Current-Potential Difference Graphs (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Physics): Revision Note
Exam code: YPH11
Current-Potential Difference Graphs
As the potential difference (voltage) across a component is increased, the current also increases (by Ohm’s law)
The precise relationship between voltage and current is different for different components and can be shown on a current-potential difference or I-V graph
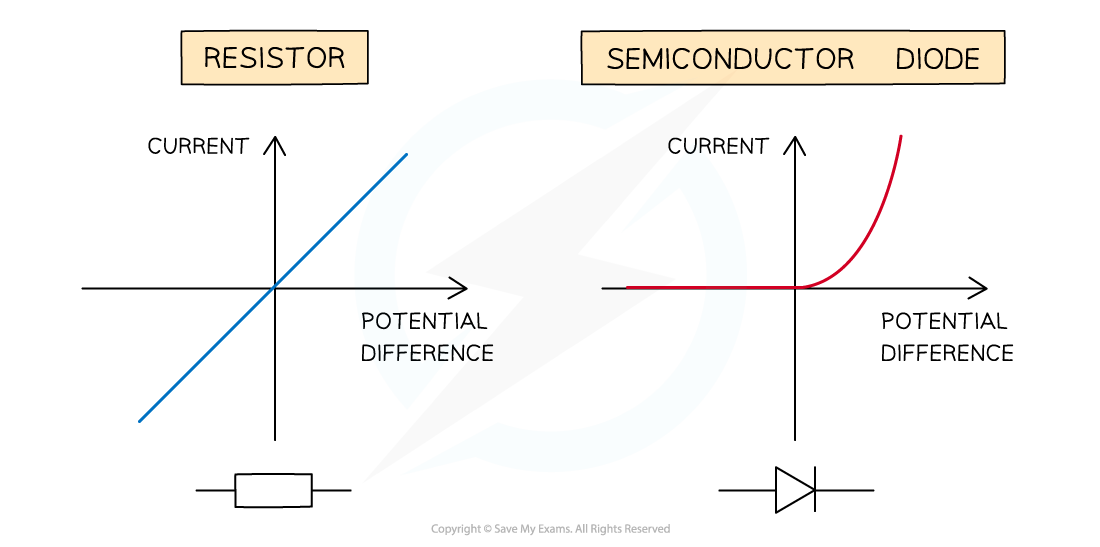
For an ohmic conductor, the I–V graph is a straight line through the origin
For a semiconductor diode, the I–V graph is a horizontal line that goes sharply upwards
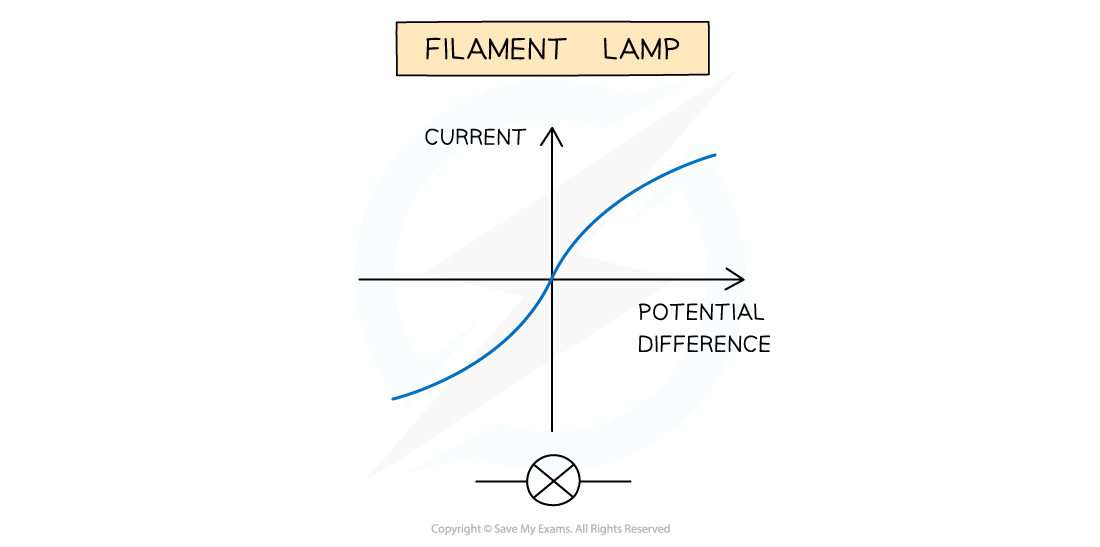
For a filament lamp, the I–V graph has an 'S' shaped curve
I–V characteristics for an ohmic conductor (e.g. resistor), semiconductor diode and filament lamp
Ohmic Conductor
The I–V graph for an ohmic conductor at constant temperature e.g. a resistor is very simple:
The current is directly proportional to the potential difference
This is demonstrated by the straight-line graph through the origin
Diode
The I–V graph for a diode is slightly different.
A diode is used in a circuit to allow current to flow only in a specific direction:
When the current is in the direction of the arrowhead symbol, this is forward bias. This is shown by the sharp increase in potential difference and current on the right side of the graph
When the diode is switched around, it does not conduct and is called reverse bias. This is shown by a zero reading of current or potential difference on the left side of the graph
The threshold voltage at which a diode starts to conduct is typically around 0.6V
Filament Lamp
The I–V graph for a filament lamp shows the current increasing at a proportionally slower rate than the potential difference
This is because:
As the current increases, the temperature of the filament in the lamp increases
Since the filament is a metal, the higher temperature causes an increase in resistance
Resistance opposes the current, causing the current to increase at a slower rate
Where the graph is a straight line, the resistance is constant
The resistance increases as the graph curves
The filament lamp obeys Ohm's Law for small voltages
Thermistor
The I–V graph for a thermistor is a shallow curve upwards

