Nomenclature (Oxford AQA International A Level (IAL) Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: 9622
Types of Chemical Formulas
Organic compounds can be represented by:
Empirical formula
Molecular formula
General formula
Structural formula
Displayed formula
Skeletal formula
Empirical and molecular formulae
The empirical formula shows the simplest whole number ratio of the elements present in one molecule of the compound
Eg. the empirical formula of ethanoic acid is CH2O
The molecular formula shows the number and type of each atom in a molecule
Eg. the molecular formula of ethanoic acid is C2H4O2
Worked Example
Deduce the molecular and empirical formula of the following compounds:

Answers:
Empirical formula = CH2Cl, molecular formula = C2H4Cl2
Empirical formula = C5H10O, molecular formula = C5H10O
Empirical formula = C7H16, molecular formula = C7H16
Empirical formula = C6H14O, molecular formula = C6H14O
Empirical formula = C3H6O, molecular formula = C6H12O2
Empirical formula = C6H13Cl, molecular formula = C6H13Cl
Empirical formula = C2H3, molecular formula = C4H6
Empirical formula = C5H12O, molecular formula = C5H12O
General and structural formulae
The general formula is a formula that represents a homologous series of compounds using letters and numbers
For example, the general formula of alkanes is CnH2n+2
A homologous series is a group of organic compounds that have the same functional group, the same general formula and the same chemical properties
The structural formula is a formula that shows how the atoms are bonded to each carbon atom in a molecule
Displayed and skeletal formulae
The displayed formula is a 2D representation of an organic molecule showing all its atoms (by their symbols) and their bonds (by single, double or triple bonds)
Worked Example
Draw the displayed formula of the following molecules:

Answers:

The skeletal formula is a simplified displayed formula with all the carbon and hydrogen (C-H) bonds removed
Worked Example
Draw the skeletal formula of the following molecules:
CH3(CH2)3OH
(CH3)2CHCH2OH
CH3CH2OCH2CH3
Answers:

Overview of the formulae of organic compounds table

Homologous Series & Functional Groups
A functional group is a specific atom or group of atoms which determine the physical and chemical properties of the molecule
Organic molecules are classified by the dominant functional group on the molecule
Alkanes are the simplest hydrocarbons with no functional group
Hydrocarbons are compounds that are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms ONLY
They are made up of carbon and hydrogen atoms bonded to each other with single covalent bonds
Table of common functional groups

Organic compounds with the same functional group, but a different number of carbon atoms, are said to belong to the same homologous series
Every time a carbon atom is added to the chain, two hydrogen atoms are also added
Homologous Series of Alkanes Table
Name of alkane | Number of carbons | Chemical formula | Boiling point in °C | State at room temp | Melting point in °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
Methane | 1 | CH4 | -162 | gas | -183 |
Ethane | 2 | C2H6 | -89 | gas | -172 |
Propane | 3 | C3H8 | -42 | gas | -188 |
Butane | 4 | C4H10 | 0 | gas | -138 |
Pentane | 5 | C5H12 | 36 | liquid | -130 |
Each member of a homologous series:
has the same functional group
has the same general formula
has similar chemical properties
differs by -CH2 -
Members of a homologous series have gradually changing physical properties
For example, boiling point, melting point and density
A graph of boiling point for the first eight alkanes

The broad trend is that boiling point increases with increased molecular size
Each additional -CH2 - increases the strength of the intermolecular forces
This leads to a higher boiling point
These trends are followed in other homologous series
Similar trends are seen in other physical properties, such as melting point and density
IUPAC Nomenclature
IUPAC nomenclature can be used to name organic compounds and therefore make it easier to refer to them
It can also be referred to as systematic nomenclature
The alkanes provide the basis of the naming system and the stem of each name indicates how many carbon atoms are in the longest chain in one molecule of the compound
Nomenclature of organic compounds table
Number of C atoms | Molecular formula of straight-chain alkane | Name of alkane | Stem used in naming |
|---|---|---|---|
1 | CH4 | methane | meth- |
2 | C2H6 | ethane | eth- |
3 | C3H8 | propane | prop- |
4 | C4H10 | butane | but- |
5 | C5H12 | pentane | pent- |
6 | C6H14 | hexane | hex- |
7 | C7H16 | heptane | hept- |
8 | C8H18 | octane | oct- |
9 | C9H20 | nonane | non- |
10 | C10H22 | decane | dec- |
If there are any side-chains or functional groups present, then the position of these groups is indicated by numbering the carbon atoms in the longest chain
Numbering starts at the end that gives the lowest possible numbers in the name
The hydrocarbon side-chain is shown in brackets in the structural formula
e.g. CH3CH(CH3)CH2CH3
The side-chain is named by adding ‘-yl’ to the normal alkane stem
This type of group is called an alkyl group
Naming branched alkanes

If there is more than one of the same alkyl side-chain or functional groups, di- (for two), tri- (for three) or tetra- (for four) is added in front of its name
The adjacent numbers have a comma between them
Numbers are separated from words by a hyphen
Naming alkanes with multiple branches

If there is more than one type of alkyl side-chain, they are listed in alphabetic order
Naming alkanes with multiple different branches

