Representing Waves on Graphs (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Graphs of Transverse & Longitudinal Waves
Graphs of Transverse Waves
There are two common graphs transverse waves;
Displacement against distance
Displacement against time
These are:
Similar because they produce a sinusoidal shaped curve
Different because displacement against distance is showing displacement of a point on the wave, but displacement against time is showing the wave itself moving along a line
On the displacement-distance graph:
Movement upwards from the centre line is given a positive sign and movement downwards a negative
The amplitude and wavelength can be found as shown below

On the displacement-time graph:
The time period can be taken directly as shown
This means that frequency can be found indirectly as f = 1/T
To determine the next position of a point on the wave
Sketch the full wave after time has passed by looking at the direction of travel
Each point oscillates perpendicular to the wave, so remains on the normal line wherever the wave intersects, this is shown in red below

Graphs of Longitudinal Waves
Plotting displacement against distance also produces a sinusoidal shaped graph
This can be used to show where the compressions and rarefactions will be found

Worked Example
The graph shows how the displacement of a particle in a wave varies with time.

Which statement is correct?
A. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and could be either transverse or longitudinal.
B. The wave has an amplitude of 2 cm and has a time period of 6 s.
C. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and has a time period of 4 s.
D. The wave has an amplitude of 4 cm and must be transverse.
Answer: A

Graphs of Stationary Waves
Stationary waves occur when a wave is reflected with a 180o phase difference, creating a wave with a series of nodes and antinodes
Stationary waves can be transverse or longitudinal
They are represented graphically in the same way as progressive (travelling) waves
Graphs of standing waves can also be used to determine the position of nodes and antinodes
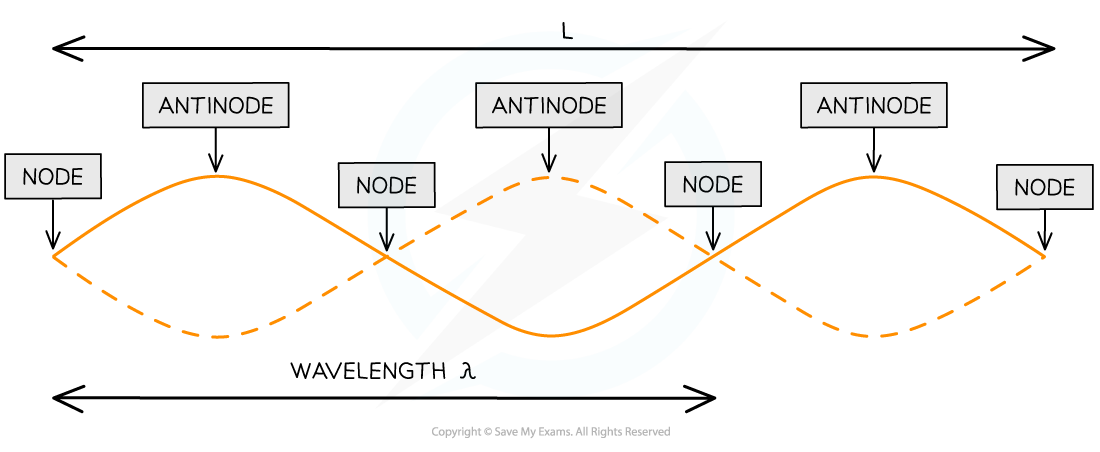
L is the length of the string
1 wavelength λ is only a portion of the length of the string
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Both transverse and longitudinal waves can look like transverse waves when plotted on a graph - make sure you read the question and look for whether the wave travels parallel (longitudinal) or perpendicular (transverse) to the direction of travel to confirm which type of wave it is.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
