Correlation & Regression (Edexcel International A Level Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
PMCC
What is the product moment correlation coefficient?
The product moment correlation coefficient (PMCC) is a way of giving a numerical value to linear correlation of bivariate data
The PMCC of a sample is denoted by the letter r
r can take any value such that
Can be written as
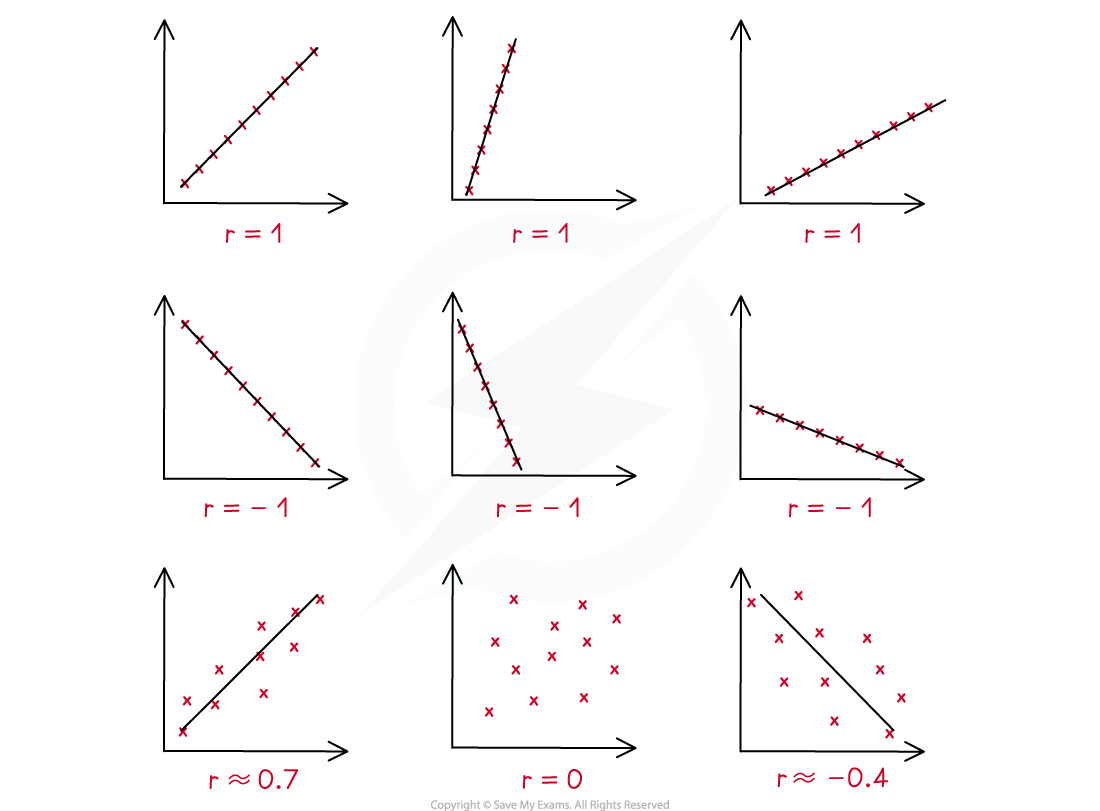
A positive value of r describes positive correlation
A negative value of r describes negative correlation
If r = 0 there is no correlation
r = 1 means perfect positive correlation and r = -1 means perfect negative correlation
The closer to 1 or -1, the stronger the correlation
The gradient of the regression line does not change the value of r
How is the product moment correlation coefficient (PMCC) calculated?
For n pairs of bivariate data (x, y) we define the following statistics
These are given in the formula booklet
These are related to variance and can be written in several different ways:
The product moment correlation coefficient (PMCC) is then calculated using the formula
This is given in the formula booklet
Did this video help you?
Calculating Regression Line
If the PMCC is close to 1 or -1 then this suggests the data follows a linear model. In this case a regression line of the form y = a + bx is appropriate.
How do I calculate the equation of the regression line of y on x?
The gradient b of the regression line is calculated using the formula
This is given in the formulae booklet
The y-intercept a of the regression line is calculated using the formula
This is given in the formulae booklet
This is found using the fact that the point
lies on the regression line
If you are asked to find the equation of the regression line of x on y
x = c + dy
These are not given in the formulae booklet
Worked Example
Ashika is a football coach to 20 children. She records how long it takes each of them to run a lap of the football pitch, seconds, and the distance that they can kick the football,
metres.
Ashika calculates the following summary statistics:
.
(a) Calculate .
(b) Calculate the product moment correlation coefficient between and
.
(c) Calculate the equation of the regression line of on
giving your answer in the form



Examiner Tips and Tricks
Questions typically use different variables instead of x and y. It might help to label the independent variable as x and the dependent variable as y, this will help you when calculating the equation of the regression line.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
