Deriving the suvat Formulae (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Maths) : Revision Note
Did this video help you?
Deriving the suvat Formulae
What is suvat?
suvat is an acronym for the five quantities used when modelling motion in a straight-line with constant acceleration
s – displacement (from the starting point)
u – initial velocity
v – final velocity
a – acceleration
t – time
All except time are vector quantities and can be negative
time is a scalar quantity
What are the suvat (constant acceleration) equations?
The five equations for motion in a straight line are:
The equations can only be used when the motion has constant acceleration
All equations connect four of the five quantities
Knowing any three allows a fourth to be found
The equations are not provided in the exam so you need to memorise them
How do I derive the suvat equations?
The four equations that involve time can be derived from a velocity-time graph
The velocity-time graph will be a straight line as the acceleration is constant
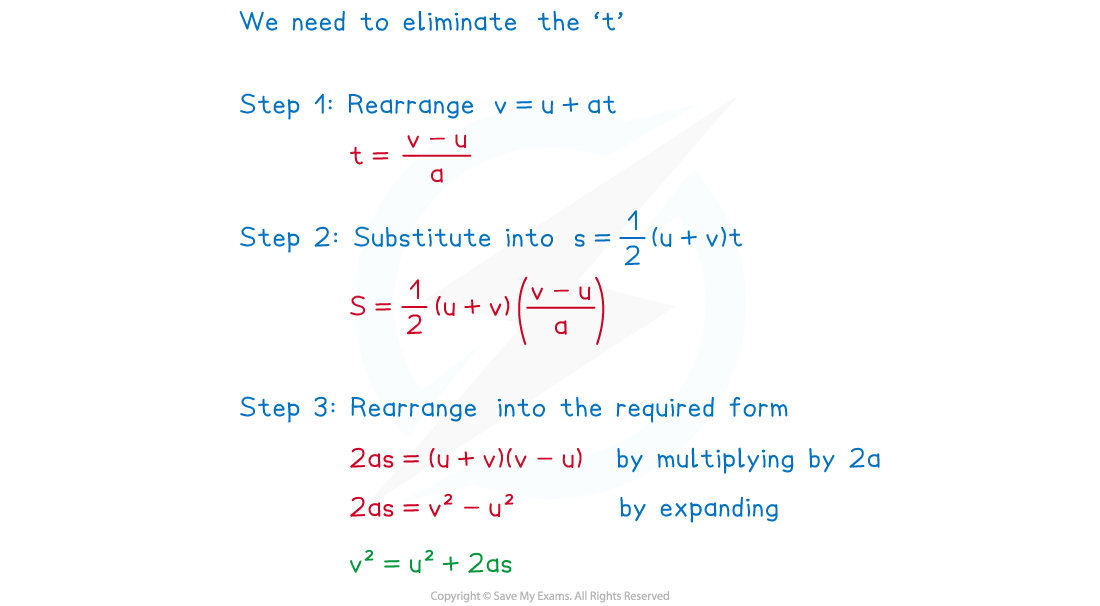
The fifth equation can be found by choosing any two of the equations and eliminating the t variable (see the worked example)


Worked Example
Use the constant acceleration equations
s = (u+v)t and v = u + at
to show that
v2 = u2 + 2as.
Examiner Tips and Tricks
If asked to derive any of the formulae there may be a velocity-time graph provided. Make sure you show each step and state any reasons such as the gradient of the graph being the acceleration.
If the question does not ask you to derive the formulae then you can use them freely without proof.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?
