Polygenic Inheritance & Continuous Variation (Edexcel International A Level Biology) : Revision Note
Polygenic Inheritance
Genes can have varying effects on an organism's phenotype:
Some characteristics (i.e. the phenotype) are controlled by a single gene - these characteristics are known as monogenic
These characteristics usually show discontinuous variation (e.g. blood group)
Inheritance of these characteristics is known as monogenic inheritance
Other characteristics are controlled by several genes - these characteristics are known as polygenic
These characteristics usually show continuous variation (e.g. height, mass, skin colour)
Inheritance of these characteristics is known as polygenic inheritance
Continuous Variation
Some phenotypes of individuals within a population show continuous variation
The phenotypes do not fall into discrete categories (unlike in discontinuous variation)
Instead, for these features, a range of values exists between two extremes, within which the phenotype will fall
For example, the mass or height of a human is an example of continuous variation
The lack of categories and the presence of a range of values can be used to identify continuous variation when it is presented in a table or graph
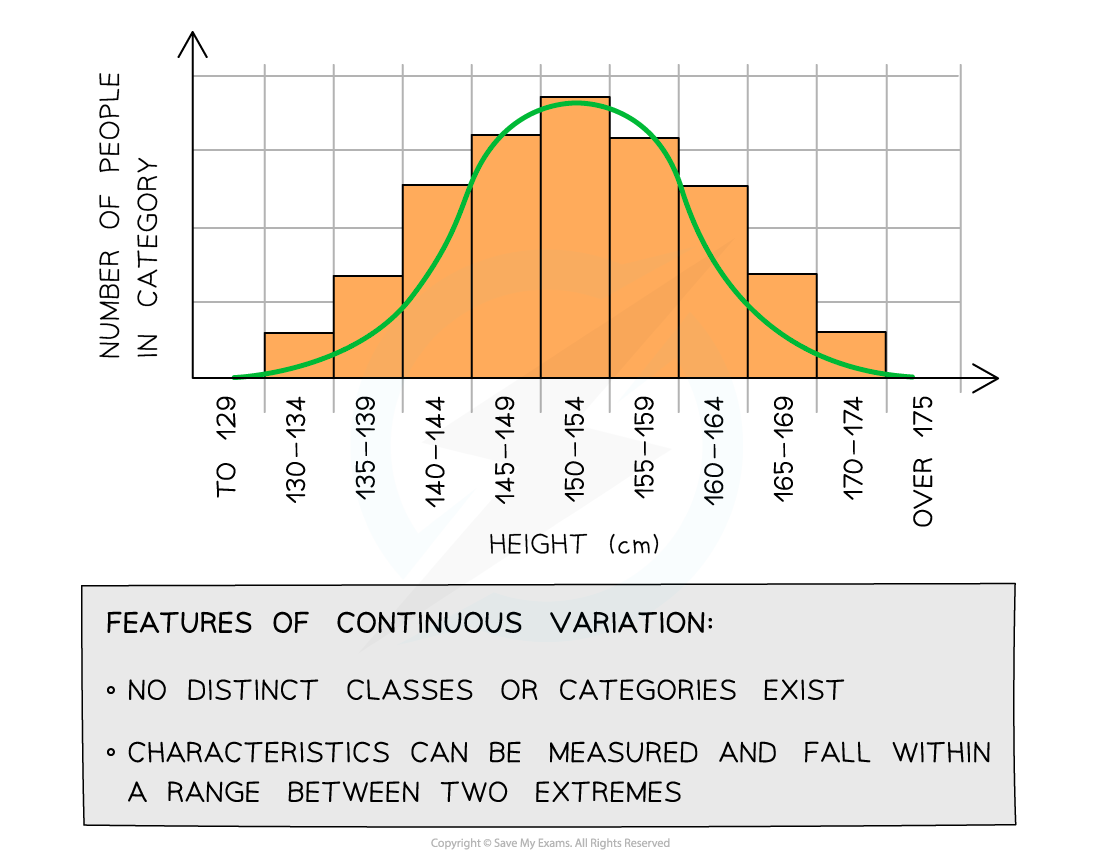
Graph showing population variation in height: an example of continuous variation with quantitative differences
Causes of continuous variation
Some phenotypes are affected by multiple different genes or by multiple alleles for the same gene at many different loci (polygenic inheritance) as well as the environment
Phenotype = genotype + environment
This often gives rise to phenotypes that show continuous variation
At the genetic level:
Different alleles at a single locus have a small effect on the phenotype
Different genes can have the same effect on the phenotype and these add together to have an additive effect
If a large number of genes have a combined effect on the phenotype they are known as polygenes
The additive effect of genes
The height of a plant is controlled by two unlinked genes H / h and T / t
The two genes have an additive effect
The recessive alleles h and t contribute x cm to the height of the plant
The dominant alleles H and T contribute 2x cm to the height of the plant
The following genotypes will have the following phenotypes:
h h t t : x + x + x + x = 4x cm
H H T T : 2x + 2x + 2x + 2x = 8x cm
H h T t : 2x + x + 2x + x = 6x cm
H H T t : 2x + 2x + 2x + x = 7x cm
H h T T : 2x + x + 2x + 2x = 7x cm
h h T t : x + x + 2x + x = 5x cm
H h t t : 2x + x + x + x = 5x cm
Examiner Tips and Tricks
Be careful when answering questions that involve polygenes or genes with an additive effect. It is not a given that each gene will have the same effect on the phenotype as in the example above so make sure to double check the information you have been given in the question.

You've read 0 of your 5 free revision notes this week
Sign up now. It’s free!
Did this page help you?