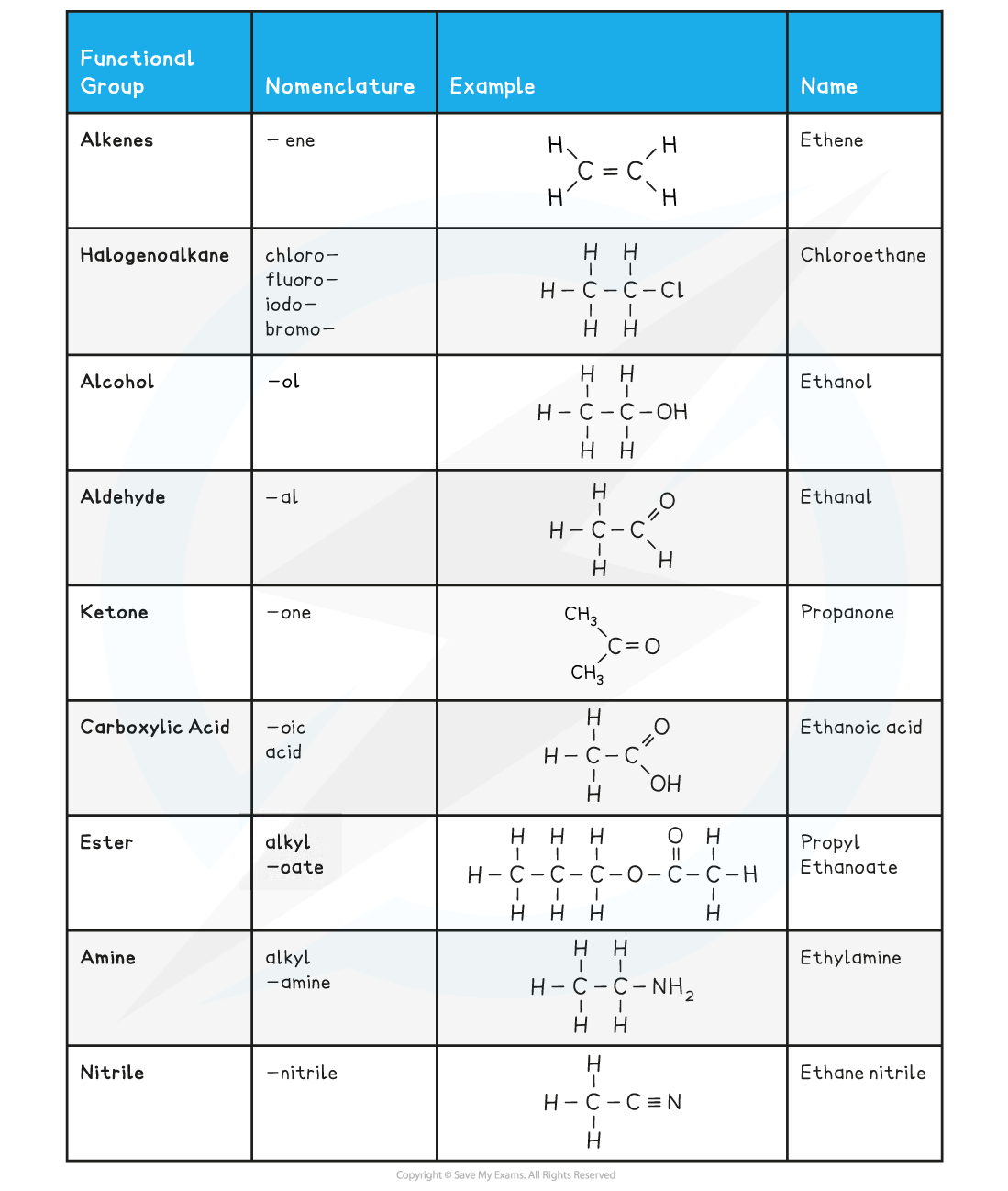
Functional groups and their nomenclature table
Worked Example
Name the following molecules using correct systematic nomenclature:
Answers:
The chemical name is 2,5,5-trimethylhex-2-ene
The longest carbon chain is six carbons long
There is an alkene / double carbon-carbon bond on carbon-2
There are 3 methyl groups on carbons 2, 5 and 5
The chemical name is propanal
The longest carbon chain is 3 carbons long with only single carbon-carbon bonds
There is an aldehyde group which is fixed as carbon-1
The chemical name is 2-methylbutanal
The longest carbon chain is 4 carbons long with only single carbon-carbon bonds
There is a methyl group on carbon-2
There is an aldehyde group which is fixed as carbon-1
The chemical name is butanoic acid
The longest carbon chain is 4 carbons long with only single carbon-carbon bonds
There is a carboxylic acid group which is fixed as carbon-1
The chemical name is 2-chlorobutane
The longest carbon chain is 4 carbons long with only single carbon-carbon bonds
There is a chlorine atom attached to carbon-2
Examiner Tips and Tricks
An aliphatic compound is straight or branched-chain and also includes cyclic organic compounds that do not contain a benzene ring.

Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?



