Diffraction (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: YPH11
Diffraction
Diffraction is the spreading out of waves when they pass an obstruction
Diffraction through a gap
This obstruction is typically a narrow gap (a slit, or aperture)
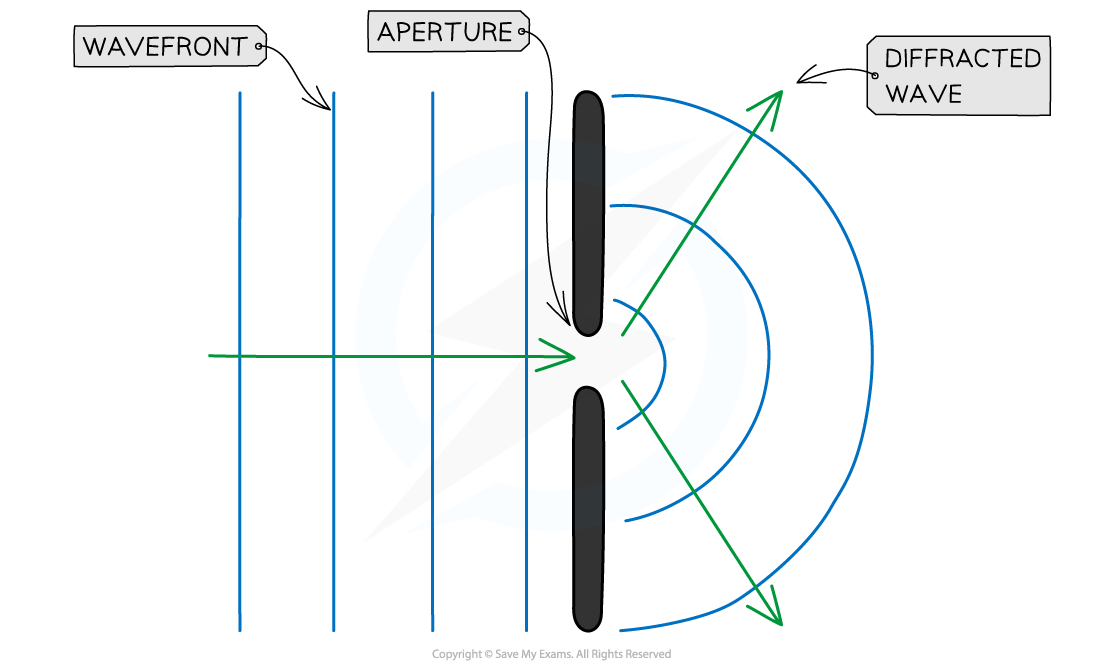
Diffraction is usually represented by a wavefront as shown by the vertical lines in the diagrams above
The only property of a wave that changes when its diffracted is its amplitude
This is because some energy is dissipated when a wave is diffracted through a gap
Diffraction around an obstacle
The diffraction pattern for a large slit can be thought of as a wave passing two completely separate obstacles
This shows that when a wave meets an obstacle a diffraction pattern forms around the edges.
Behind the obstacle a ‘shadow’ forms where no part of the wave reaches
Factors that affect diffraction
The effects of diffraction are most prominent when the gap size or obstacle is approximately the same or smaller than the wavelength of the wave
As the size of the gap or obstacle increases, the effect gradually gets less pronounced
When the gap is much larger than the wavelength, the waves are no longer spread out
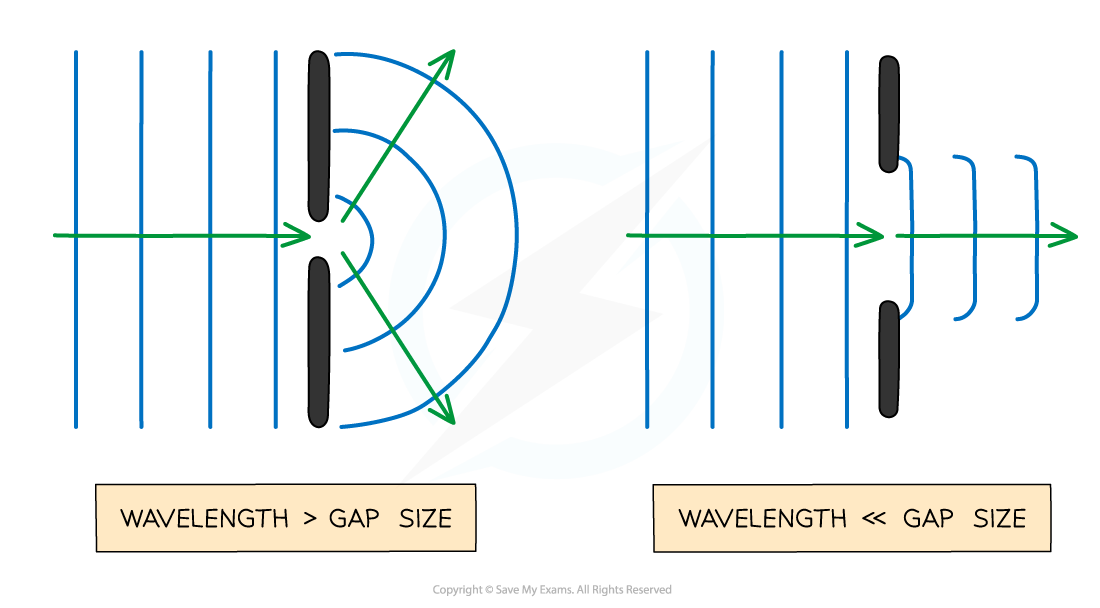
The size of the gap (compared to the wavelength) affects how much the waves spread out
Explaining diffraction
Huygens developed a model for wave propagation which suggested that every point on a wavefront can be considered to be a point source of secondary waves (which he called wavelets)
This leads to a diagram, called Huygens’ construction, which shows that new wavefronts are tangential to the secondary wavelets
The tangents create the curve of the new wavefront emerging either through the gap or around the obstacle

When a wave meets an obstacle a diffraction pattern forms around the edges, with a ‘shadow’ created behind the obstacle where no part of the wave reaches
Huygens' Construction for Diffraction Through a Gap

Those point sources which pass through the gap create new wavelets on the other side, leading to the characteristic curved shape of the diffracted wave
Huygens' Construction for Diffraction Around an Obstacle

Those point sources which pass around the obstacle create new wavelets on the other side, leaving empty space where the 'shadow' is seen
Worked Example
When a wave is travelling through air, which scenario best demonstrates diffraction?
A. UV radiation through a gate post
B. Sound waves passing a steel rod
C. Radio waves passing between human hair
D. X-rays passing through atoms in a crystalline solid
Answer: D
Diffraction is most prominent when the wavelength is close to the aperture size
UV waves have a wavelength between 4 × 10-7 – 1 × 10-8 m so won’t be diffracted by a gate post
Sound waves have a wavelength of 1.72 × 10-2 – 17 m so would not be diffracted by the diffraction grating
Radio waves have a wavelength of 0.1 – 106 m so would not be diffracted by human hair
X-rays have a wavelength of 1 × 10-8 – 4 × 10-13 m which is roughly the gap between atoms in a crystalline solid
Therefore, the correct answer is D
Examiner Tips and Tricks
When drawing diffracted waves, take care to keep the wavelength constant. It is only the amplitude of the wave that changes when diffracted.
Huygen's diagrams can be tricky to draw, so are definitely worth practicing.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?