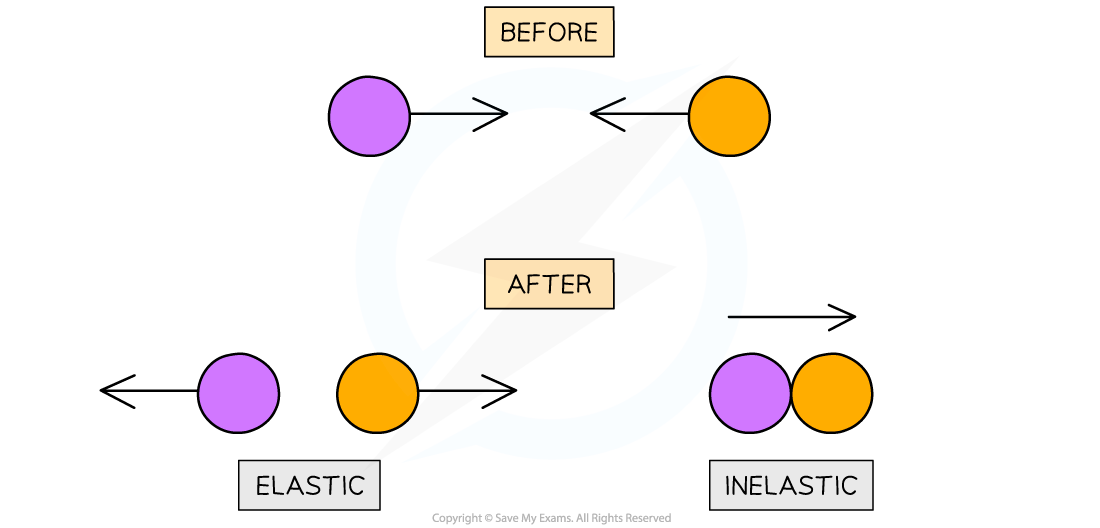
Elastic collisions are those following which objects move away in opposite directions. Inelastic collisions are where two objects stick together
An explosion is commonly to do with recoil
For example, a gun recoiling after shooting a bullet or an unstable nucleus emitting an alpha particle and a daughter nucleus
To find out whether a collision is elastic or inelastic, compare the kinetic energy before and after the collision
The equation for kinetic energy is:
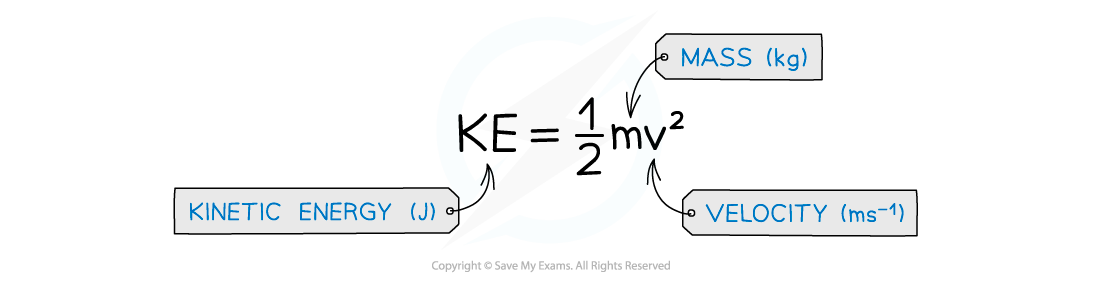
Worked Example
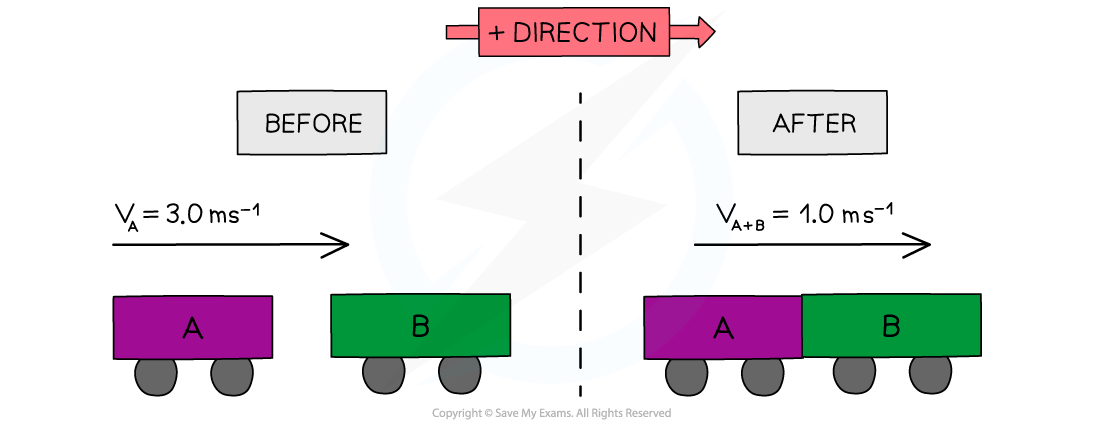
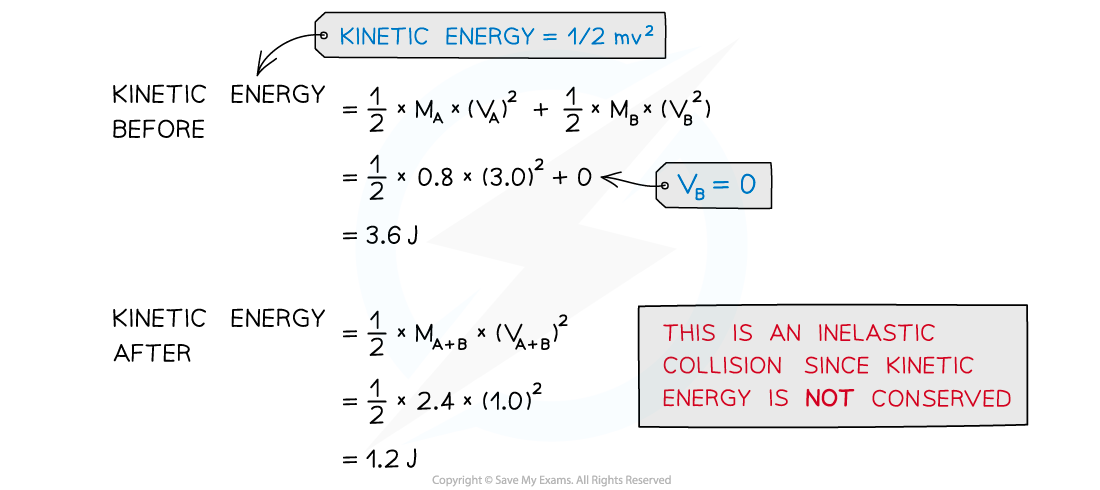
Trolley A of mass 0.80 kg collides head-on with stationary trolley B at speed 3.0 m s–1. Trolley B has twice the mass of trolley A.
The trolleys stick together and travel at a velocity of 1.0 m s–1. Determine whether this is an elastic or inelastic collision.
Answer:
Worked Example
Discuss whether a head-on collision between two cars is likely to be an elastic or inelastic collision.
Answer:
Step 1: Define an elastic and inelastic collision
An elastic collision is one in which kinetic energy is conserved
An inelastic collision is one in which kinetic energy is not conserved, but is transferred to other forms, e.g. heat and sound
Step 2: Describe the effects of head-on car collisions
When cars collide, a large amount of kinetic energy is transferred due to work by internal forces
This is mainly due to crumpling where the collision of the car causes plastic defamation of the car's bodywork
Other energy transfers will include kinetic energy into heat and sound
Step 3: Link the effects to energy transfers
Since the cars are brought to rest by the collision, the total KE before the collision does not equal the total KE after
Therefore, the collision is inelastic
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If an object is stationary or at rest, its velocity equals 0, therefore, the momentum and kinetic energy are also equal to 0.
When a collision occurs in which two objects stick together, treat the final object as a single object with a mass equal to the sum of the two individual objects.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
