Capacitance (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Capacitance
Capacitors are electrical devices used to store energy in electronic circuits, commonly for a backup release of energy if the power fails
Capacitors do this by storing electric charge, which creates a build up of electric potential energy
They are made in the form of two conductive metal plates connected to a voltage supply (parallel plate capacitor)
There is commonly a dielectric in between the plates, to ensure charge does not flow across them
The capacitor circuit symbol is:

The capacitor circuit symbol is two parallel lines
Capacitors are marked with a value of their capacitance
Capacitance is defined as:
The charge stored per unit potential difference (between the plates)
The greater the capacitance, the greater the charge stored in the capacitor
The capacitance of a capacitor is defined by the equation:

Where:
C = capacitance (F)
Q = charge stored (C)
V = potential difference across the capacitor plates (V)
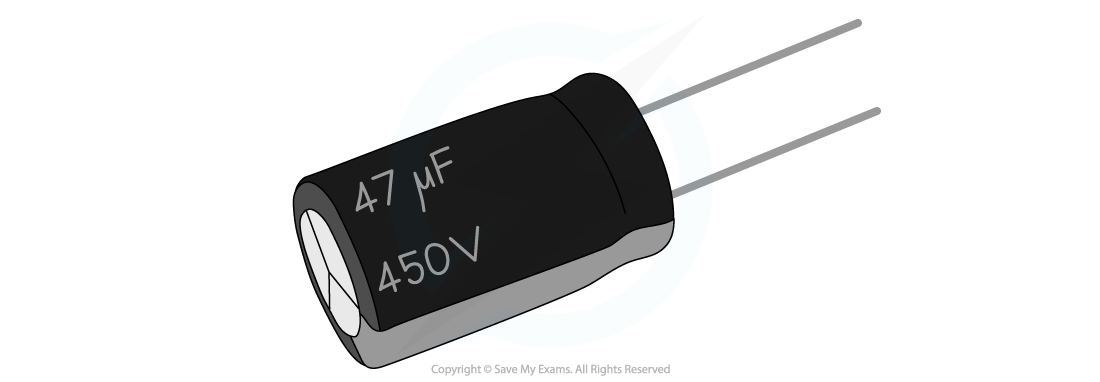
A capacitor used in small circuits
Capacitance is measured in the unit Farad (F)
In practice, 1 F is a very large unit
Often it will be quoted in the order of micro Farads (μF), nanofarads (nF) or picofarads (pF)
If the capacitor is made of parallel plates, Q is the charge on the plates and V is the potential difference across the capacitor
The charge Q is not the charge of the capacitor itself, it is the charge stored on the plates
This capacitance equation shows that an object’s capacitance is the ratio of the charge stored by the capacitor to the potential difference between the plates
Worked Example
A parallel plate capacitor has a capacitance of 1 nF and is connected to a voltage supply of 0.3 kV.
Calculate the charge on the plates.
Answer:
Step 1: Write down the known quantities
Capacitance, C = 1 nF = 1 × 10-9 F
Potential difference, V = 0.3 kV = 0.3 × 103 V
Step 2: Write out the equation for capacitance

Step 3: Rearrange for charge Q
Q = CV
Step 4: Substitute in values
Q = (1 × 10-9) × (0.3 × 103) = 3 × 10-7 C = 300 nC
Examiner Tips and Tricks
The ‘charge stored’ by a capacitor refers to the magnitude of the charge stored on each plate in a parallel plate capacitor or on the surface of a spherical conductor. The letter ‘C’ is used both as the symbol for capacitance as well as the unit of charge (coulombs). Take care not to confuse the two!

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