The increase in the potential difference results in an increase in current which causes the temperature of the thermistor to rise
As its temperature rises, its resistance decreases
This means even more current is able to flow through
Since the current is not directly proportional to the potential difference (the graph is still curved), the thermistor does not obey Ohm's Law
The I–V graph for a thermistor shows the current increasing at a proportionally slower rate than the potential difference
This is because:
As the current increases, the temperature of the thermistor increases
Which causes an increase in resistance
Resistance opposes the current, causing the current to increase at a slower rate
Worked Example
The I–V graph of two electrical components X and Y are shown

Which statement is correct?
A. The resistance of X increases as the current increases
B. At 2 V, the resistance of X is half the resistance of Y
C. Y is a semiconductor diode and X is a resistor
D. X is a resistor and Y is a filament lamp
Answer: C
Step 1: Consider the characteristics of graph X
The I–V graph X is linear
This means the graph has a constant gradient. I/V and the resistance is therefore also constant (since gradient = 1/R)
This is the I–V graph for a conductor at constant temperature e.g. a resistor
Step 2: Consider the characteristics of graph Y
The I–V graph Y starts with zero gradient and then the gradient increases rapidly
This means it has infinite resistance at the start which then decreases rapidly
This is characteristic of a device that only has current in one direction e.g a semiconductor diode
Step 3: Compare this information with the statements A-D
A. Resistance is constant
therefore this statement is incorrect
B. At 2V the current of X is 0.5 A and the current of Y is 0 A.
therefore this statement is incorrect
D. X is an ohmic component such as a resistor, however Y is the graph for a diode not a filament bulb.
therefore this statement is incorrect
Step 4: State the correct answer
The correct answer is C
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Make sure you're confident in drawing the I–V graphs for different components, as you may be asked to sketch these from memory in exam questions
You may get a question asking you to explain why resistance in a metal increase with temperature. This is usually two marks given for:
The vibrations of metal atoms are faster and of greater displacement from equilibrium
Therefore there are more collisions between the conduction electrons and the atoms

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?