Did this video help you?
Using Calculus in 2D (Edexcel International A Level Maths: Mechanics 2): Revision Note
Using Calculus in 2D
How can I use vectors in 2D Kinematics?
- It is important you understand Calculus in 1D first
- Also recall the differences between key vector and scalar quantities
- Displacement - from starting point
- Distance – from start/origin/another particle (all could be different)
- Speed and Velocity
- acceleration and magnitude of acceleration/deceleration
- time is a scalar quantity
How do I use calculus with vectors in 2D?
- To differentiate a vector:
- Differentiate both (i and j) components of the vector
- To integrate a vector:
- Integrate both (i and j) components of the vector
- There will be a constant of integration, c, which will be a vector made up of two values (an i-component constant and a j-component constant)
- Find c by substituting in any known vectors, in the same way as you would if it were in 1D
- Find the separate components of the vector c by equating the i-components and the j-components separately
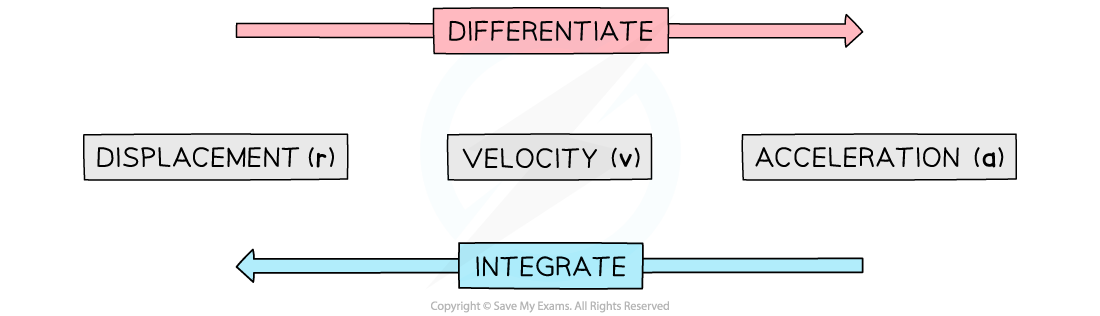
How does calculus link to kinematics?
- In 2D we normally use the vector r to represent displacement instead of s
- Just like in 1D:
- Differentiate displacement to get velocity and velocity to get acceleration
- Integrate acceleration to get velocity and velocity to get displacement
Harder problems involving vectors, calculus, position vectors and F=ma
- Harder problems could involve:
- using Newton’s Second Law (N2L) F = ma
- two vectors being equal requiring both i and j components to be equal
- exponentials, logarithms, trigonometric functions (not just polynomials)
- suvat equations (in vector form) would only be involved if acceleration is constant
- You may have to find the magnitude of the vectors
- The magnitude of the velocity is the speed
- The magnitude of the displacement is the distance from the starting point
- The position vector of a particle is r = r0 + s
- r0 is the initial position of the particle
- s is the displacement of the particle from its initial position
Worked example

(a) Find an expression for the position vector of the ship after seconds.

(b) Find the magnitude of the acceleration when .
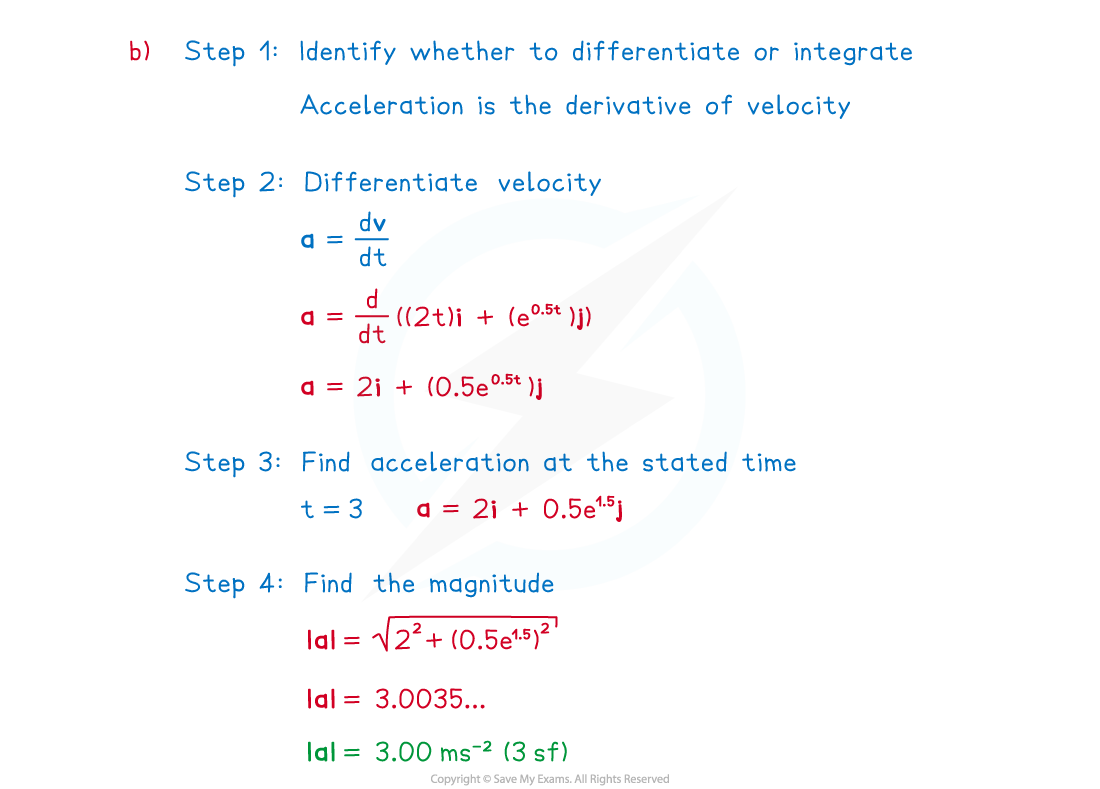
Examiner Tip
- If the question refers to the direction that the particle is travelling, then you would use the velocity. If the direction of motion is asked for then it should be clear from the question whether they want an angle, bearing or vector which it is parallel to.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
