Acid Strength (Edexcel International A Level (IAL) Chemistry): Revision Note
Exam code: YCH11
Acids - Dissociation
Strong acids
A strong acid is an acid that dissociates almost completely in aqueous solutions
HCl (hydrochloric acid), HNO3 (nitric acid) and H2SO4 (sulfuric acid)
The position of the equilibrium is so far over to the right that you can represent the reaction as an irreversible reaction

The diagram shows the complete dissociation of a strong acid in aqueous solution
Weak acids
A weak acid is an acid that partially (or incompletely) dissociates in aqueous solutions
Eg. most organic acids (ethanoic acid), HCN (hydrocyanic acid), H2S (hydrogen sulfide) and H2CO3 (carbonic acid)
The position of the equilibrium is more over to the left and an equilibrium is established

The diagram shows the partial dissociation of a weak acid in aqueous solution
Acids - Ka Expressions
For weak acids as there is an equilibrium we can write an equilibrium constant expression for the reaction

This constant is called the acid dissociation constant, Ka, and has the units mol dm-3
Values of Ka are very small, for example for ethanoic acid Ka = 1.74 x 10-5 mol dm-3
When writing the equilibrium expression for weak acids, the following assumptions are made:
The concentration of hydrogen ions due to the ionisation of water is negligible
The value of Ka indicates the extent of dissociation
The higher the value of Ka the more dissociated the acid and the stronger it is
The lower the value of Ka the weaker the acid
pKa
The range of values of Ka is very large and for weak acids, the values themselves are very small numbers
Table of Ka values
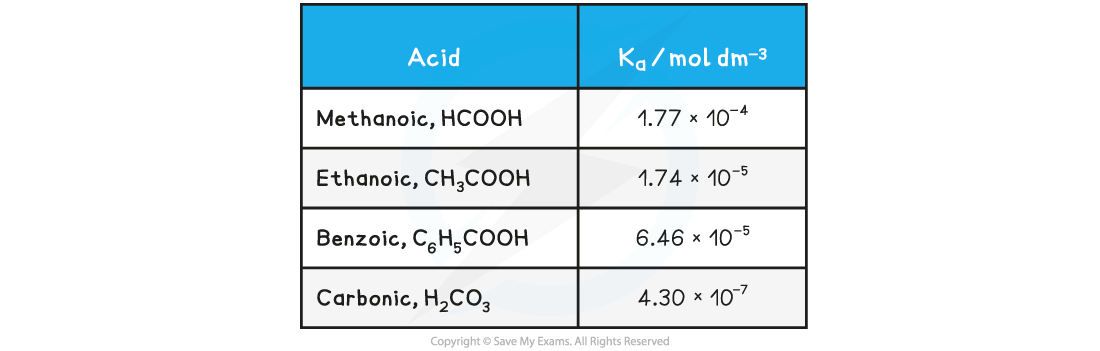
For this reason it is easier to work with another term called pKa
The pKa is the negative log of the Ka value, so the concept is analogous to converting [H+] into pH values
pKa = -logKa
Looking at the pKa values for the same acids:
Table of pKa values
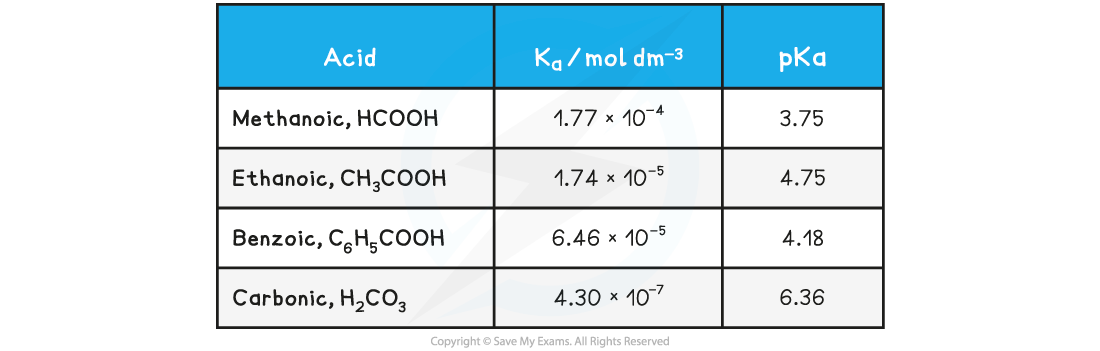
The range of pKa values for most weak acids lies between 3 and 7

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Unlock more, it's free!
Did this page help you?