Resistance & Temperature (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics) : Revision Note
Modelling the Variation of Resistance with Temperature
All materials have some resistance to the flow of charge
As free electrons move through a metal wire, they collide with ions which get in their way
As a result, they transfer some, or all, of their kinetic energy on collision, which causes electrical heating

Free electrons collide with ions which resist their flow
As temperature increases, the vibrations of the ions in the lattice also increase
This increases the chance of collisions between the conduction electrons and the ions
Since current is the flow of charge, the ions resisting the flow of electrons cause resistance
Therefore as temperature increases so does resistance
At small increases of temperature this increase is linear
A higher current will cause temperature to rise
This is due to more collisions between free electrons and ions
The collisions cause the ions to vibrate more
Resistance & Temperature for Metallic Conductors
All solids are made up of vibrating atoms
This includes metal solids
As the temperature in a metal rises, the ions vibrate with a greater frequency and amplitude
The electrons collide with the vibrating atoms which impede their flow, hence the current decreases
electric current is the flow of free electrons in a material

Metal atoms and free electrons at low and high temperatures
Current decreases because the resistance has increased (from V = IR)
This is because resistivity has increased
This is from ρ ∝ R (if the area A and length L is constant)
For a metallic conductor which obeys Ohm's law:
An increase in temperature causes an increase in resistance and resistivity
A decrease in temperature causes a decrease in resistance and resistivity
The I-V graph for a filament lamp shows this effect
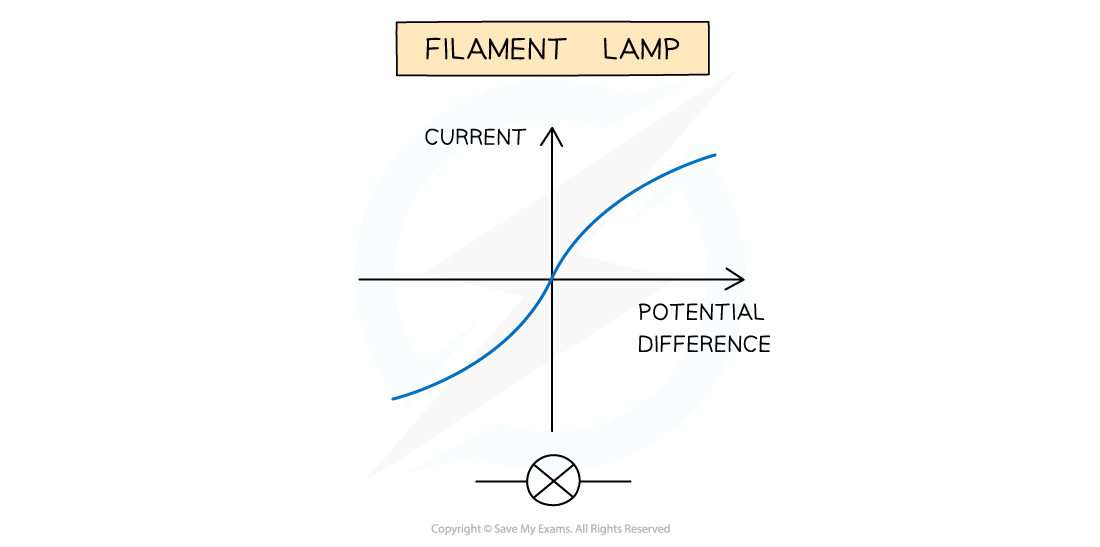
I-V characteristics for a filament lamp
As the current increases, the number of collisions between free electrons and the lattice of ions increases
This increases the temperature of the filament in the lamp
An increase in temperature:
Causes greater vibrations in the lattice of ions
Therefore increased collisions between free electrons and the ions
And so an increased resistance
Resistance opposes the current, causing the current to increase at a slower rate
This is seen as a curve in the graph
Worked Example
The temperature of a non-ohmic resistor increases as the current through it increases.
Explain this is terms of the structure of a metal.
Answer:
Step 1: Consider the effect on rate of electron flow:
Rate of flow of electrons increases
Step 2: Consider the effect on number of collisions of conduction electrons with the lattice
This increases the number of collisions of conduction electrons with the ions in the lattice
Step 3: Describe what happens to the vibrations of the lattice
Therefore vibrations of the lattice ions increase
Resistance & Temperature for Thermistors
The resistivity of a thermistor behaves in the opposite way to metals
This is because it is a type of semiconductor
Semiconductors behave in a different way to metals
The number density of charge carriers (such as electrons) increases with increasing temperature
Therefore, for a thermistor:
An increase in temperature causes a decrease in resistance and resistivity
A decrease in temperature causes an increase in resistance and resistivity
Thermistors are often used in temperature sensing circuits such as thermometers and thermostats
A thermistor is a non-ohmic conductor and sensory resistor whose resistance varies with temperature
Most thermistors are negative temperature coefficient ntc) components.
This means that if the temperature increases, the resistance of the thermistor decreases (and vice versa)
The temperature-resistance graph for a thermistor is shown below

Thermistors are temperature sensors and are used in circuits in ovens, fire alarms and digital thermometers
As the thermistor gets hotter, its resistance decreases
As the thermistor gets cooler, its resistance increases

The resistance through a thermistor is dependent on the temperature of it
Worked Example
A thermistor is connected in series with a resistor R and a battery.

The resistance of the thermistor is equal to the resistance of R at room temperature.
Which statement describes the effect when the temperature of the thermistor decreases?
A. The p.d across the thermistor increases
B. The current in R increases
C. The current through the thermistor decreases
D. The p.d across R increases
Answer: A
Step 1: Outline the nature of a thermistor
The resistance of the thermistor increases as the temperature decreases
Step 2: Consider the properties of current in a series circuit
Since the thermistor and resistor R are connected in series, the current I in both of them is the same
Step 3: Consider a relevant equation
Ohm’s law states that V = IR
Since the resistance of the thermistor increases, and I is the same, the potential difference V across it increases
Step 4: State the conclusion
Therefore, statement A is correct

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
