Electric Field & Potential (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Electric Field & Potential
A positive test charge has electric potential energy due to its position in an electric field
The amount of electric potential energy depends on:
The magnitude of charge
The value of the electric potential in the field

Work is done on a positive test charge Q to move it from the negatively charged plate A to the positively charged plate B. This means its electric potential energy increases
Electric potential is defined as the amount of work done per unit of charge at that point
A stronger electric field means the electric potential changes more rapidly with distance as the test charge moves through it
Hence, the relationship between the electric field strength and the electric potential is summarised as:
The electric field strength is proportional to the gradient of the electric potential
This means:
If the electric potential changes very rapidly with distance, the electric field strength is large
If the electric potential changes very gradually with distance, the electric field strength is small
An electric field can be defined in terms of the variation of electric potential at different points in the field:
The electric field at a particular point is equal to the gradient of a potential-distance graph at that point
The potential gradient in an electric field is defined as:
The rate of change of electric potential with respect to displacement in the direction of the field
The graph of potential V against distance r for a negative or positive charge is:
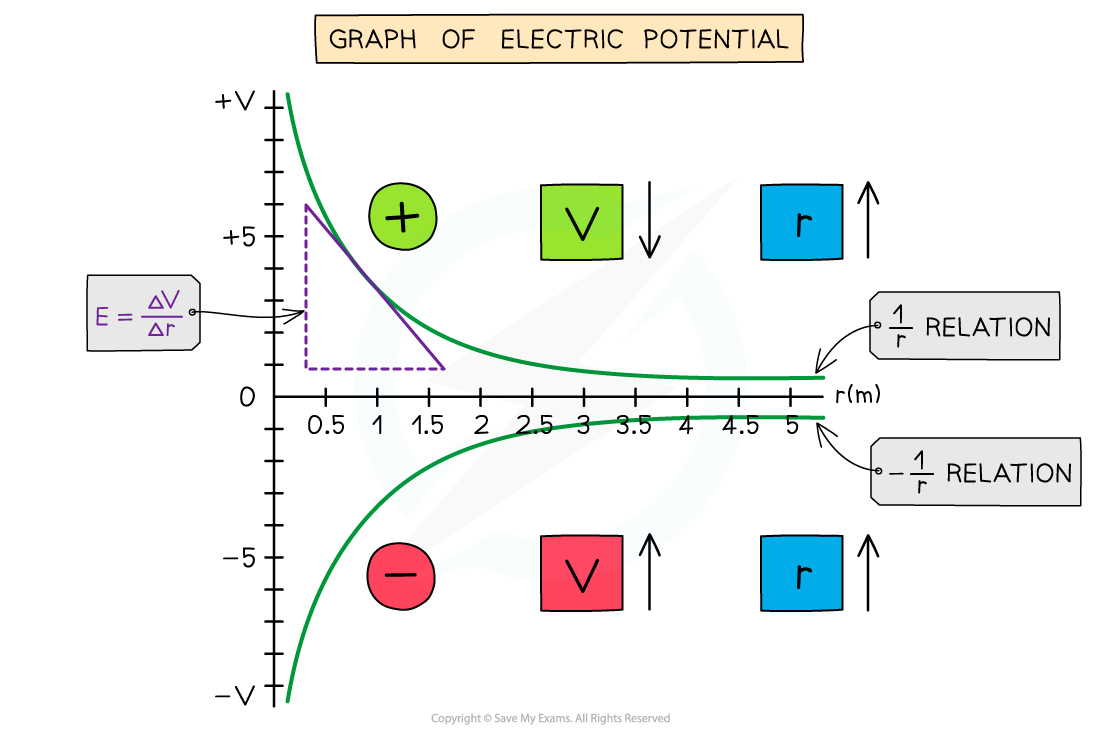
The electric potential around a positive charge decreases with distance and increases with distance around a negative charge
The key features of this graph are:
The values for V are all negative for a negative charge
The values for V are all positive for a positive charge
As r increases, V against r follows a 1/r relation for a positive charge and -1/r relation for a negative charge
The gradient of the graph at any particular point is the value of E at that point
The graph has a shallow increase (or decrease) as r increases
The electric potential changes according to the charge creating the potential as the distance r increases from the centre:
If the charge is positive, the potential decreases with distance
If the charge is negative, the potential increases with distance
Worked Example
An electric field is set up between two pairs of oppositely charged plates, set X and set Y.
A graph showing how the electric potential V varies with distance d is shown for both set X and set Y.

State and explain which set creates the largest electric field strength.
Answer:
Step 1: Recall the relationship between electric field strength and electric potential
The electric field strength is proportional to the gradient of the electric potential
Step 2: Interpret the gradient of the potential-distance graph
Set X has a larger gradient than set Y

Step 3: State and explain the conclusion
Set X creates a larger electric field strength
This is because the gradient of the potential between the plates is larger than it is for set Y
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Remember that whether the electric potential increases or decreases depends on the charge that is producing the potential!

You've read 1 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?


